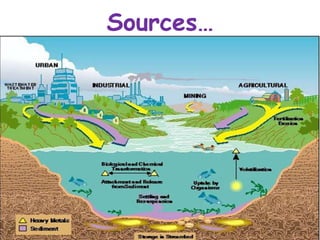
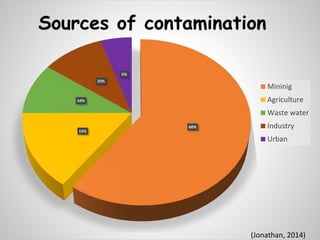
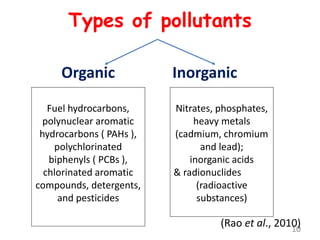
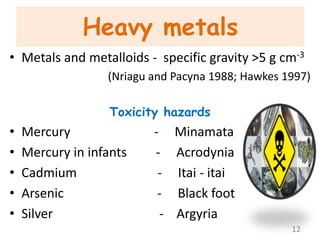
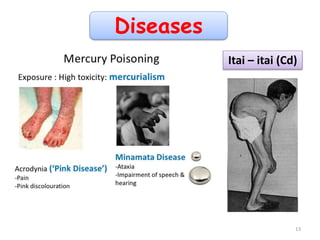
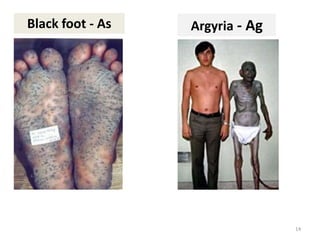
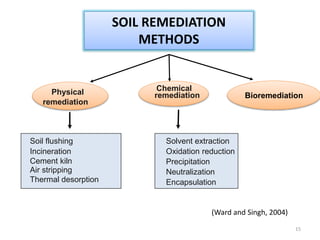
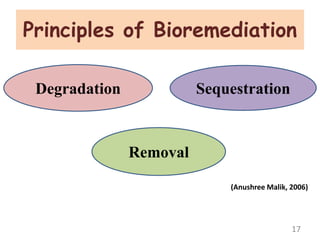
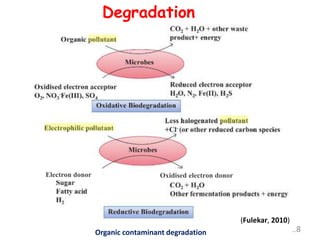
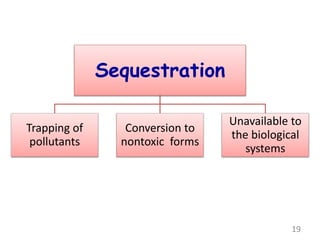
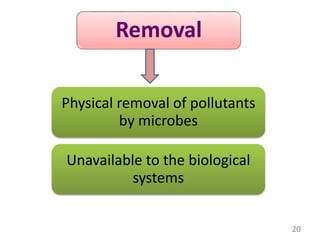
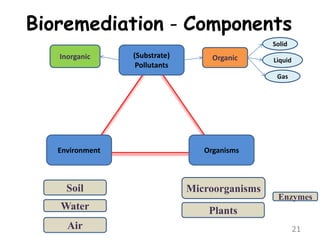
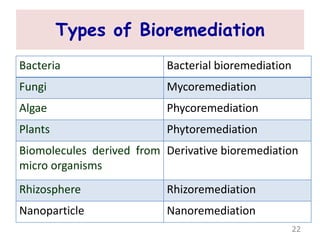
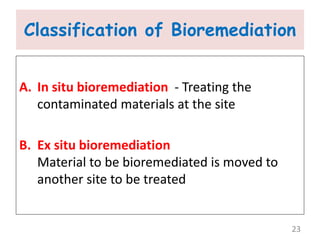
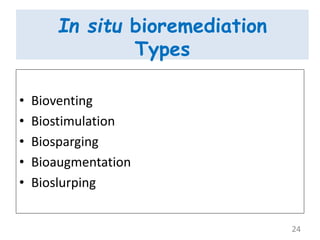
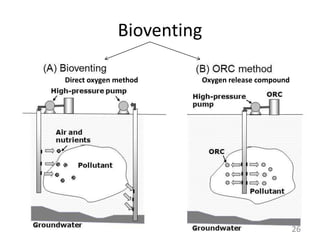
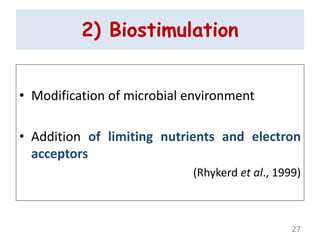
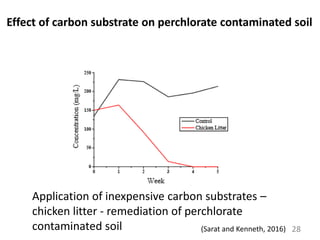
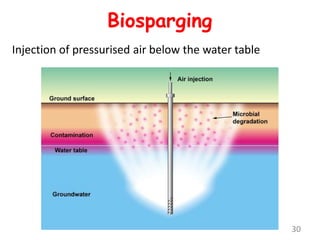
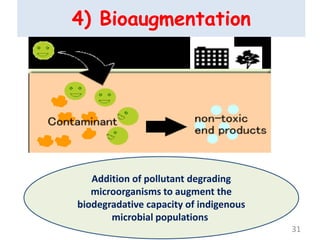
