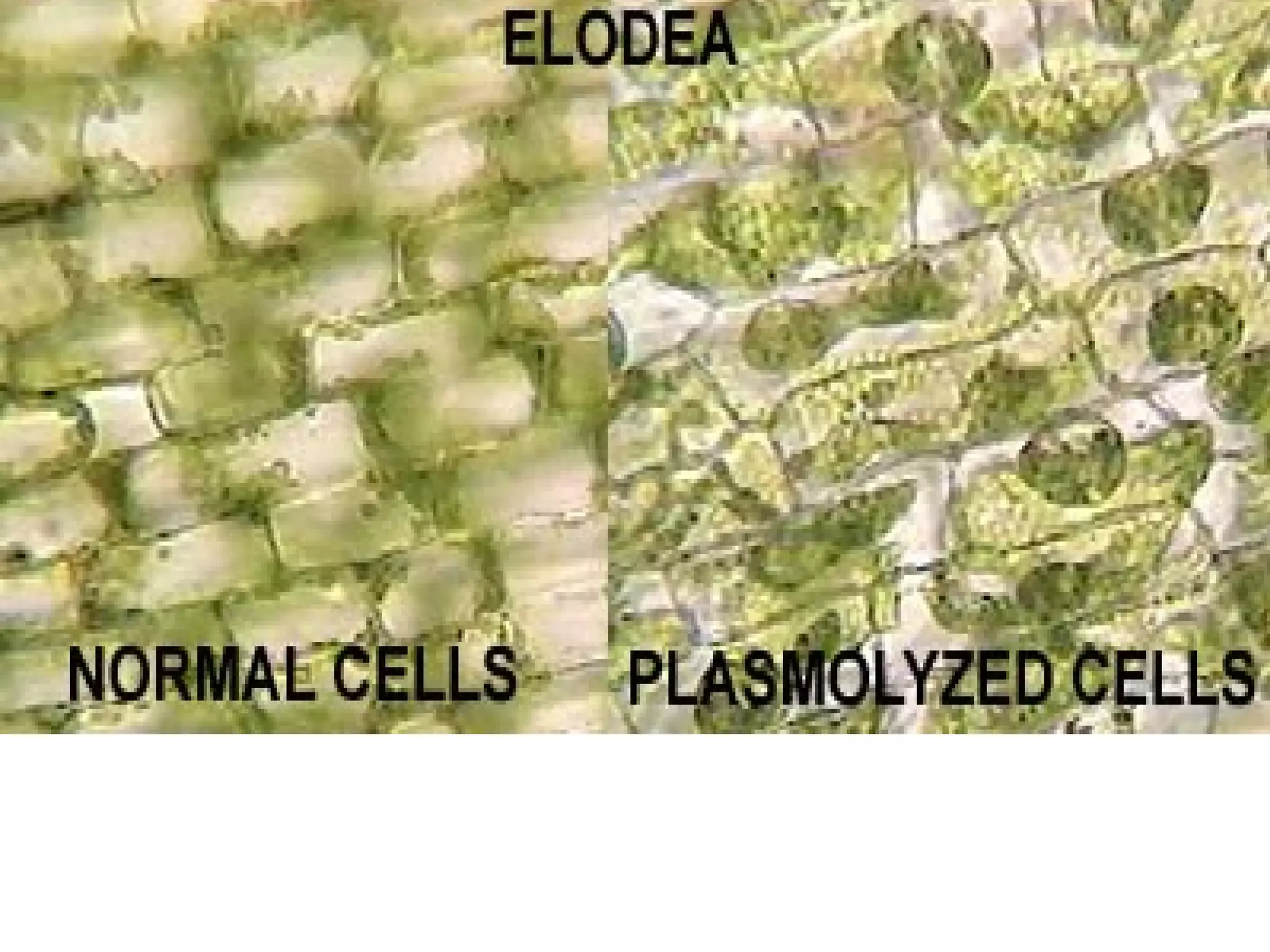
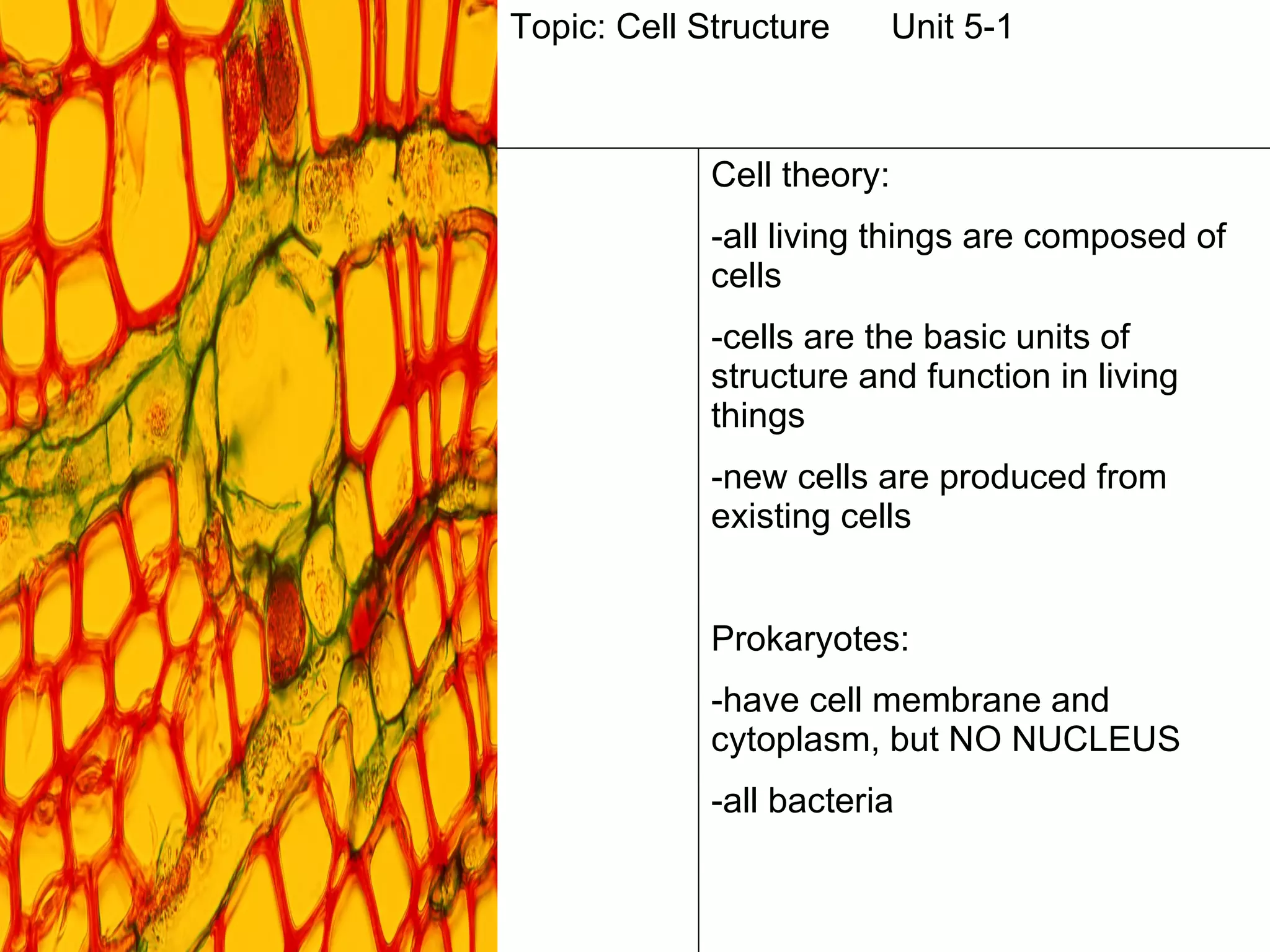
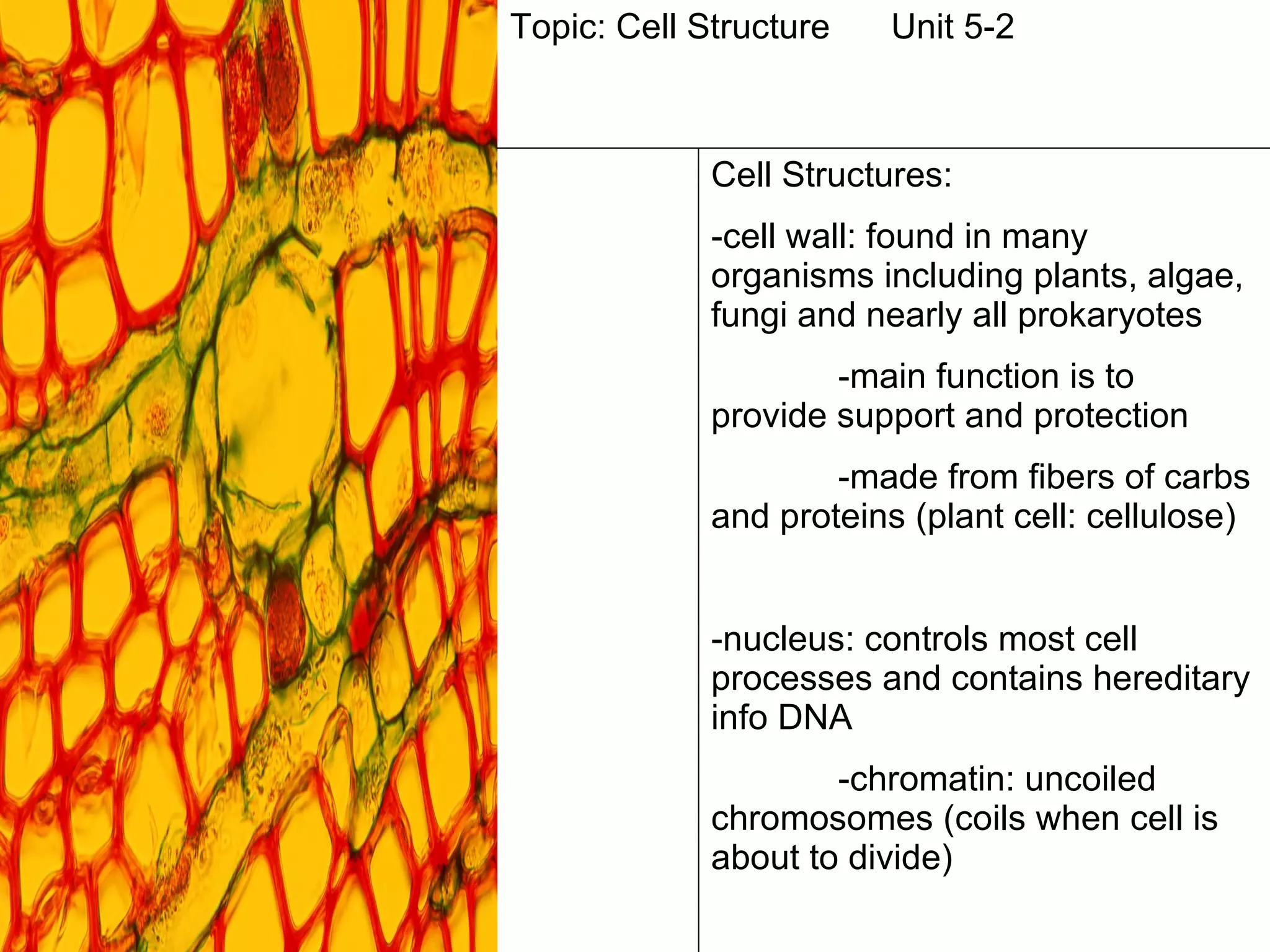
The document contains notes from a biology class covering topics of cell structure and function over multiple class periods. It includes definitions of key terms like prokaryote and eukaryote, an overview of the cell theory, descriptions of major cell organelles like the nucleus, cell membrane, mitochondria and chloroplasts, and what was covered each day like bell ringers, notes, activities and homework assignments.