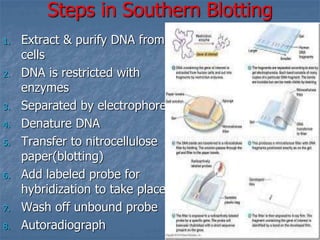
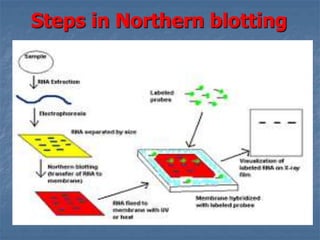
This document discusses blotting techniques used to detect and analyze DNA, RNA, and proteins. It describes the principles and steps of Southern blotting (used for DNA), Northern blotting (used for RNA), and Western blotting (used for proteins). Some key applications are identifying specific sequences, measuring expression levels, and detecting proteins for diagnostic purposes. The techniques allow target molecules to be separated, transferred to a carrier, and detected using labeled probes.