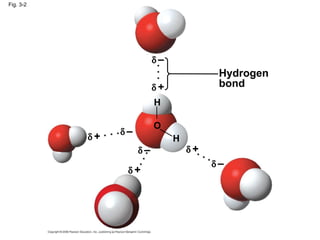
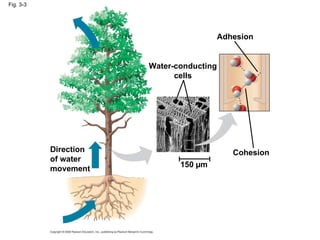
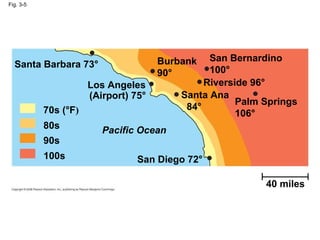
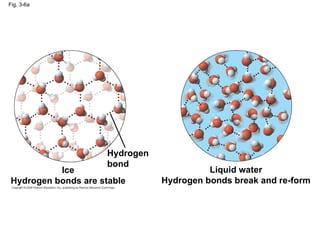
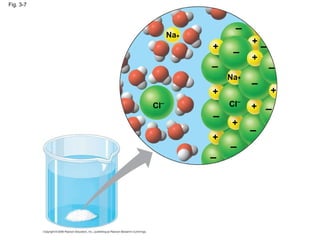
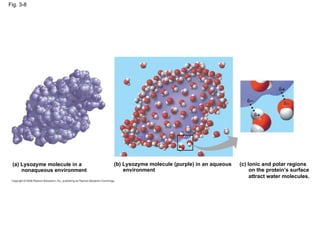
Water is essential for life on Earth. It has unique properties including its ability to form hydrogen bonds which allow it to moderate temperature fluctuations, expand upon freezing, and act as a versatile solvent. These properties emerge from water's polarity and hydrogen bonding, and help create a habitable environment.


















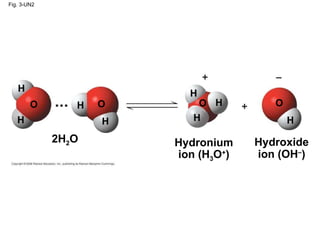


![The pH Scale In any aqueous solution at 25°C the product of H + and OH – is constant and can be written as [H + ][OH – ] = 10 –14 The pH of a solution is defined by the negative logarithm of H + concentration, written as pH = –log [H + ] For a neutral aqueous solution [H + ] is 10 –7 = –(–7) = 7 Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioch3pwpt-100128155333-phpapp01/85/Bio-Ch-3-Pwpt-31-320.jpg)

![Fig. 3-UN5 Bases donate OH – or accept H + in aqueous solutions Acids donate H + in aqueous solutions Acidic [H + ] > [OH – ] Neutral [H + ] = [OH – ] Basic [H + ] < [OH – ] 14 7 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioch3pwpt-100128155333-phpapp01/85/Bio-Ch-3-Pwpt-33-320.jpg)
![Fig. 3-9 Neutral solution Acidic solution Basic solution OH – OH – OH – OH – OH – OH – OH – H + H + H + OH – H + H + H + H + OH – OH – OH – OH – H + OH – H + H + H + H + H + H + H + OH – Neutral [H + ] = [OH – ] Increasingly Acidic [H + ] > [OH – ] Increasingly Basic [H + ] < [OH – ] pH Scale 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Battery acid Gastric juice, lemon juice Vinegar, beer, wine, cola Tomato juice Black coffee Rainwater Urine Saliva Pure water Human blood, tears Seawater 9 10 Milk of magnesia Household ammonia Household bleach Oven cleaner 11 12 13 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioch3pwpt-100128155333-phpapp01/85/Bio-Ch-3-Pwpt-34-320.jpg)

