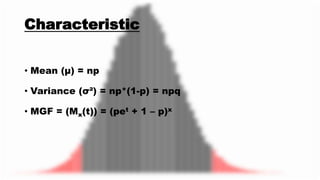
The document discusses the binomial distribution and its applications. It begins by explaining the origin of the binomial distribution, which was discovered by Jacob Bernoulli in the early 1700s. It then defines the binomial distribution as giving two possible results of an experiment with a fixed number of independent Bernoulli trials - success or failure. The key properties are outlined as having two outcomes, a fixed number of trials, constant probability of success/failure per trial, and independent trials. Applications mentioned include using it to model consumer behavior data from market research surveys, success/failure of medical drug trials, and quality control processes.