This document presents guidelines on biosafety from the Government of India. It discusses the history and necessity of biosafety, describing the four biosafety levels established by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for handling infectious agents. It also outlines the roles of the Institutional Biosafety Committee, which reviews research using hazardous organisms, and the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee, which approves large-scale production of genetically modified organisms. The document emphasizes the importance of containment methods like physical barriers and biological techniques to prevent the spread of microbes in laboratories.


![Amity Institute of Pharmacy
BIOSAFETY
1. Biosafety define the bio-containment (prevention from microbes) conditions under which
infectious agents can be safely manipulated.
2. “Biosafety” refers to the efforts that ensure safety in using, transporting, transferring, and
realsing biological organism including genetically modified organism which are capable of
harming humans, animals, plants or environment.[1]
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biosafetylevel-200708063716/85/Biosafety-level-3-320.jpg)
![Amity Institute of Pharmacy
HISTORY AND NECCESITY OF BIOSAFETY
Innovation and development of biosafety in the United States is reflected accurately
in the history and pre-history of the American Biological Safety Association (ABSA).
The first unofficial meeting was held on April 18, 1955 at Camp Detrick in the presence
of 14 representatives from three principle laboratories of U.S. Army.
New safety programs and trainings were introduced which were related to biosafety
chemical, radiological and industrial safety issue.
Later in the united states the Centers for disease control (CDC) specified 4 different
level of biocontainment which ranges from biosafety level-1 to biosafety level -4.
NECCESITY-
In order to avoid infections /biohazards to the laboratory personnel and the environment
biosafety levels are very important.[1]
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biosafetylevel-200708063716/85/Biosafety-level-4-320.jpg)
![Amity Institute of Pharmacy
5
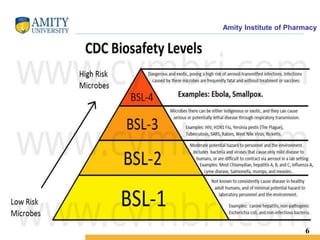
BIOSAFETY LEVEL
A biosafety level is a set of biocontainment precautions required to isolate dangerous
biological agents in an enclosed laboratory facility.
The levels of containment range from the lowest biosafety level 1 (BSL-1) to the highest
at level 4 (BSL-4).
In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have
specified these levels.
The CDC is the leading national public health institute of the United States.
Its main goal is to protect public health and safety through the control and prevention of
disease, injury, and disability in the US and internationally.[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biosafetylevel-200708063716/85/Biosafety-level-5-320.jpg)


![Amity Institute of Pharmacy
9
BSL Agent Practice Primary barriers and
safety equipment
Facilities (secondary
Barriers)
3.
Indigenous or
exotic agents
that may cause
serious or
potentially
lethal disease
through the
inhalation route
of exposure
BSL-2
practice plus:
• Controlled
access
•
Decontamina
tion of all
waste
•
Decontamina
tion of
laboratory
clothing
Primary barriers:
• BSCs or other physical
containment devices
used for all open
manipulations of agents
• PPE: Protective
laboratory clothing,
gloves, face, eye and
respiratory protection, as
needed
Physical separation
from access corridors
• Self-closing, double-
door access
• Exhausted air not
re-circulated
• Hand washing sink
near laboratory exit
[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biosafetylevel-200708063716/85/Biosafety-level-9-320.jpg)
![Amity Institute of Pharmacy
10
BSL Agent Practice Primary barriers
and safety equipment
Facilities
(secondary
Barriers)
4.
•
Dangerous/exotic
agents which post
high individual
risk of aerosol-
transmitted
laboratory
infections that are
frequently fatal,
BSL-3 practices
plus:
• Clothing
change before
entering
• Shower on
exit
• All material
decontaminated
on exit from
facility
Primary barriers:
• All procedures
conducted in Class III
BSCs or Class I or II
BSCs in combination
with full body, air-
supplied, positive
pressure suit
• Separate
building or
isolated zone
• Dedicated
supply and
exhaust,
vacuum, and
decontamination
systems
• Other
requirements
outlined in the
text
[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biosafetylevel-200708063716/85/Biosafety-level-10-320.jpg)
![Amity Institute of Pharmacy
BIOSAFETY GUIDELINES- GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
11
Policy proposed or adopted by the Government to avoid the risks of GEOs on
environment and public health.
Minimizing the possibilities of occasional release of GEOs from the laboratory.
Banning the release of GEOs if they are supposed to be causing potential risks in the
environment .
rDNA Biosafety Guidelines Of India
The Indian Government first issued rules and procedures for handling GM organisms
in December 1989. The Department of Biotechnology, inside the Ministry of Science
and Technology, published these rules and procedures in January 1990 (Department of
Biotechnology 1990).
These guidelines deals with a set of rules for production, use, import, export and
storage of hazardous organisms.[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biosafetylevel-200708063716/85/Biosafety-level-11-320.jpg)







