Computational simulations were used to investigate possible dimer structures of the neuronal protein alpha-synuclein. Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations were performed on dimers formed from alpha-helical and beta-sheet conformations of alpha-synuclein monomers. Binding energies and interactions between monomers in the dimer structures were analyzed. Both hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions contributed significantly to dimer stability, even though alpha-synuclein is highly charged. The central hydrophobic region of alpha-synuclein formed the majority of the interface between monomers in the dimer structures.
![Research paper
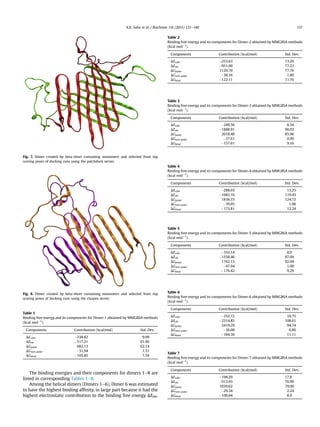
a-synuclein dimer structures found from computational simulations
Kamlesh Kumar Sahu a
, Michael T. Woodside a, b
, Jack A. Tuszynski a, c, *
a
Department of Physics, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
b
National Institute for Nanotechnology, National Research Council, Edmonton, AB, Canada
c
Cross Cancer Institute, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
a r t i c l e i n f o
Article history:
Received 22 April 2015
Accepted 12 July 2015
Available online 18 July 2015
Keywords:
Docking
Molecular dynamics
MMGBSA
Alpha-synuclein
Alzheimers
Neurodegenerative disease
a b s t r a c t
Dimer formation is likely the first step in the oligomerization of a-synuclein in Lewy bodies. In order to
prevent a-synuclein aggregation, knowledge of the atomistic structures of possible a-synuclein dimers
and the interaction affinity between the dimer domains is a necessary prerequisite in the process of
rational design of dimerization inhibitors. Using computational methodology, we have investigated
several possible a-synuclein dimer structures, focusing on dimers formed from a-helical forms of the
protein found when it is membrane-bound, and dimers formed from b-sheet conformations predicted by
simulations. Structures and corresponding binding affinities for the interacting monomers in possible a-
synuclein dimers, along with properties including the contributions from different interaction energies
and the radii of gyration, were found through molecular docking followed by MD simulations and
binding-energy calculations. We found that even though a-synuclein is highly charged, hydrophobic
contributions play a significant role in stabilizing dimers.
© 2015 Elsevier B.V. and Societe Française de Biochimie et Biologie Moleculaire (SFBBM). All rights
reserved.
1. Introduction
Many neurodegenerative diseases are associated with accumu-
lation of misfolded proteins, as in the case of Parkinson's disease
and a-synuclein, and lead to decline of neuronal function, even-
tually resulting in neuronal cell death [1e3]. Under normal condi-
tions, misfolded protein aggregates and oligomers generated in
various compartments of a cell, e.g. the nucleus, cytoplasm and
endoplasmic reticulum (ER), are removed from the body by control
mechanisms involving proteolysis [4]. However, some aggregates
may be resistant to these proteolytic pathways and may cause
cytotoxicity and neuronal cell damage.
a-Synuclein is a neuronal protein predominantly found in pre-
synaptic terminals of neurons [5,6]. It has attracted considerable
attention of neuroscientists as it is important to understand syn-
ucleinopathies, a group of neurodegenerative disorders including
Parkinson's disease, dementia involving Lewy bodies, and multiple
system atrophy that is characterized by the presence of aggregated
a-synuclein. Because it lacks stable native structure [7], it is known
as a natively unfolded protein or intrinsically disordered protein
(IDP). Fibrils of a-synuclein are a major component of the Lewy
bodies that are a characteristic clinical feature of synucleinopathies
[8,9] [10,11], and small oligomers have been identified as key
neurotoxic species in these diseases [12e14].
The primary structure of a-synuclein can be divided into three
sections. The first is the N-terminal region from residue 1 to 60. This
region is made up of 11-residue repeats containing an almost-
conserved KTKEGV hexamer motif, which has been proposed to
play an important role in a-synuclein binding to membrane phos-
pholipids [15]. This region also contains several residues (A30, E46,
H50 G51 and A53) whose mutations (A30P, E46K, H50Q, G51D,
A53T) alter the aggregation process [16e23] and are linked to fa-
milial forms of Parkinson's disease [24,25]. The central region,
consisting of residues 61e95, is highly hydrophobic [26,27]. It is
thought to be the core region for aggregation, mediated by its hy-
drophobicity [26]. Finally, the C-terminal region, residues 96e140,
is highly acidic and negatively charged. This region is believed to
stay in extended conformation during polymerization [28].
