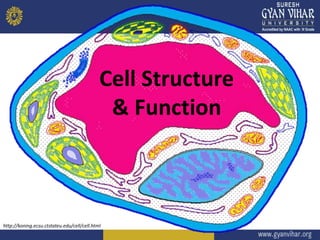
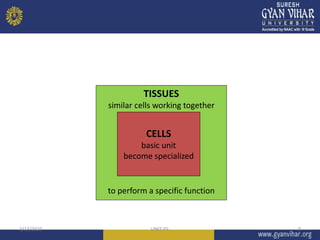
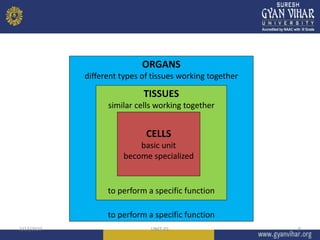
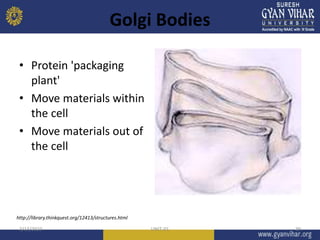
This document discusses cell structure and function. It begins by outlining the learning objectives and outcomes, which include describing the structure and function of organelles like the cell membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm. It then provides details on the parts of a cell, including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and various organelles. Examples are given for prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell types. Key organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, and lysosomes are explained in terms of their structures and roles in cellular processes.