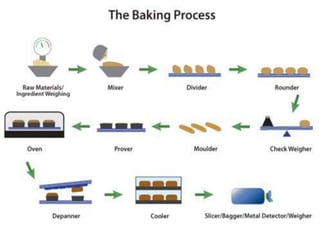
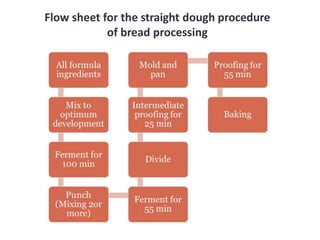
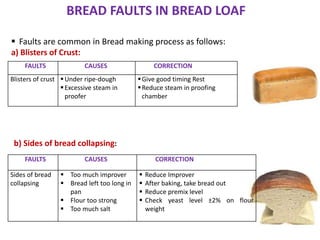
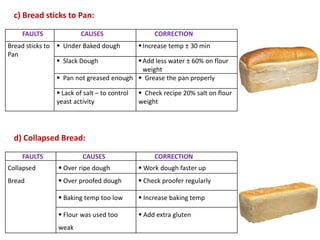
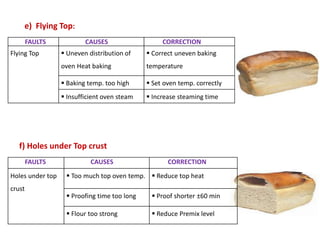
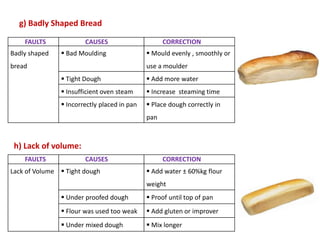
This document discusses various methods of bread making. It begins by introducing traditional bread making processes and how modern processes are faster and more efficient. The document then defines lean and rich doughs. It describes five common bread making methods: straight dough method, salt delayed method, no dough time method, sponge and dough method, and ferment and dough method. Each method is explained in one to three sentences. The document concludes by listing common bread faults, their causes, and suggested corrections.