Although a-synuclein is disordered in vitro, it can take on a
variety of structures in different contexts. It binds to lipids, micelles,
and membranes, forming structures such as broken and extended
helices [29e31], it oligomerizes to form both helical and b-rich
structures [13,32,33] and it assembles into amyloid fibrils consist-
ing of stacked b-sandwiches [34]. Single-molecule measurements
* Corresponding author. Department of Physics, University of Alberta, Edmonton,
AB, Canada.
E-mail addresses: jackt@ualberta.ca, jack.tuszynski@gmail.com (J.A. Tuszynski).
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Biochimie
journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/biochi
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2015.07.011
0300-9084/© 2015 Elsevier B.V. and Societe Française de Biochimie et Biologie Moleculaire (SFBBM). All rights reserved.
Biochimie 116 (2015) 133e140](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adc705d1-92fd-4fef-a74d-dd2b27809d03-160205184651/85/biochimie-paper-final-version-1-320.jpg)
![have shown that it forms a rich variety of structures of different
sizes on a transient basis [35]. The conformational ensemble of a-
synuclein has also been explored by computational simulations,
finding that it is more compact than a random coil, with long-range
interactions causing partial condensation of a-synuclein [36].
Simulations have also explored such questions as why b-synuclein
resists aggregation despite having high sequence similarity to a-
synuclein, finding that the aggregation-resistance arises from the
shorter distance between N- and C-termini [37].
We approached the question of how a-synuclein oligomerizes
and aggregates from the point of view of the first step, the forma-
tion of a dimer, using computational tools to model possible
structures for dimers. Methods such as docking and molecular
dynamics (MD) simulations can provide useful insights into the
structures and properties of proteineprotein complexes. Free-
energy calculations using the Molecular Mechanics Pois-
soneBoltzmann/GeneralizedeBorn (MMPB/GB) surface area
method [38,39] can provide a quantitative estimate of the strength
of binding in these complexes. A particular advantage of the
MM(PB/GB)SA method for studying a-synuclein is that it can esti-
mate binding energies with all the individual contributions (van
der Waals, electrostatic, polar and non-polar contributions to sol-
vation free energy, etc.). The sum total of the van der Waals and
non-polar contributions provides an estimate of the strength of
hydrophobic interactions; although electrostatic contributions play
an important role in IDPs [40], non-polar interactions should be
very important for the central hydrophobic region in a-synuclein,
and cannot be neglected. Because it is not yet known which
structures are most important in the aggregation process, we
modeled interfaces both between two helical-structured mono-
mers as well as between two b-structured monomers. Knowledge
of these interfaces and type of interactions contributing to affinity
gives us an idea of what features may be important in a pharma-
cophore that is expected to select putative inhibitors of these in-
teractions from small molecule databases. Therefore, breakdown of
binding affinity into its interaction components is necessary in
order to assist in pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening
for small molecules that may be able to disrupt this interaction and
eventually in rational drug design aimed at clinical treatments of a-
synuclein aggregation.
2. Methods
The initial structure of the a-synuclein monomer used for
modeling helical dimers was obtained from the RCSB protein data
bank (1XQ8) [29], whereas the initial structure for modeling b-
structured dimers resulted from Monte-Carlo simulations (Healey
M et al., in preparation) similar to those published previously [41].
The structures were energy-minimized using the molecular
modeling force field of the Molecular Operating Environment
(MOE, chemical computing group) software [42]. Cluspro and
Patchdock proteineprotein docking servers were used to dimerize
the monomer structures [43e50]. Top-scoring poses were taken for
molecular dynamics simulation using Amber12. Dimers 1 (Fig. 1), 2
(Fig. 2) and 5 (Fig. 5) were three of the top scoring poses obtained
by proteineprotein docking using the Patchdock server for helical
a-synuclein, whereas Dimers 3 (Fig. 3), 4 (Fig. 4) and 6 (Fig. 6) were
the top three helical dimers found using Cluspro. Dimers 1e4 were
obtained by docking the 1XQ8 structure onto itself, but in the case
of Dimers 5 and 6, a linear model of 1XQ8 was created by stretching
this pdb in MOE and then docking the result onto itself. Dimer 7
(Fig. 7) was created by docking the b-structured monomer onto
itself using the Patchdock server, whereas Dimer 8 (Fig. 8) was
found using the Cluspro server.
