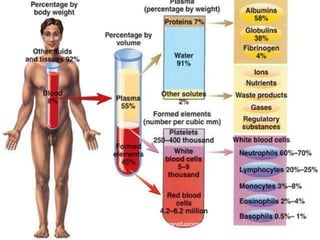
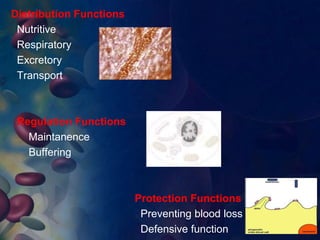
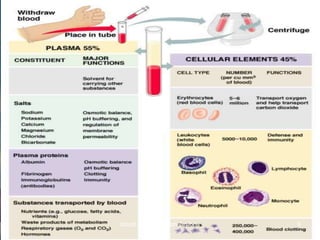
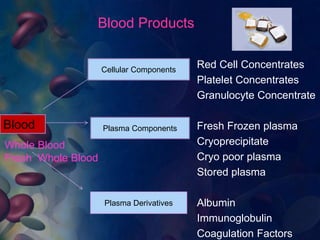
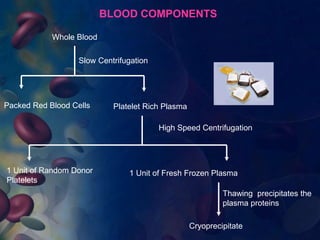
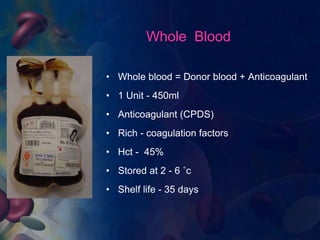
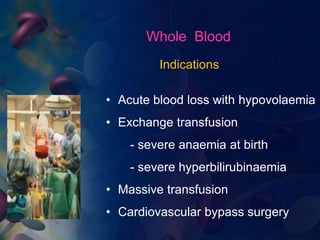
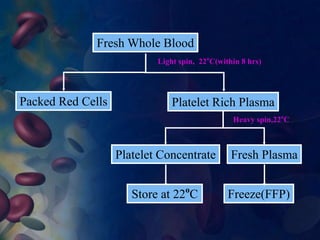
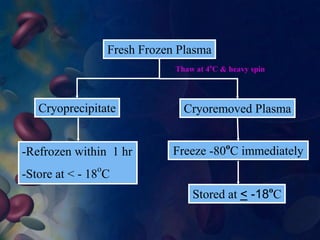
This document provides an overview of blood and its components, detailing its properties, functions, and the various blood products used in transfusions. It discusses types of blood products such as red cell concentrates, fresh frozen plasma, and cryoprecipitate, along with their indications and storage requirements. Additionally, the document includes multiple-choice questions related to blood transfusion practices.