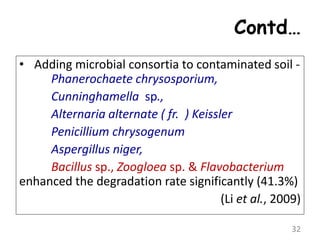
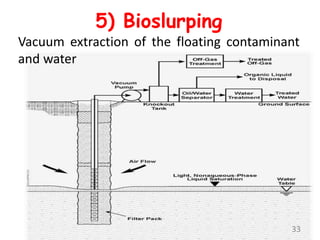
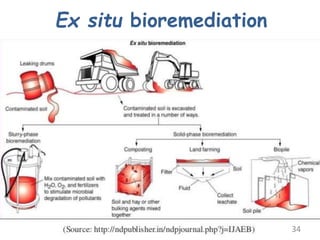
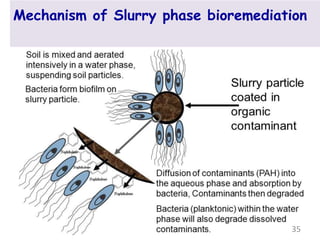
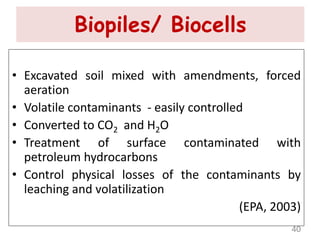
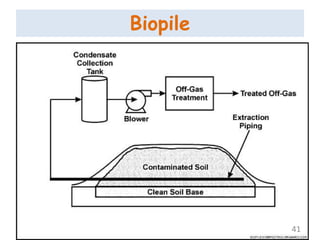
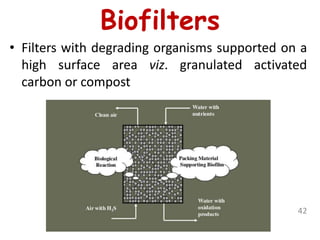
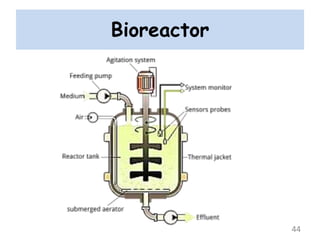
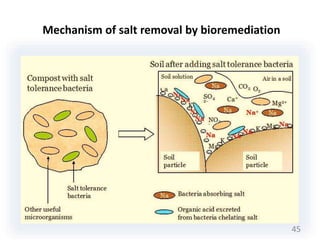
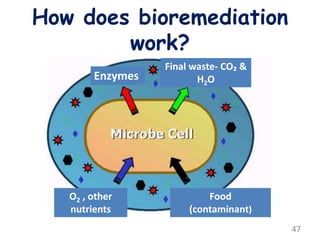
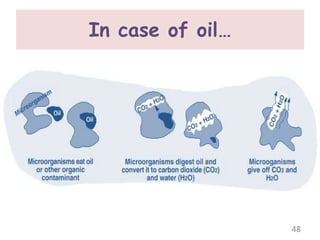
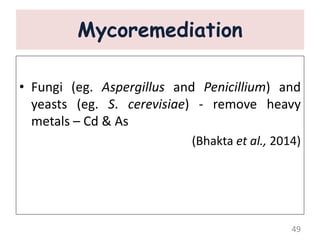
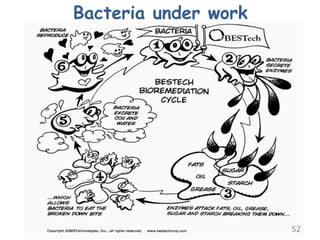
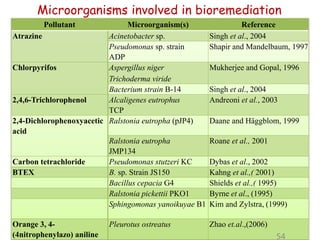
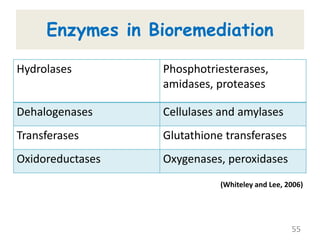
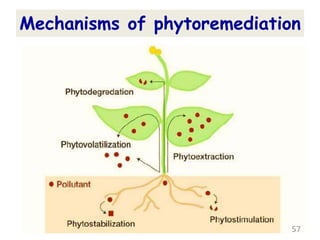
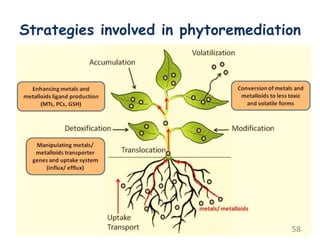
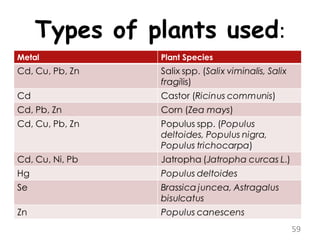
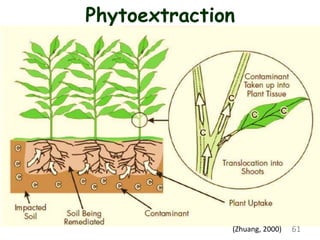
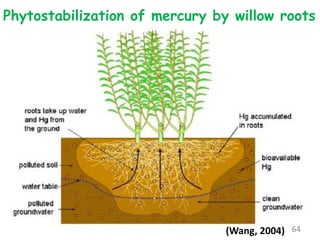