The leap module of Amber [51] was used to add missing
hydrogen atoms and heavy atoms using the Amber force field (ff10)
parameters [52]. To neutralize the charge of the system, we added
an appropriate number of sodium ions. The model was immersed in
a truncated cube-shaped shell of TIP3P water molecules [53]. The
numbers of TIP3P molecules added were as follows: 81181 to
Dimer-1, 82016 to Dimer-2, 28588 to Dimer-3, 52941 to Dimer-4,
86860 to Dimer-5, 50985 to Dimer-6, 18107 to Dimer-7 and
26516 to Dimer-8. A time step of 2 fs and a direct-space, non-
bonded cutoff of 10 Å were used. After the protein preparation, all
systems were minimized to remove steric clashes. The systems
Fig. 1. Dimer-1, first of the two dimers selected from top scoring poses of docking runs
using the patchdock server.
Fig. 2. Dimer-2, second of the two dimers selected from top scoring poses of docking
runs using the patchdock server.
K.K. Sahu et al. / Biochimie 116 (2015) 133e140134](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adc705d1-92fd-4fef-a74d-dd2b27809d03-160205184651/85/biochimie-paper-final-version-2-320.jpg)
![were then gradually heated from 0 to 300 K over a period of 50 ps
with constraints on solute, and then maintained in the iso-
thermaleisobaric ensemble (NPT) at a target temperature of 300 K
and pressure of 1 bar using a Langevin thermostat [54] and [55]
Berendsen barostat, with a collision frequency of 2 ps and a pres-
sure relaxation time of 1 ps, respectively. Hydrogen bonds were
constrained using SHAKE [56].
MD simulations were performed using the velocity-
Verlet algorithm (default algorithm for the Amber MD package).
The particle-mesh Ewald (PME) method was used to treat long-
range electrostatic interactions using default parameters [57].
Once our systems reached the target temperature, they were
equilibrated for 500 ps and the production run was continued for
100 ns in the isothermaleisobaric ensemble using the same Lan-
gevin thermostat and Berendsen barostat. Systems were simulated
for a total of 100,600 ps (ps). Out of this simulation time, 50 ps
accounted for heating, 50 ps was density equilibration and 500 ps
was equilibration at NPT, so that the system was simulated for
600 ps in addition to 100 ns of production run. Representative
structures in the trajectories were collected at 10-ps intervals. The
analysis of trajectories was performed with the PTRAJ module of
Amber.
For the binding free energy calculations, we used the MMeGBSA
method [58], via MMPBSA.py python script [59]. Prior to the
MMeGBSA analysis, all water molecules and the sodium ions were
excluded. The dielectric constant value of 1 for solute and 80 for
surrounding water was used. During the analysis of the MMeGBSA
trajectory, 100 snapshots were collected at the interval of 10 ps
from the last 1 ns of the 100 ns trajectory.
The final estimated binding energy was calculated using the
following equation
DGbind ¼ GComplex À GReceptor À GLigand (1)
where G stands for Gibbs free energy. The change in binding free
energy is calculated as the sum of energies from molecular me-
chanics calculations, polar contribution and non-polar contribution
to solvation free energy
DGbind ¼ DEMM þ DGPolar þ DGnonÀPolar (2)
In Equation (2), EMM ¼ Eint þ Eele þ Evdw. DGPolar is the polar
contribution to the solvation free energy and DGnon-Polar is the non
polar contribution to the solvation free energy, the latter defined as
Fig. 3. Dimer-3, first of the two dimers selected from top scoring poses of docking runs
using the cluspro server.
Fig. 4. Dimer-4, second of the two dimers selected from top scoring poses of docking
runs using the cluspro server.
K.K. Sahu et al. / Biochimie 116 (2015) 133e140 135](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adc705d1-92fd-4fef-a74d-dd2b27809d03-160205184651/85/biochimie-paper-final-version-3-320.jpg)
![DGnon-Polar ¼ GSASA þ b, where gamma (surface tension constant) is
expressed as G (gamma) ¼ 0.0072 kcal molÀ1
ÅÀ2
and b ¼ 0 for
Amber GBSA calculations, and SASA is the solvent accessible surface
area. The entropic energy TDS is normally subtracted from DGbind in
Equation (2) but it is typically calculated by computationally
expensive normal mode analysis; since other ligands (same
monomers) will bind to the same protein, we neglected entropic
contributions to the binding free energy in our calculations as
relatively insignificant. DEMM is the molecular mechanics contri-
bution to binding in vacuo expressed as the sum of the internal,
electrostatic and van der Waals contributions. Since this is a single
trajectory approach, the internal energy Eint will cancel out, so that
EMM ¼ Eele þ Evdw.
Calculated binding energies have the following components
that appear in Tables 1e8: (a) DEvdw, the van der Waals contribution
from MM; (b)Eele, the electrostatic energy as calculated by the MM
force field; (c), DGPolar, the electrostatic contribution to the solva-
tion free energy calculated by GB; (d)DGnon-Polar, the non-polar
contribution to the solvation free energy calculated by an empir-
ical model; and (e), DGbind, the final estimated binding free energy
calculated from the all the terms (a to d).
