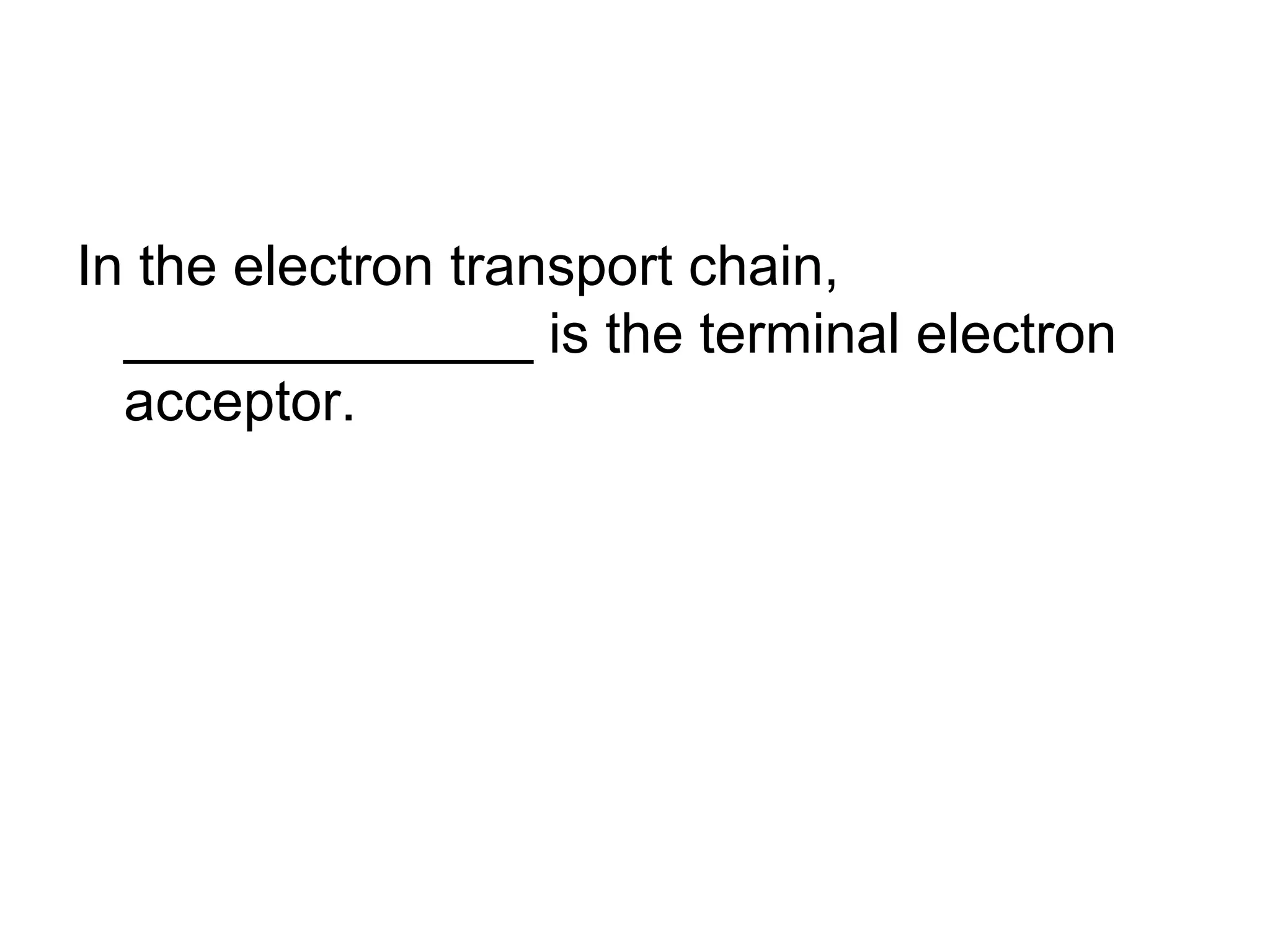
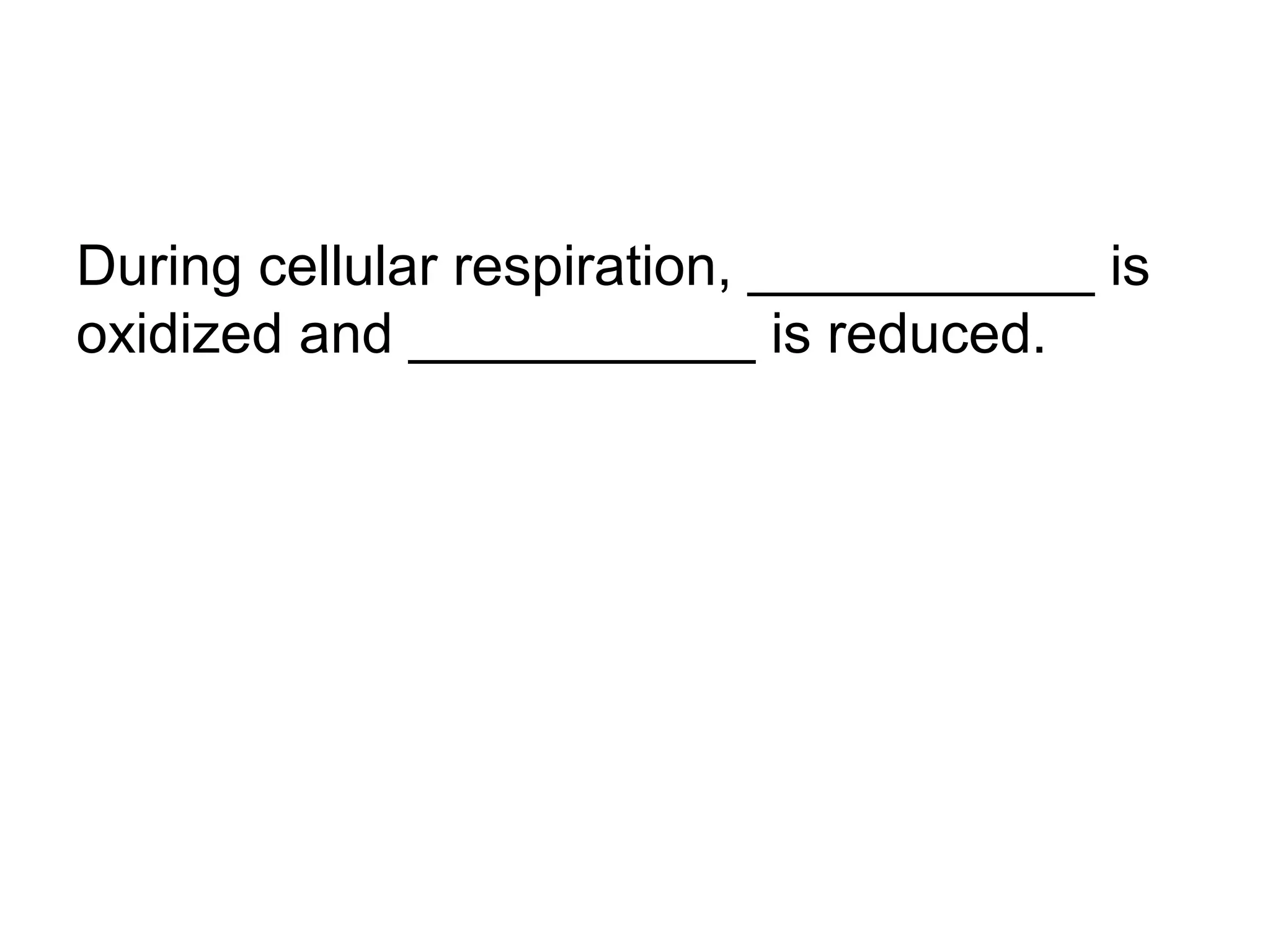
