Embed presentation
Download to read offline


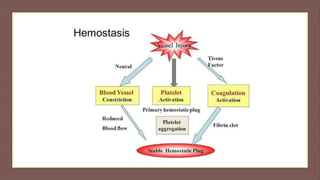














Bleeding disorders are conditions that lead to excessive bleeding, classified into vessel disorders, platelet disorders, and coagulation cascade issues. Hemophilia A and B, caused by deficiencies in clotting factors, are hereditary and vary in severity based on factor levels, while von Willebrand disease is a hereditary abnormality resulting in mucous membrane bleeding. General management includes factor replacement therapy tailored to the severity of bleeding.
