3. Results and discussion
The top-scoring structures found from docking a monomer to
another and used as initial structures for MD simulation are shown
in Figs. 1e8.
After the 50-ps heating phase, all dimers had consistently stable
kinetic, potential and total energies, indicating that the initial
dimer structures were minimized correctly and well-equilibrated,
and that the system did not become destabilized. Several com-
mon features can be discerned in these dimer structures. First, the
C-terminal domains end up being well-separated, owing to elec-
trostatic repulsion between these charged domains: they have high
negative charge (net charge of À8 at pH 7.2 for residues 120e140
[60]). The C-termini also stayed in extended conformation, and
were the most mobile part of the structures. In contrast, the central
region, which has only a slightly positive charge (net charge of þ3
for residues 30e100) and is more hydrophobic, formed the majority
of the interface between monomer domains.
Fig. 5. Dimer-5, a dimer obtained from top scoring poses of docking linear monomers
using the patchdock server.
Fig. 6. Dimer-6, a dimer obtained from top scoring poses of docking linear monomers
using the cluspro server.
K.K. Sahu et al. / Biochimie 116 (2015) 133e140136](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adc705d1-92fd-4fef-a74d-dd2b27809d03-160205184651/85/biochimie-paper-final-version-4-320.jpg)
![Hydrophobic interactions (van der Waals and non-polar contribu-
tions) were strongest in the case of Dimer 4 and Dimer 5, with a
free-energy contribution of À327.9 kcal/mol and 380.0 kcal/mol,
respectively, and weakest in the case of Dimer 1, at À270.7 kcal/
mol. Dimer 1 was also the least stable in terms of total binding
energy, with binding energies of À105.85 kcal/mol. The binding
stability of the dimers was generally correlated with the strength of
the hydrophobic interactions with the exception of Dimer 6: in
terms of decreasing stability for the helical dimers, we found:
Dimer 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1, whereas ranking them according to a
decreasing hydrophobic interaction strength we found: Dimer 5, 4,
2, 6, 3, and 1.
Turning to the two dimers containing b-sheets as secondary-
structure motifs (Dimers 7 and 8), Dimer 8 had the higher contri-
bution from hydrophobic interactions (À271.8 kcal/mol as
compared to À227.6 kcal/mol in Dimer 7) and the higher binding
energy, mirroring the correlation between binding strength and
hydrophobic interactions seen for the helical dimers. Dimer 7 had
lower binding energy mostly owing to a lesser contribution from
hydrophobic interactions. The b-structured dimers were, however,
less stable than the helical dimers, with the most stable b-structured
dimer less stable than all helical dimers except Dimers 1 and 2.
In order to detect changes in the compactness of the dimer
structures over time, the radii of gyration, Rg, were calculated
(Fig. 9) from the MD simulations.
Decreases in Rg indicate increased interactions during the sim-
ulations drawing the residues closer. The helical dimers, Dimers
1e6, all had larger radii of gyration as compared to the b-structured
dimers (7 and 8), indicating the b-sheets led to more compact
structure formation. Rg was quite stable over the course of the
simulation for the b-structured dimers, indicating almost optimal
packing of the monomer domains after the initial docking calcu-
lation, whereas all helical dimers demonstrated some degree of
compaction over time during the MD simulation.
It is somewhat surprising how a disordered protein can
assemble itself into an organized structure like a fibril. a-Synuclein
is known to have great conformational plasticity and can have
different configurations depending upon the environment it is in
Ref. [61]. This study of potential dimer structures formed from
either helical or b-structured monomers is a starting point in
exploring the structural possibilities in a-synuclein oligomers. At
least at the stage of modeling dimers, our results suggest that a b-
structured oligomer may be less stable than a helical oligomer.
However, helical dimers are less compact, suggesting that matu-
ration from helical to b-rich structures [13] should be accompanied
by an overall compaction of the oligomer, which will counteract to
some extent the increase in size associated with addition of more
monomer subunits. Further simulations of other potential dimer
structures, as well as higher-order oligomers (in the ~4e30-mer
range matching observations in single-molecule studies [13,35] as
well as purified oligomers [32,62]) will be needed to understand
better the early aggregation intermediates of a-synuclein associ-
ated with neurodegeneration.
We note that the affinities with which monomers bind to form a
dimer represent an important parameter from the point of view of
designing drugs to inhibit oligomer formation. Designing a small
molecule to disrupt the interactions between monomers will pose a
challenge when dealing with monomers that interact with high
affinity. In such cases, it will be desirable to discover a molecule
with very high affinity towards a-synuclein that simultaneously
possesses favorable pharmacological properties such as low mo-
lecular weight, low polar surface area and a limited number of
hydrogen bond donors, which will allow the molecule to cross the
blood brain barrier as is required for therapies involving neurode-
generative diseases. The role of hydrophobic regions of a-synuclein
Table 8
Binding free energy and its components for Dimer-8 obtained by MMGBSA methods
(kcal molÀ1
).