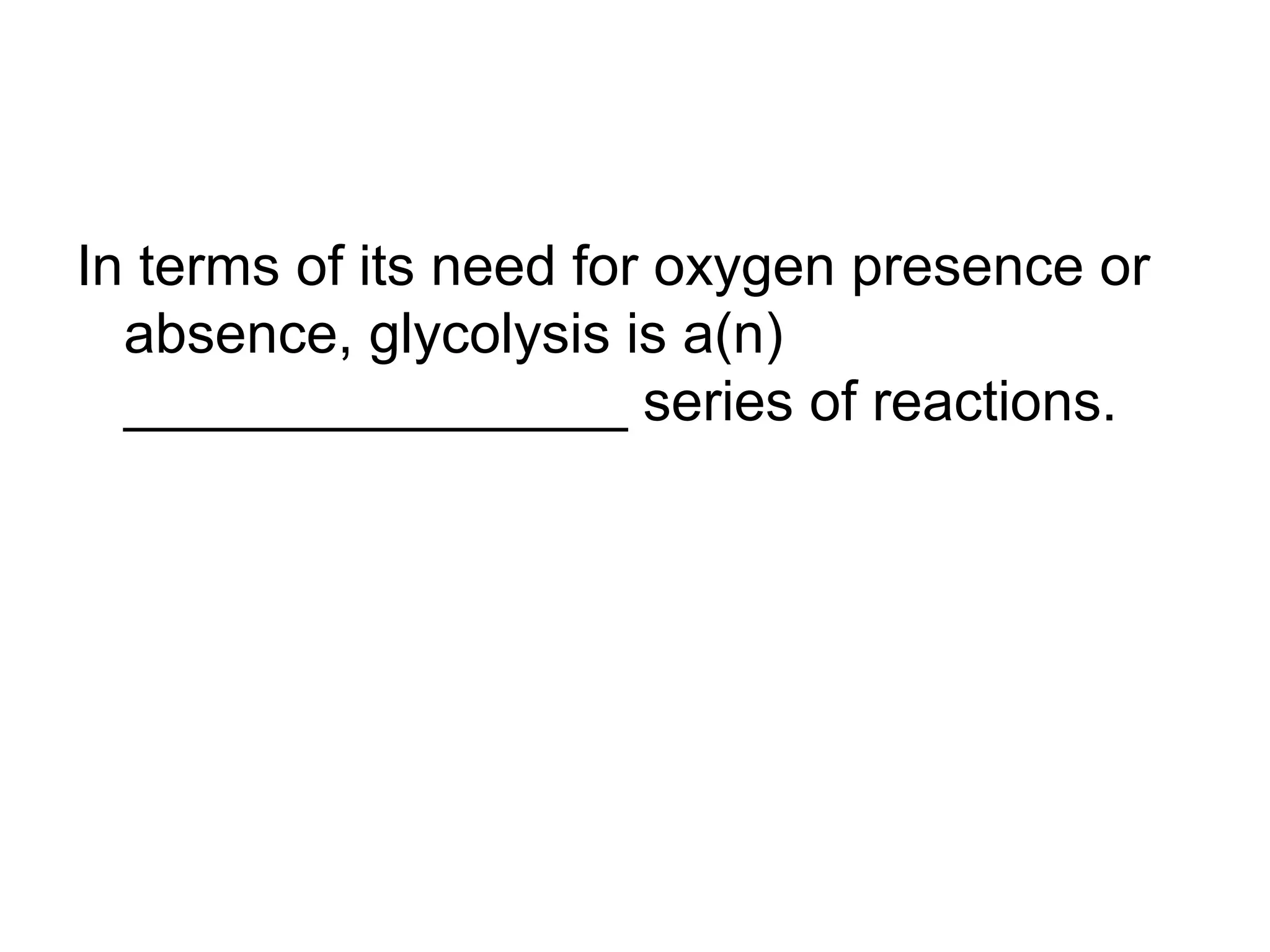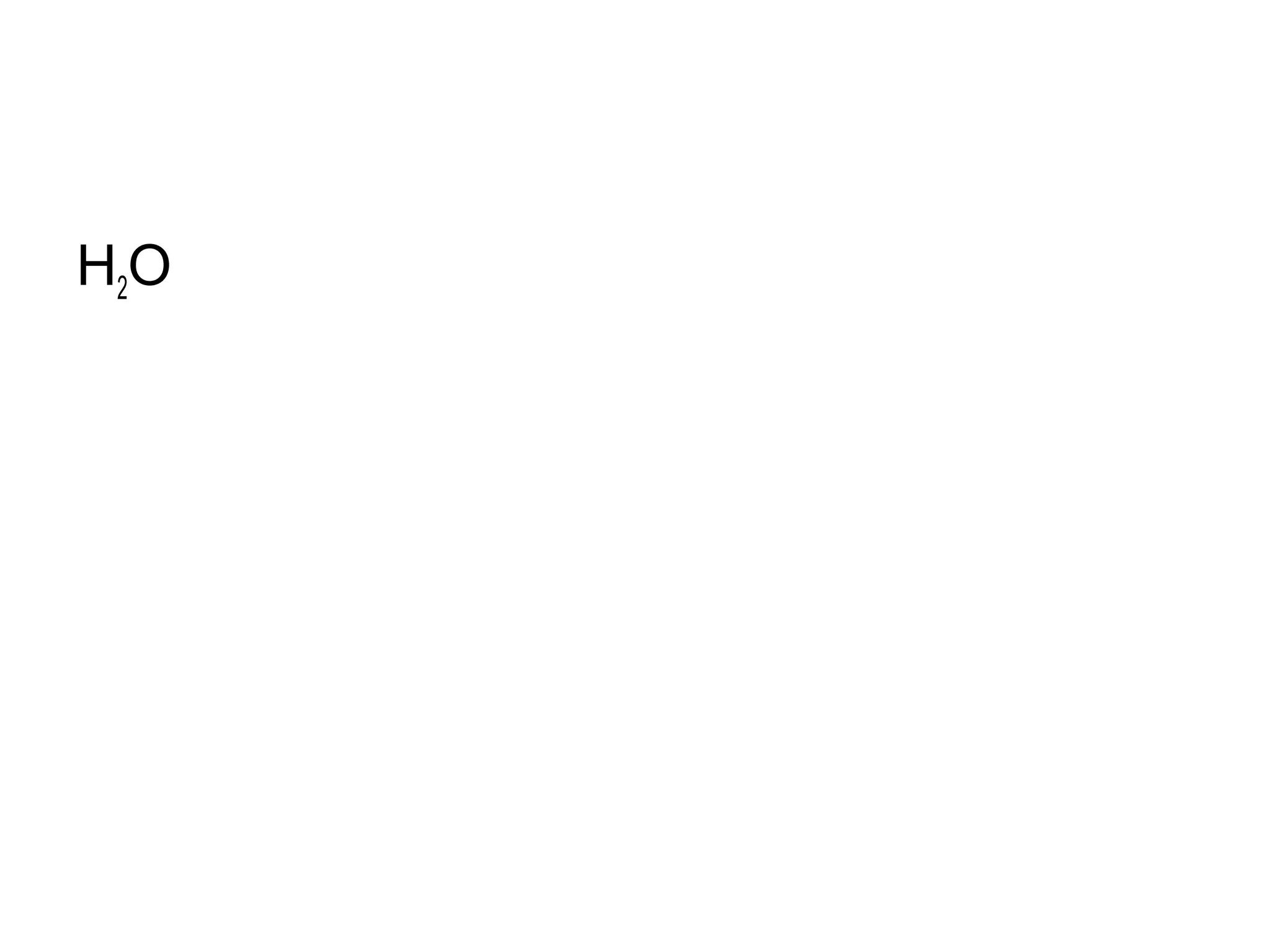