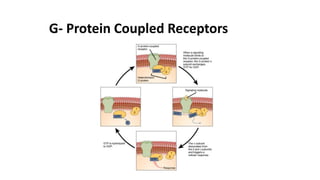
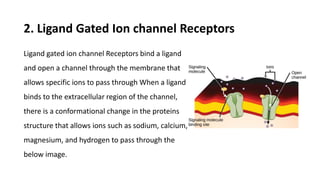
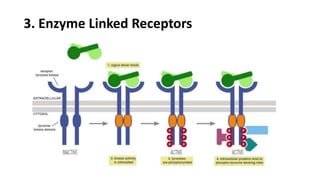
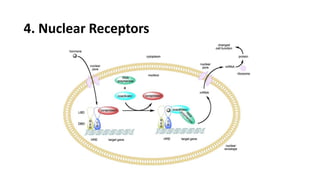
This document summarizes the main types of biological drug targets: receptors. It discusses four main classes of receptors: 1) G-protein coupled receptors, which bind ligands and activate G-proteins to interact with ion channels or enzymes, 2) ligand gated ion channel receptors, which open channels to allow ion passage upon ligand binding, 3) enzyme linked receptors with intracellular enzyme domains that are activated by ligand binding to induce intracellular signaling cascades, and 4) nuclear receptors within cells that directly bind DNA to regulate gene expression in response to ligands such as steroid hormones.