Components Contribution (kcal/mol) Std. Dev.
DEvdw À239.89 9.4
DEele À875.95 121.83
DGpolar 1003.22 122.31
DGnon-polar À31.97 1.06
DGbind À144.60 7.82
Fig. 9. Radii of Gyration over 100,600 ps of simulation for all 8 dimers.
K.K. Sahu et al. / Biochimie 116 (2015) 133e140138](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adc705d1-92fd-4fef-a74d-dd2b27809d03-160205184651/85/biochimie-paper-final-version-6-320.jpg)
![monomers in dimer formation cannot be ignored as our binding
energy calculations indicate hydrophobicity plays an important
role. Therefore, an effective small molecule inhibitor of this inter-
action is expected to have hydrophobic moieties as major design
features.
4. Conclusions
The results of our computational simulations of dimers formed
by the intrinsically disordered protein a-synuclein have led to the
conclusion that stable dimers could be formed from helical as well
as b-structured forms of the monomer. The central hydrophobic
region of the a-synuclein monomer was a prominent feature in all
dimer structures obtained, suggesting that hydrophobic in-
teractions play an important role in the binding affinity. The helical
dimer structures were generally more stable than the b-structured
dimers, but dimers containing b-sheets were more compact than
helical dimers, which could produce stronger interactions between
residues of different monomers when b-structured and play a role
in driving the oligomerization process toward fibrillar structures.
Interfaces between the domains in these dimers may be helpful for
future work in creating a pharmacophore for use in hierarchical or
parallel virtual screening to identify compounds from small mole-
cule databases that may disrupt monomeremonomer interactions.
Author contributions
Sahu, KK e Designed research; Performed research; Analyzed
data; Wrote the Manuscript.
Woodside, MT e Helped design research, Contributed to data
interpretation and writing of manuscript.
Tuszynski, JA e Helped design research, Contributed to data
interpretation and writing of manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by an Alberta Innovates Health Solu-
tions CRIO (201200841) grant. The authors thank the funding
agency for their valuable resources, which made this research
possible. All computational work was performed on Pharmamatrix
cluster and Westgrid distributed computing network.
References
[1] C. Duyckaerts, Neurodegenerative lesions: seeding and spreading, Rev. Neurol.
169 (2013) 825e833.
[2] B.S. Gadad, G.B. Britton, K.S. Rao, Targeting oligomers in neurodegenerative
disorders: lessons from alpha-synuclein, tau, and amyloid-beta peptide,
J. Alzheimer's Dis. JAD 24 (Suppl. 2) (2011) 223e232.
[3] M. Hashimoto, E. Rockenstein, L. Crews, E. Masliah, Role of protein aggregation
in mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's and
Parkinson's diseases, Neuromol. Med. 4 (2003) 21e36.
[4] A. Ciechanover, Y.T. Kwon, Degradation of misfolded proteins in neurode-
generative diseases: therapeutic targets and strategies, Exp. Mol. Med. 47
(2015) e147.
[5] T. Yasuda, Y. Nakata, H. Mochizuki, Alpha-synuclein and neuronal cell death,
Mol. Neurobiol. 47 (2013) 466e483.
[6] N. Cavallarin, M. Vicario, A. Negro, The role of phosphorylation in synuclei-
nopathies: focus on Parkinson's disease, CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 9
(2010) 471e481.
[7] V.N. Uversky, J. Li, A.L. Fink, Evidence for a partially folded intermediate in
alpha-synuclein fibril formation, J. Biol. Chem. 276 (2001) 10737e10744.
[8] K. Iwanaga, K. Wakabayashi, M. Yoshimoto, I. Tomita, H. Satoh, H. Takashima,
A. Satoh, M. Seto, M. Tsujihata, H. Takahashi, Lewy body-type degeneration in
cardiac plexus in Parkinson's and incidental Lewy body diseases, Neurology 52
(1999) 1269e1271.
[9] H. Kaufmann, K. Hague, D. Perl, Accumulation of alpha-synuclein in autonomic
nerves in pure autonomic failure, Neurology 56 (2001) 980e981.
[10] M.G. Spillantini, R.A. Crowther, R. Jakes, M. Hasegawa, M. Goedert, Alpha-
synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson's disease
and dementia with Lewy bodies, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95 (1998)
6469e6473.
