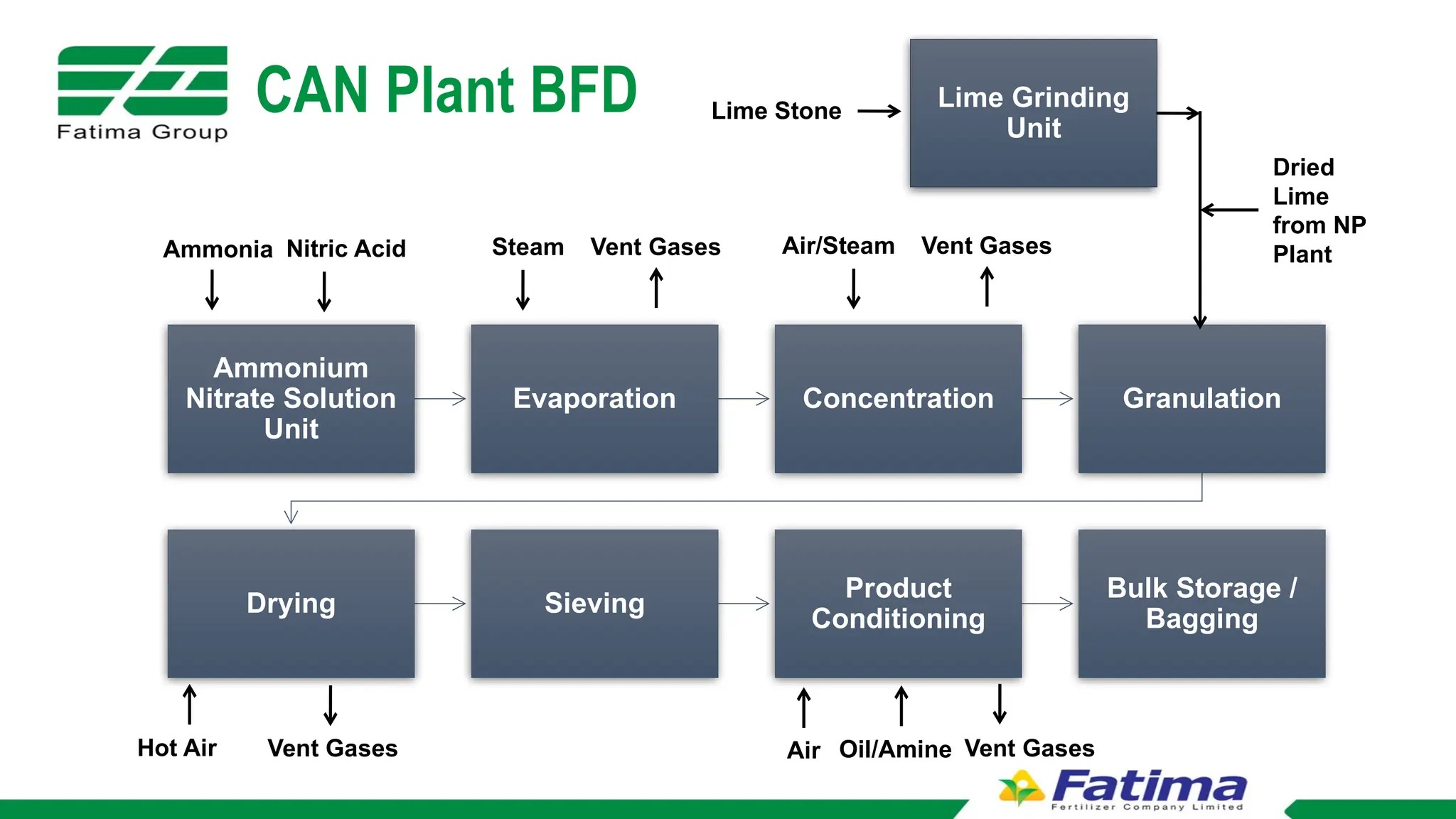
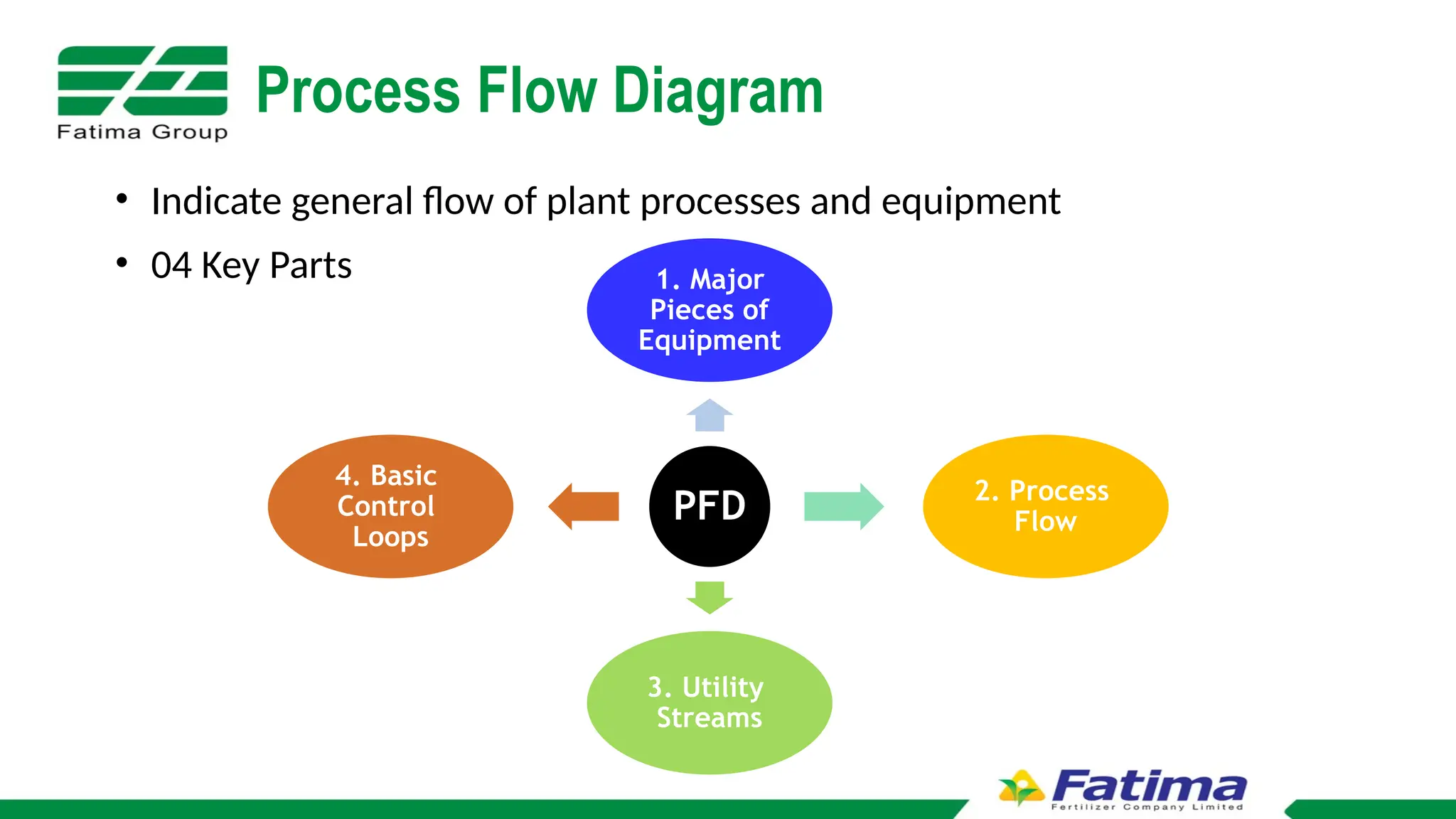
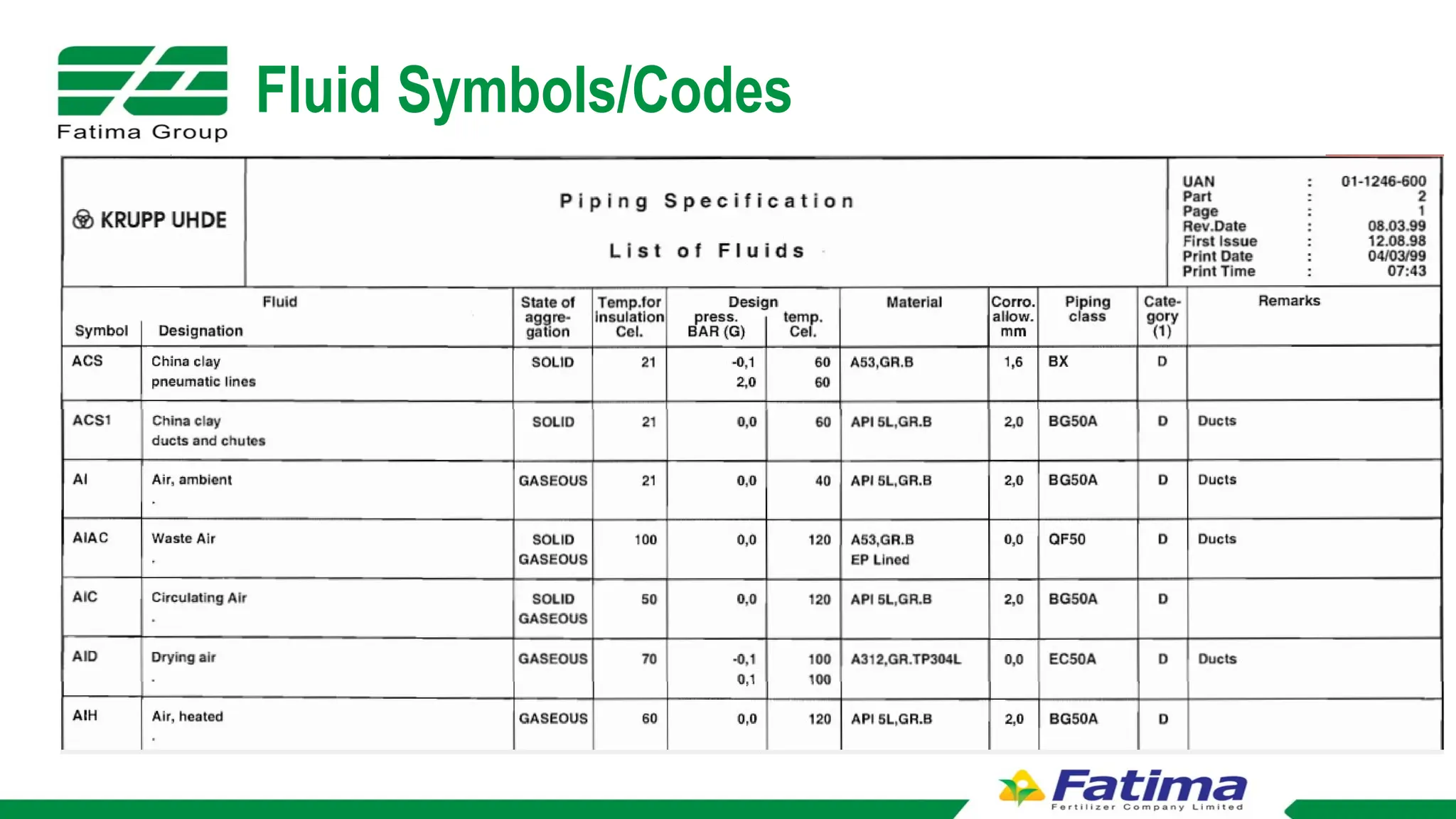
The document provides an overview of Block Flow Diagrams (BFD), Process Flow Diagrams (PFD), and Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID), explaining their complexity and purpose in process engineering. It details key components of each diagram type, including equipment symbols, utility streams, control loops, and tagging formats. Additionally, it outlines the significance of P&IDs in illustrating process sequences, interlocks, and connections within a system.