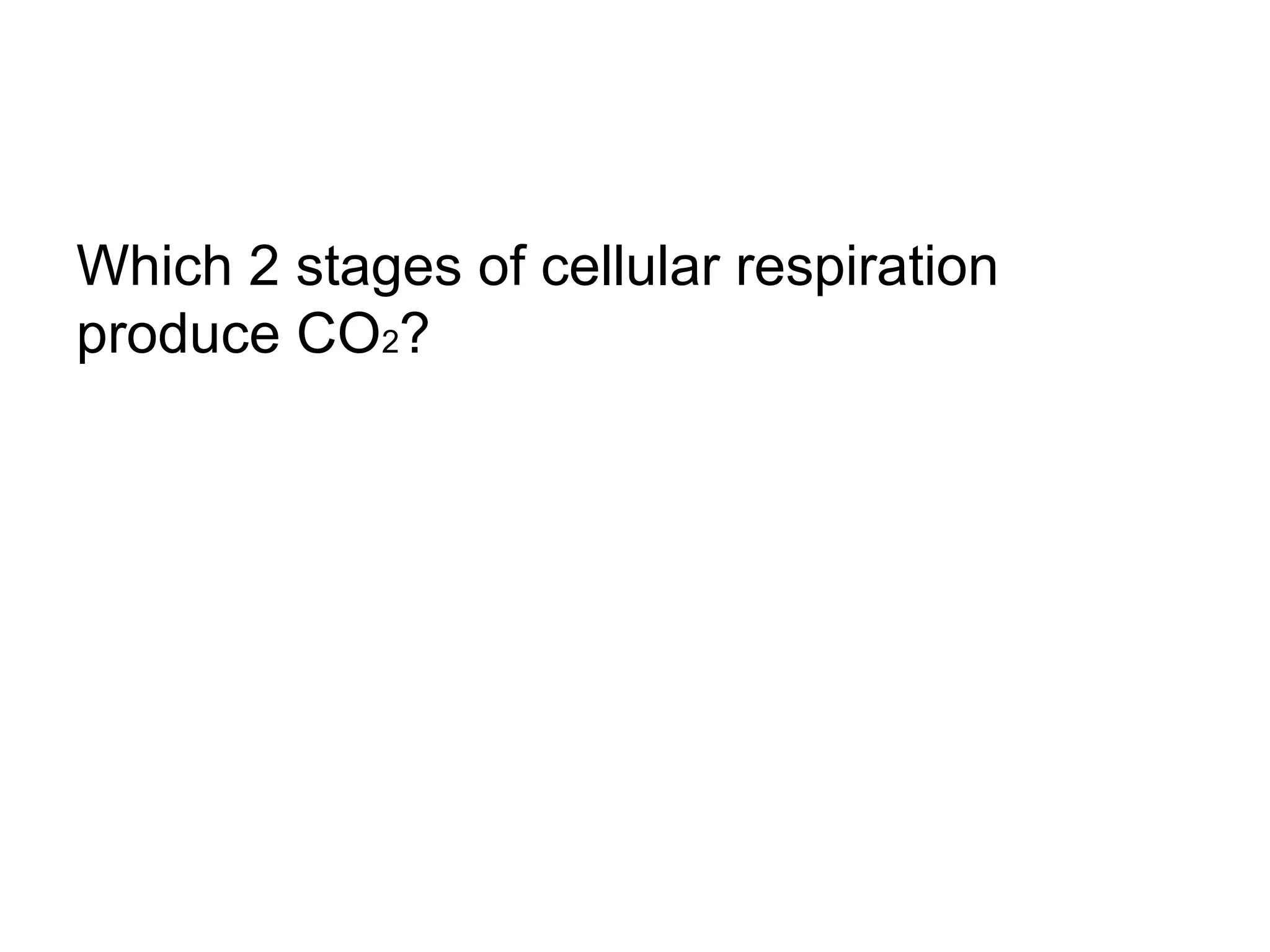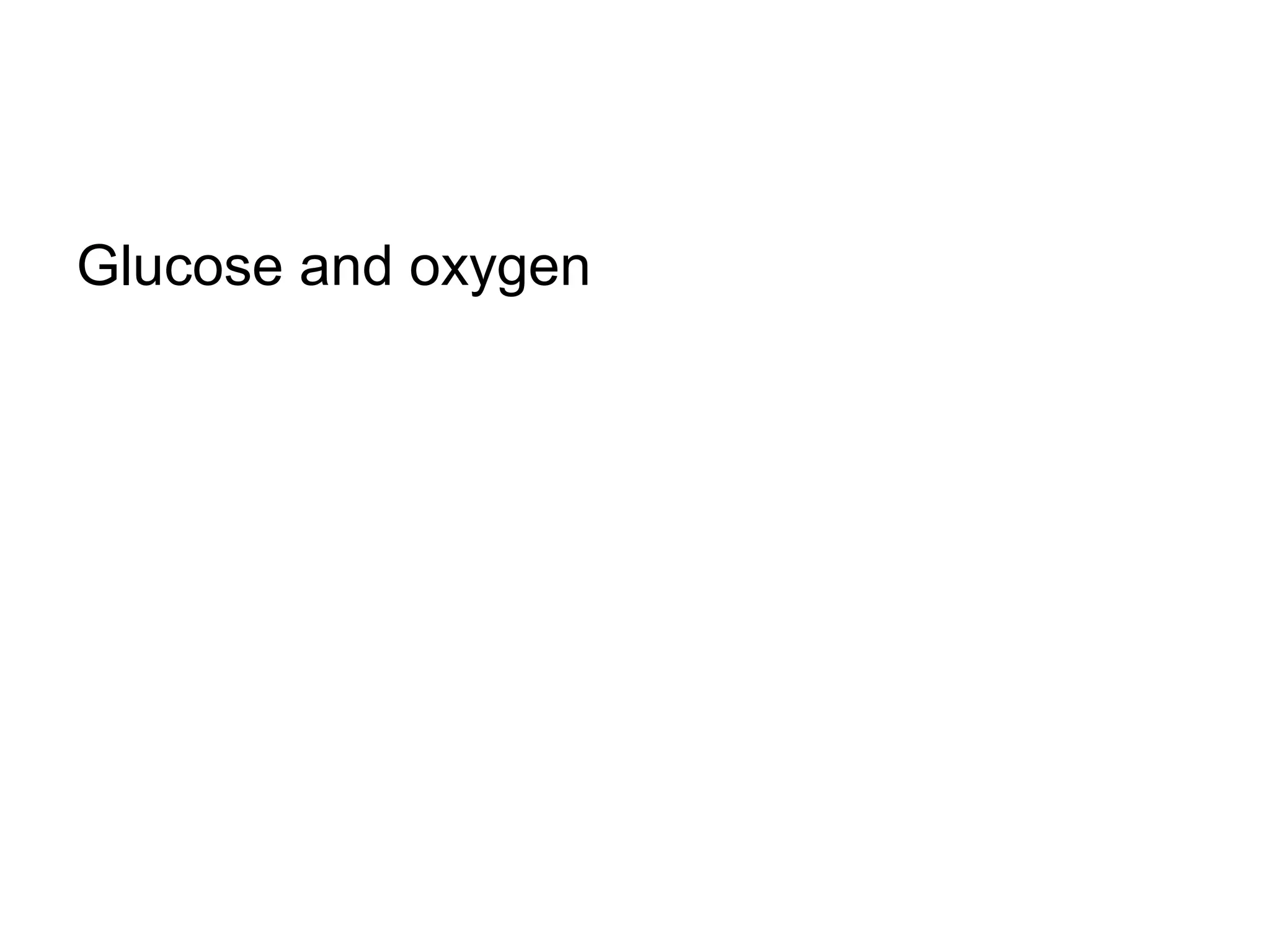