[11] M.G. Spillantini, R.A. Crowther, R. Jakes, N.J. Cairns, P.L. Lantos, M. Goedert,
Filamentous alpha-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with
Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies, Neurosci. Lett. 251
(1998) 205e208.
[12] H.A. Lashuel, B.M. Petre, J. Wall, M. Simon, R.J. Nowak, T. Walz,
P.T. Lansbury Jr., Alpha-synuclein, especially the Parkinson's disease-
associated mutants, forms pore-like annular and tubular protofibrils, J. Mol.
Biol. 322 (2002) 1089e1102.
[13] N. Cremades, S.I. Cohen, E. Deas, A.Y. Abramov, A.Y. Chen, A. Orte, M. Sandal,
R.W. Clarke, P. Dunne, F.A. Aprile, C.W. Bertoncini, N.W. Wood, T.P. Knowles,
C.M. Dobson, D. Klenerman, Direct observation of the interconversion of
normal and toxic forms of alpha-synuclein, Cell 149 (2012) 1048e1059.
[14] H.A. Lashuel, P.T. Lansbury Jr., Are amyloid diseases caused by protein ag-
gregates that mimic bacterial pore-forming toxins? Q. Rev. Biophys. 39 (2006)
167e201.
[15] Y. Zarbiv, D. Simhi-Haham, E. Israeli, S.A. Elhadi, J. Grigoletto, R. Sharon, Lysine
residues at the first and second KTKEGV repeats mediate alpha-synuclein
binding to membrane phospholipids, Neurobiol. Dis. 70 (2014) 90e98.
[16] S.B. Nielsen, F. Macchi, S. Raccosta, A.E. Langkilde, L. Giehm, A. Kyrsting,
A.S. Svane, M. Manno, G. Christiansen, N.C. Nielsen, L. Oddershede,
B. Vestergaard, D.E. Otzen, Wildtype and A30P mutant alpha-synuclein form
different fibril structures, PloS One 8 (2013) e67713.
[17] K.A. Conway, S.J. Lee, J.C. Rochet, T.T. Ding, R.E. Williamson, P.T. Lansbury Jr.,
Acceleration of oligomerization, not fibrillization, is a shared property of both
alpha-synuclein mutations linked to early-onset Parkinson's disease: impli-
cations for pathogenesis and therapy, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97 (2000)
571e576.
[18] M.S. Goldberg, P.T. Lansbury Jr., Is there a cause-and-effect relationship be-
tween alpha-synuclein fibrillization and Parkinson's disease? Nat. Cell Biol. 2
(2000) E115eE119.
[19] R.A. Fredenburg, C. Rospigliosi, R.K. Meray, J.C. Kessler, H.A. Lashuel, D. Eliezer,
P.T. Lansbury Jr., The impact of the E46K mutation on the properties of alpha-
synuclein in its monomeric and oligomeric states, Biochemistry 46 (2007)
7107e7118.
[20] W. Choi, S. Zibaee, R. Jakes, L.C. Serpell, B. Davletov, R.A. Crowther, M. Goedert,
Mutation E46K increases phospholipid binding and assembly into filaments of
human alpha-synuclein, FEBS Lett. 576 (2004) 363e368.
[21] C.W. Bertoncini, C.O. Fernandez, C. Griesinger, T.M. Jovin, M. Zweckstetter,
Familial mutants of alpha-synuclein with increased neurotoxicity have a
destabilized conformation, J. Biol. Chem. 280 (2005) 30649e30652.
[22] A.C. Ferreon, C.R. Moran, J.C. Ferreon, A.A. Deniz, Alteration of the alpha-
synuclein folding landscape by a mutation related to Parkinson's disease,
Angew. Chem. 49 (2010) 3469e3472.
[23] R. Bussell Jr., D. Eliezer, Residual structure and dynamics in Parkinson's
disease-associated mutants of alpha-synuclein, J. Biol. Chem. 276 (2001)
45996e46003.
[24] I.F. Tsigelny, Y. Sharikov, V.L. Kouznetsova, J.P. Greenberg, W. Wrasidlo,
C. Overk, T. Gonzalez, M. Trejo, B. Spencer, K. Kosberg, E. Masliah, Molecular
determinants of alpha-synuclein mutants' oligomerization and membrane
interactions, ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6 (2015) 403e416.
[25] N.J. Rutherford, B.D. Moore, T.E. Golde, B.I. Giasson, Divergent effects of the
H50Q and G51D SNCA mutations on the aggregation of alpha-synuclein,
J. Neurochem. 131 (2014) 859e867.
[26] S. Sahay, D. Ghosh, S. Dwivedi, A. Anoop, G.M. Mohite, M. Kombrabail,
G. Krishnamoorthy, S.K. Maji, Familial Parkinson disease-associated mutations
alter the site-specific microenvironment and dynamics of alpha-synuclein,
J. Biol. Chem. 290 (2015) 7804e7822.
[27] D.F. Clayton, J.M. George, The synucleins: a family of proteins involved in
synaptic function, plasticity, neurodegeneration and disease, Trends Neurosci.
