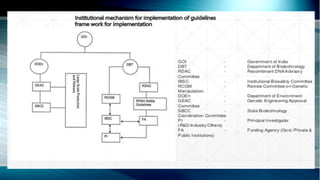
The document outlines India's biosafety guidelines for genetically engineered organisms (GEOs). It discusses the various committees that implement the guidelines: the Institutional Biosafety Committee regulates research, the Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation reviews high-risk research, and the Genetic Engineering Approval Committee approves large-scale use of GEOs. The guidelines establish containment levels and review processes to minimize risks from GEOs and ensure public health and environmental safety.