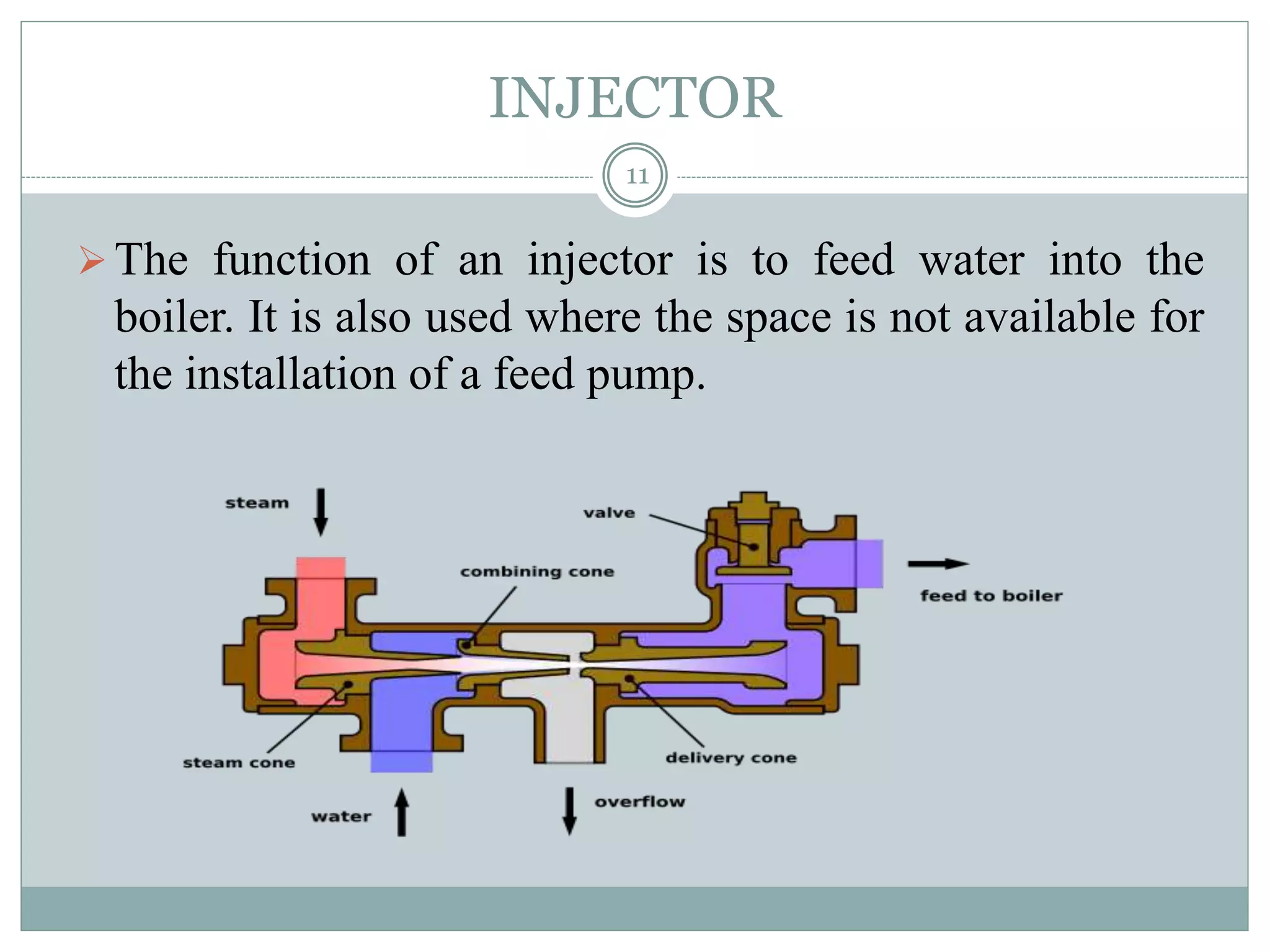
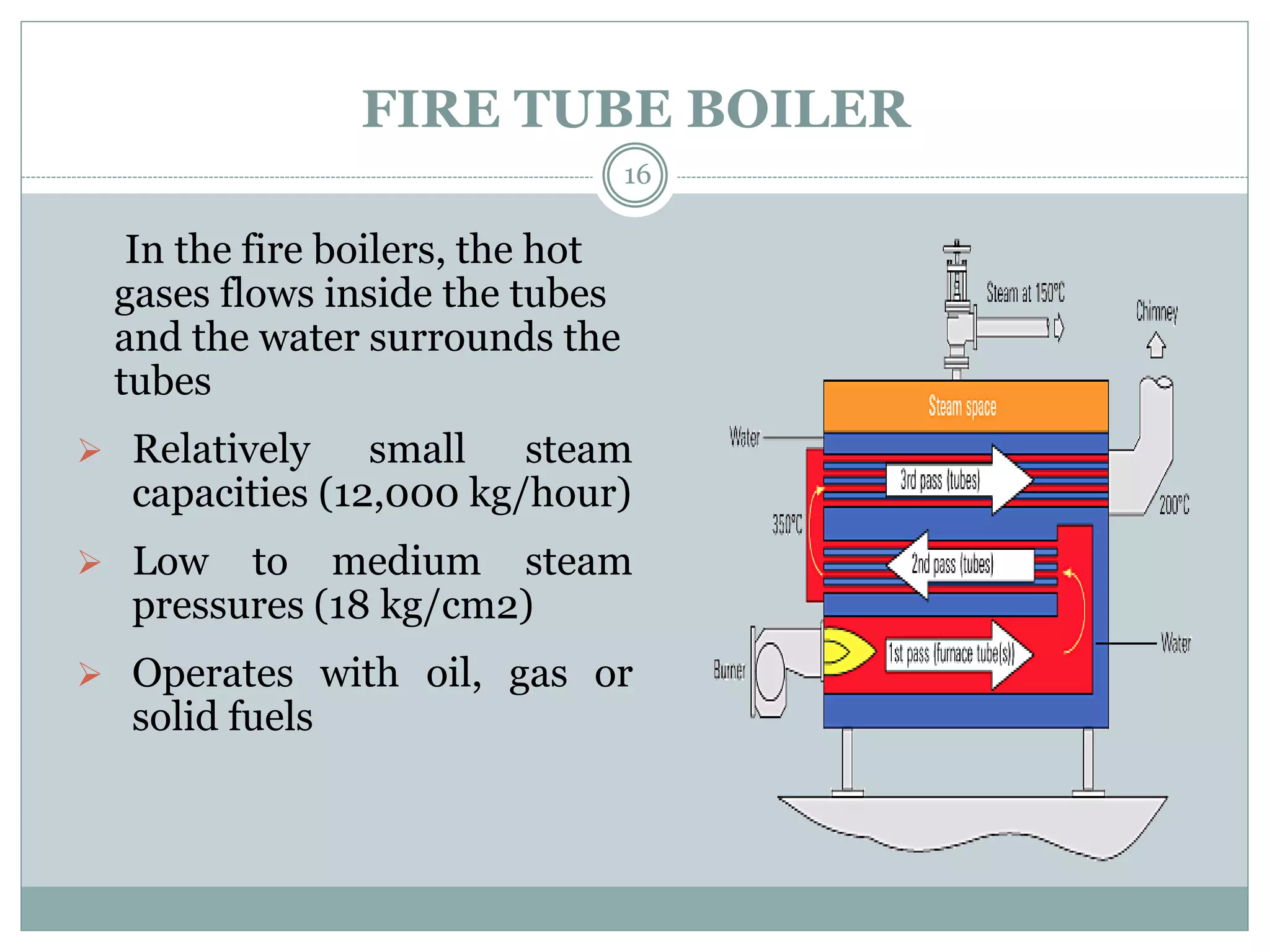
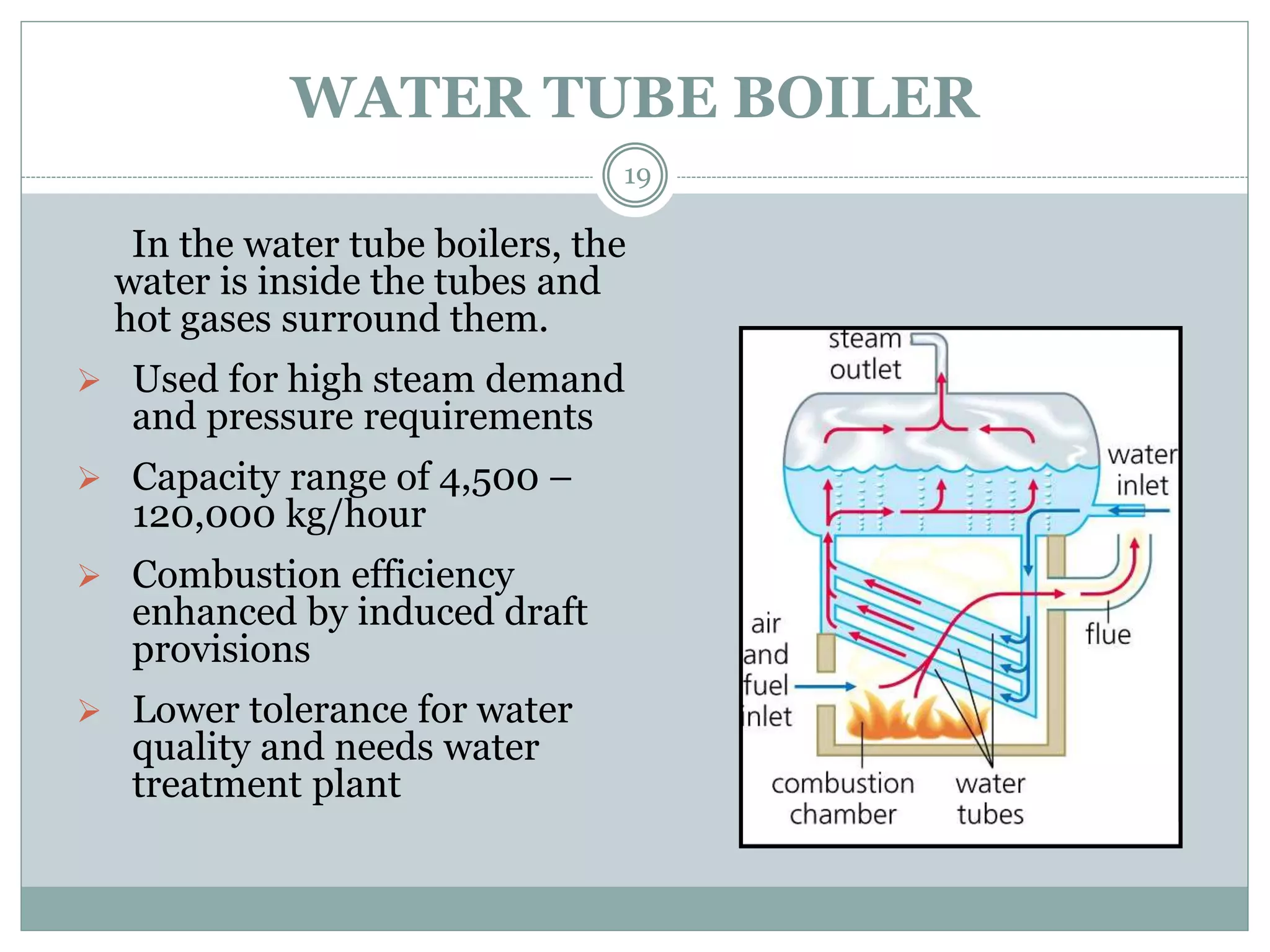
This document discusses boilers, including their purpose, classification, components, and maintenance. It begins by explaining that a boiler is a closed vessel that transfers heat from fuel combustion to water to produce steam. It then classifies boilers based on factors like orientation, tube configuration, firing method, pressure, portability, and number of tubes. The document also describes key boiler components like feed pumps, injectors, economizers, and air preheaters. It concludes by discussing maintenance aspects such as performance assessment, blowdown, and feedwater treatment.