21 (1998) 249e254.
[28] D. Ghosh, P.K. Singh, S. Sahay, N.N. Jha, R.S. Jacob, S. Sen, A. Kumar, R. Riek,
S.K. Maji, Structure based aggregation studies reveal the presence of helix-rich
intermediate during alpha-synuclein aggregation, Sci. Rep. 5 (2015) 9228.
[29] T.S. Ulmer, A. Bax, N.B. Cole, R.L. Nussbaum, Structure and dynamics of
micelle-bound human alpha-synuclein, J. Biol. Chem. 280 (2005) 9595e9603.
[30] W.S. Davidson, A. Jonas, D.F. Clayton, J.M. George, Stabilization of alpha-
synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes, J. Biol.
Chem. 273 (1998) 9443e9449.
[31] R.J. Perrin, W.S. Woods, D.F. Clayton, J.M. George, Interaction of human alpha-
synuclein and Parkinson's disease variants with phospholipids. Structural
analysis using site-directed mutagenesis, J. Biol. Chem. 275 (2000)
34393e34398.
[32] W. Paslawski, M. Andreasen, S.B. Nielsen, N. Lorenzen, K. Thomsen,
J.D. Kaspersen, J.S. Pedersen, D.E. Otzen, High stability and cooperative
unfolding of alpha-synuclein oligomers, Biochemistry 53 (2014) 6252e6263.
[33] W. Hoyer, T. Antony, D. Cherny, G. Heim, T.M. Jovin, V. Subramaniam,
Dependence of alpha-synuclein aggregate morphology on solution conditions,
J. Mol. Biol. 322 (2002) 383e393.
[34] M. Vilar, H.T. Chou, T. Luhrs, S.K. Maji, D. Riek-Loher, R. Verel, G. Manning,
H. Stahlberg, R. Riek, The fold of alpha-synuclein fibrils, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.
S. A. 105 (2008) 8637e8642.
[35] K. Neupane, A. Solanki, I. Sosova, M. Belov, M.T. Woodside, Diverse metastable
structures formed by small oligomers of alpha-synuclein probed by force
spectroscopy, PloS One 9 (2014) e86495.
K.K. Sahu et al. / Biochimie 116 (2015) 133e140 139](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adc705d1-92fd-4fef-a74d-dd2b27809d03-160205184651/85/biochimie-paper-final-version-7-320.jpg)
![[36] M.M. Dedmon, K. Lindorff-Larsen, J. Christodoulou, M. Vendruscolo,
C.M. Dobson, Mapping long-range interactions in alpha-synuclein using spin-
label NMR and ensemble molecular dynamics simulations, J. Am. Chem. Soc.
127 (2005) 476e477.
[37] J.R. Allison, R.C. Rivers, J.C. Christodoulou, M. Vendruscolo, C.M. Dobson,
A relationship between the transient structure in the monomeric state and
the aggregation propensities of alpha-synuclein and beta-synuclein,
Biochemistry 53 (2014) 7170e7183.
[38] P.A. Kollman, I. Massova, C. Reyes, B. Kuhn, S. Huo, L. Chong, M. Lee, T. Lee,
Y. Duan, W. Wang, O. Donini, P. Cieplak, J. Srinivasan, D.A. Case,
T.E. Cheatham 3rd, Calculating structures and free energies of complex mol-
ecules: combining molecular mechanics and continuum models, Acc. Chem.
Res. 33 (2000) 889e897.
[39] V. Tsui, D.A. Case, Theory and applications of the generalized Born solvation
model in macromolecular simulations, Biopolymers 56 (2000) 275e291.
[40] E.B. Gibbs, S.A. Showalter, Quantitative biophysical characterization of
intrinsically disordered proteins, Biochemistry 54 (2015) 1314e1326.
[41] S.A.E. Jonsson, S. Mitternacht, A. Irback, Mechanical resistance in unstructured
proteins, Biophys. J. 104 (2013) 2725e2732.
[42] Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), Chemical Computing Group Inc,
1010 Sherbooke St. West, Suite #910, Montreal, QC, Canada, H3A 2R7, 2013,
2013.08.
[43] D. Duhovny, R. Nussinov, H.J. Wolfson, Efficient unbound docking of rigid
molecules, in: Gusfield, et al. (Eds.), Proceedings of the 2'nd Workshop on
Algorithms in Bioinformatics(WABI) Rome, Italy, Lecture Notes in Computer
Science 2452, Springer Verlag, Rome, Italy, 2002, pp. 185e200.