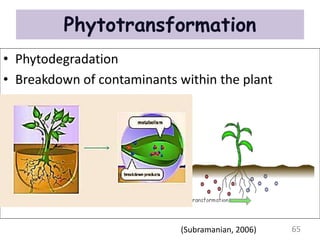
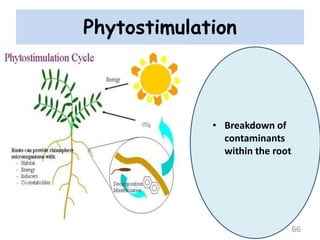
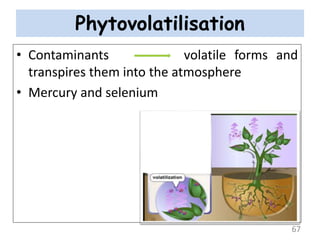
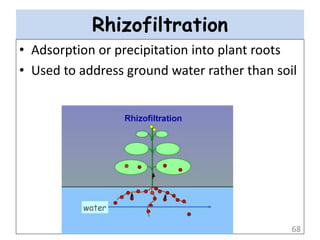
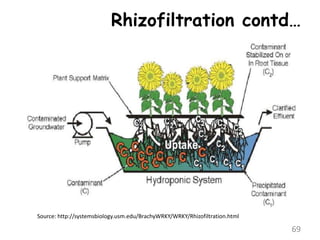
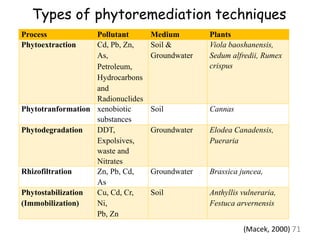
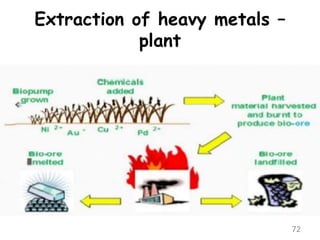
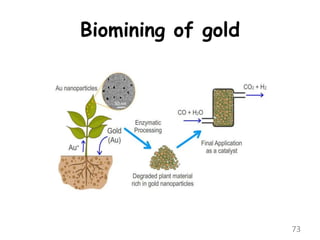
The document discusses bioremediation as a method for improving soil health by breaking down hazardous substances using naturally occurring organisms. It outlines sources of soil contamination, types of pollutants, various bioremediation techniques including phytoremediation and mycoremediation, and emphasizes the advantages and limitations of this approach. The conclusion highlights bioremediation as an eco-friendly and cost-effective strategy for achieving sustainable soil health and rejuvenating degraded lands.