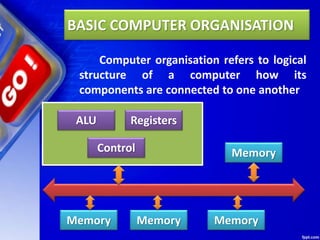
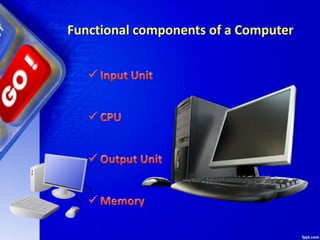
A computer is a device that can carry out arithmetic and logical operations automatically by following programs. Data refers to raw facts and figures that are input into a computer, while information is what results from processing the data. The basic components of a computer are the input unit, central processing unit (CPU), and output unit. The CPU contains the arithmetic logic unit for calculations, control unit for coordinating operations, and memory registers for temporary storage. It processes data received from input devices and sends the resulting information to output devices.