[44] D. Schneidman-Duhovny, Y. Inbar, R. Nussinov, H.J. Wolfson, PatchDock and
SymmDock: servers for rigid and symmetric docking, Nucleic Acids Res. 33
(2005) W363eW367.
[45] N. Andrusier, R. Nussinov, H.J. Wolfson, FireDock: fast interaction refinement
in molecular docking, Proteins 69 (2007) 139e159.
[46] E. Mashiach, D. Schneidman-Duhovny, N. Andrusier, R. Nussinov, H.J. Wolfson,
FireDock: a web server for fast interaction refinement in molecular docking,
Nucleic Acids Res. 36 (2008) W229eW232.
[47] D. Kozakov, D. Beglov, T. Bohnuud, S.E. Mottarella, B. Xia, D.R. Hall, S. Vajda,
How good is automated protein docking? Proteins 81 (2013) 2159e2166.
[48] D. Kozakov, R. Brenke, S.R. Comeau, S. Vajda, PIPER: an FFT-based protein
docking program with pairwise potentials, Proteins 65 (2006) 392e406.
[49] S.R. Comeau, D.W. Gatchell, S. Vajda, C.J. Camacho, ClusPro: a fully automated
algorithm for protein-protein docking, Nucleic Acids Res. 32 (2004)
W96eW99.
[50] S.R. Comeau, D.W. Gatchell, S. Vajda, C.J. Camacho, ClusPro: an automated
docking and discrimination method for the prediction of protein complexes,
Bioinformatics 20 (2004) 45e50.
[51] D.A. Case, T.E. Cheatham 3rd, T. Darden, H. Gohlke, R. Luo, K.M. Merz Jr.,
A. Onufriev, C. Simmerling, B. Wang, R.J. Woods, The Amber biomolecular
simulation programs, J. Comput. Chem. 26 (2005) 1668e1688.
[52] K. Lindorff-Larsen, S. Piana, K. Palmo, P. Maragakis, J.L. Klepeis, R.O. Dror,
D.E. Shaw, Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB
protein force field, Proteins 78 (2010) 1950e1958.
[53] W.L. Jorgensen, J. Chandrasekhar, J.D. Madura, R.W. Impey, M.L. Klein, Com-
parison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water, J. Chem.
Phys. 79 (1983) 926e935.
[54] J.A. Izaguirre, D.P. Catarello, J.M. Wozniak, R.D. Skeel, Langevin stabilization of
molecular dynamics, J. Chem. Phys. 114 (2001) 2090e2098.
[55] H.J.C. Berendsen, J.P.M. Postma, W.F. van Gunsteren, A. DiNola, J.R. Haak,
Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath, J. Chem. Phys. 81
(1984) 3684e3690.
[56] J.P. Ryckaert, G. C, H.J.C. Berendsen, Numerical integration of the cartesian
equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-
alkanes, J. Comput. Phys. 23 (1977) 327e341.
[57] T. Darden, D. York, L. Pedersen, Particle mesh Ewaldean N-log(N) method for
Ewald sums in large systems, J. Chem. Phys. 98 (1993) 10089e10092.
[58] H. Gohlke, D.A. Case, Converging free energy estimates: MM-PB(GB)SA studies
on the protein-protein complex Ras-Raf, J. Comput. Chem. 25 (2004)
238e250.
[59] B.R. Miller III, T.D. McGee Jr., J.M. Swails, N. Homeyer, H. Gohlke, A.E. Roitberg,
MMPBSA.py: an efficient program for end-state free energy calculations,
J. Chem. Theory Comput. 8 (2012) 3314e3321.
[60] W. Zhou, C. Long, S.H. Reaney, D.A. Di Monte, A.L. Fink, V.N. Uversky, Methi-
onine oxidation stabilizes non-toxic oligomers of alpha-synuclein through
strengthening the auto-inhibitory intra-molecular long-range interactions,
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1802 (2010) 322e330.
[61] V.N. Uversky, A protein-chameleon: conformational plasticity of alpha-
synuclein, a disordered protein involved in neurodegenerative disorders,
J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 21 (2003) 211e234.
[62] M.T. Stockl, N. Zijlstra, V. Subramaniam, Alpha-synuclein oligomers: an am-
yloid pore? Insights into mechanisms of alpha-synuclein oligomer-lipid in-
teractions, Mol. Neurobiol. 47 (2013) 613e621.
K.K. Sahu et al. / Biochimie 116 (2015) 133e140140](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adc705d1-92fd-4fef-a74d-dd2b27809d03-160205184651/85/biochimie-paper-final-version-8-320.jpg)