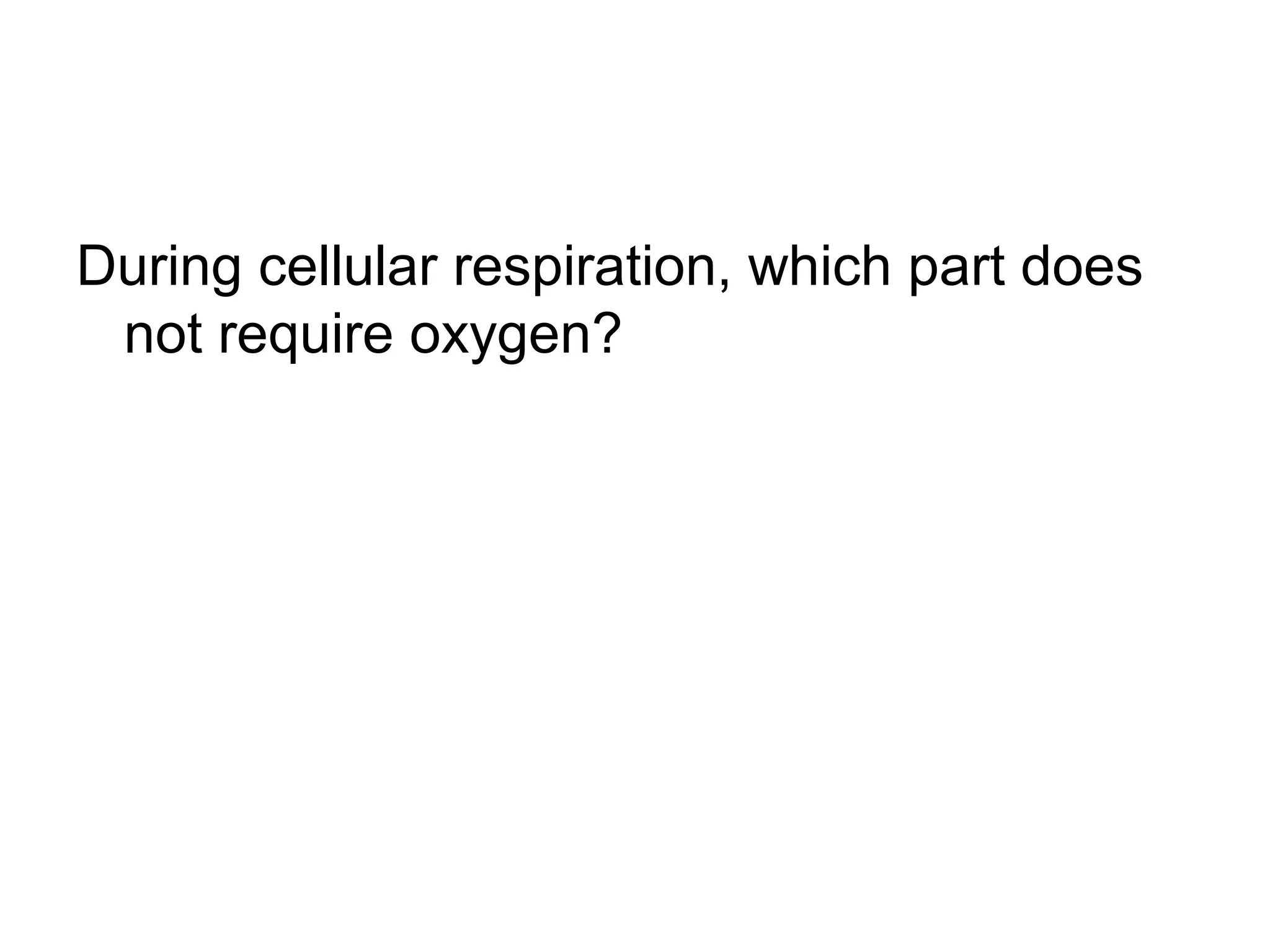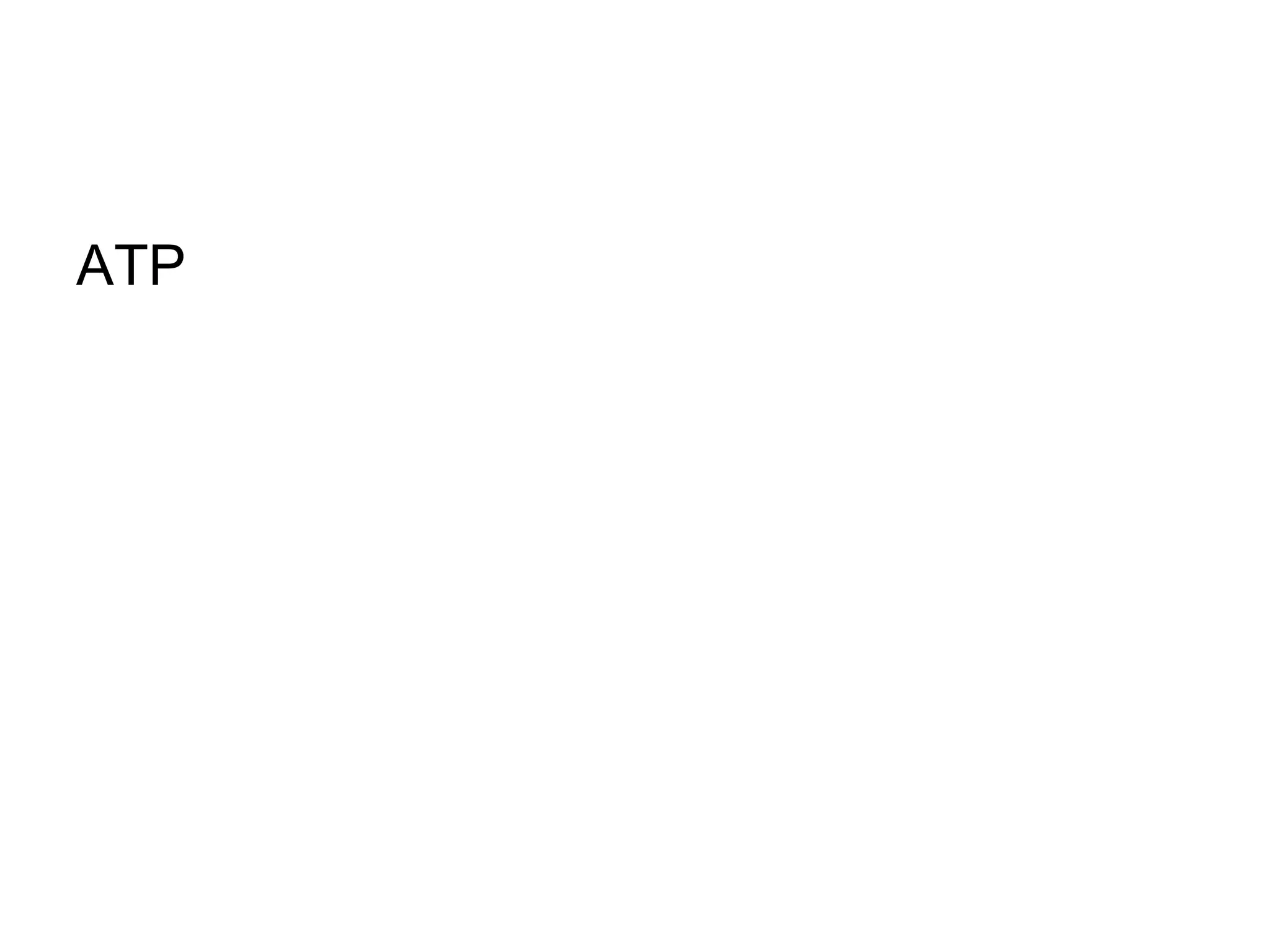During cellular respiration, glucose and oxygen are used as reactants to produce energy in the form of ATP. There are three main stages - glycolysis in the cytoplasm produces 2 ATP and pyruvate, the preparatory reaction moves pyruvate into the mitochondria, and the electron transport chain uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor to produce the most ATP.