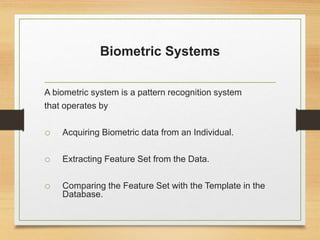
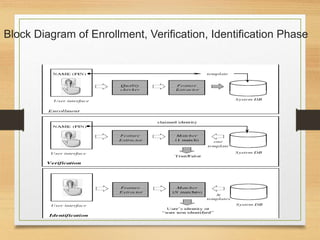
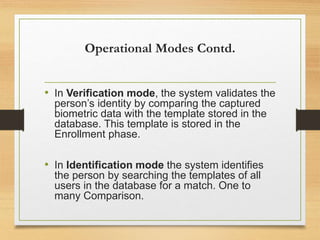
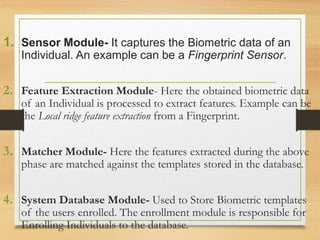
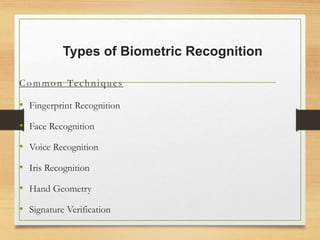
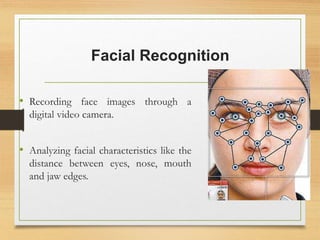
Biometrics uses physiological or behavioral characteristics to identify individuals. A biometric system acquires biometric data from an individual, extracts features from the data, and compares the features to a template in a database. There are two modes of operation - verification, which validates an identity by comparing captured data to a stored template, and identification, which searches all templates to find a match. Common biometric techniques include fingerprint, face, voice, and iris recognition. Biometrics have applications in security and identification and advantages of being difficult to forge, but also have disadvantages like cost and potential inaccuracies.