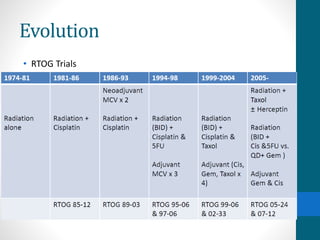
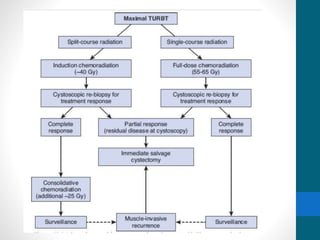
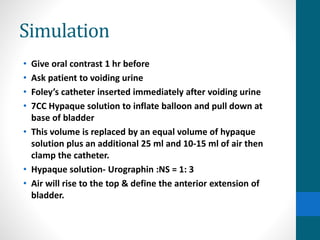
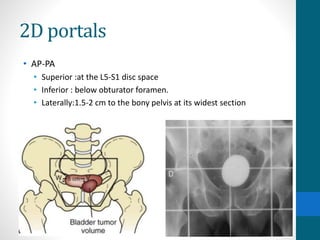
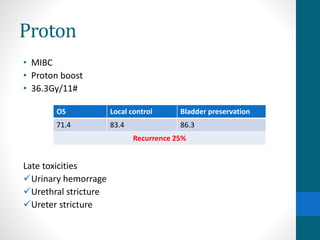
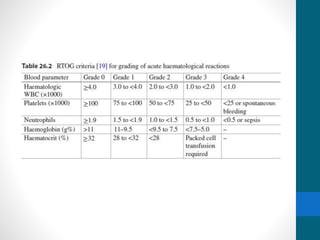
This document provides an overview of bladder cancer, including its subtypes, risk factors, molecular landscape, management approaches, and outcomes. Key points include:
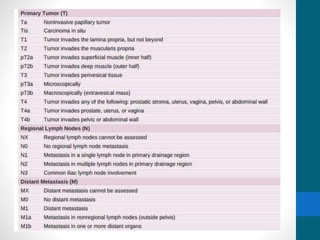
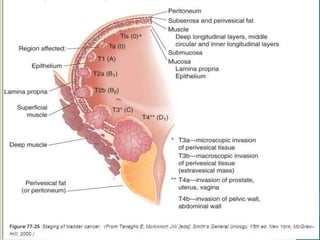
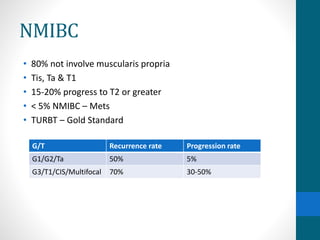
- Bladder cancer is categorized into non-muscle invasive (75%) and muscle invasive (25%) subtypes with different prognoses.
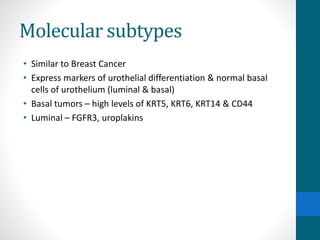
- Risk factors include smoking, chemical exposures, and infections. Molecular subtypes include luminal, basal, and neuroendocrine types.
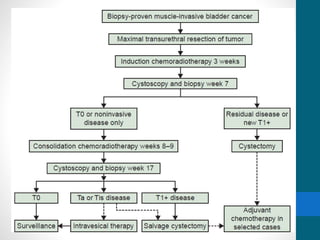
- Treatment depends on invasiveness and risk level. Non-muscle invasive types often receive transurethral resection and adjuvant BCG therapy. Muscle invasive types may undergo radical cystectomy or trimodality therapy with chemotherapy and radiation.
- Prognosis depends