Embed presentation










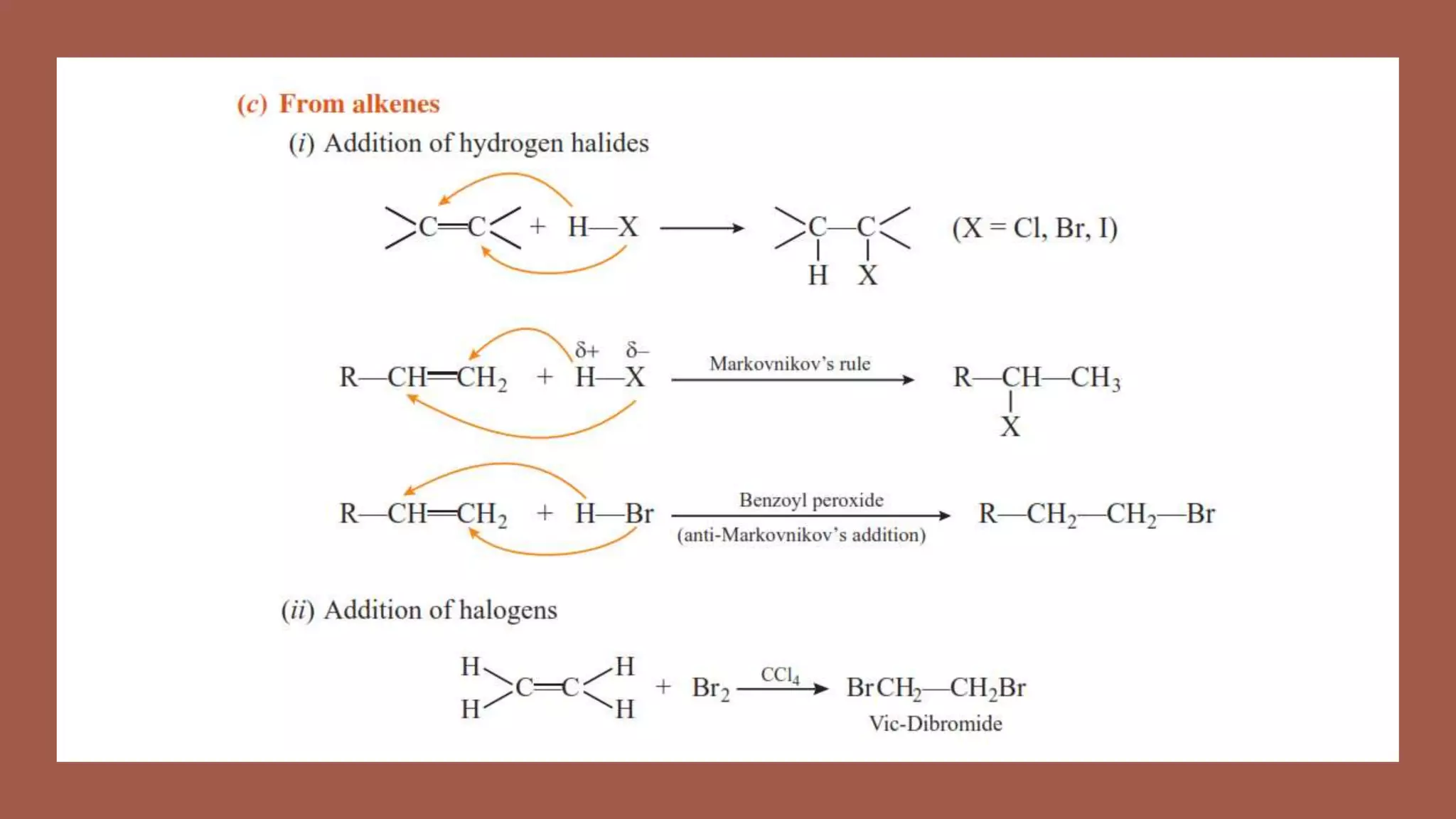








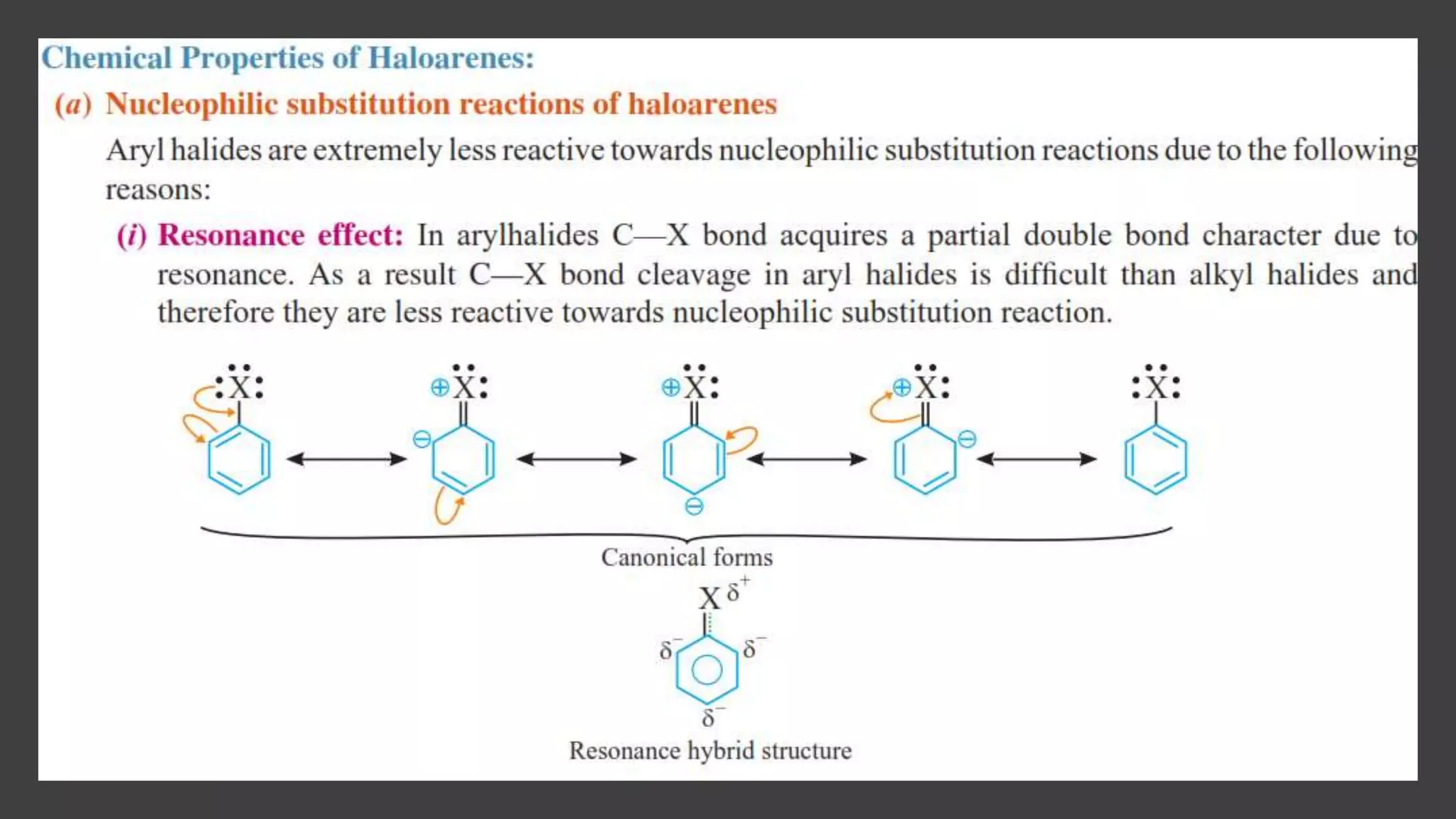




















Haloalkanes have higher boiling points than alkanes due to their polar nature. Among isomeric alkyl halides, boiling point decreases with increased branching in the alkyl group as branching leads to a more spherical shape with less surface area. Bromo, iodo, and polychloro derivatives are denser than water, with density increasing with more carbon/halogen atoms or larger halogen atomic mass. Haloalkanes and haloarenes are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents due to inability to form hydrogen bonds with water. Haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution, dehydrohalogenation, and reactions with metals. Carbon tetrachloride is produced for refrigerants and aeros






































