This document discusses various methods for identifying similar biological sequences, including:
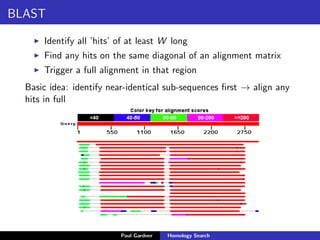
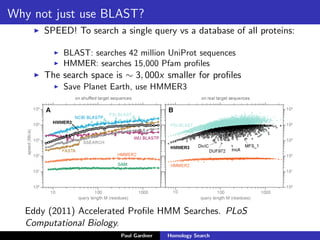
- BLAST, which uses fast heuristic algorithms to identify near-identical sub-sequences for alignment.
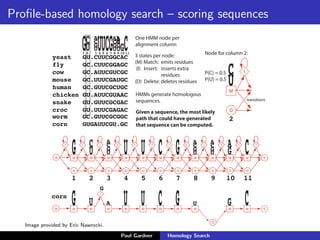
- Profile-based searches like HMMER that use hidden Markov models built from multiple sequence alignments, providing more accurate results than single-sequence methods.
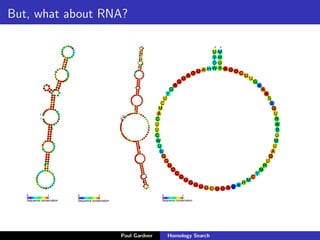
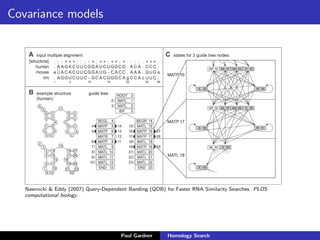
- Covariance models for RNA sequence searches, which incorporate information about base pairing into the models.
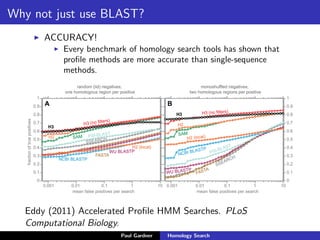
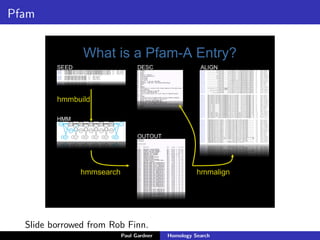
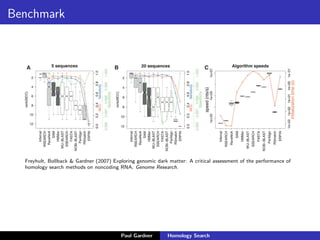
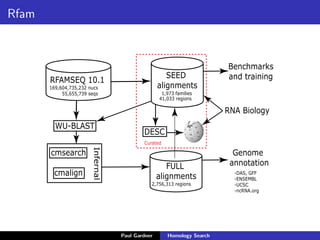
- Benchmarking of tools showed profile methods like HMMER and covariance models are more accurate than BLAST for detecting remote homology. Resources like Pfam and Rfam provide profile databases for protein and RNA families.