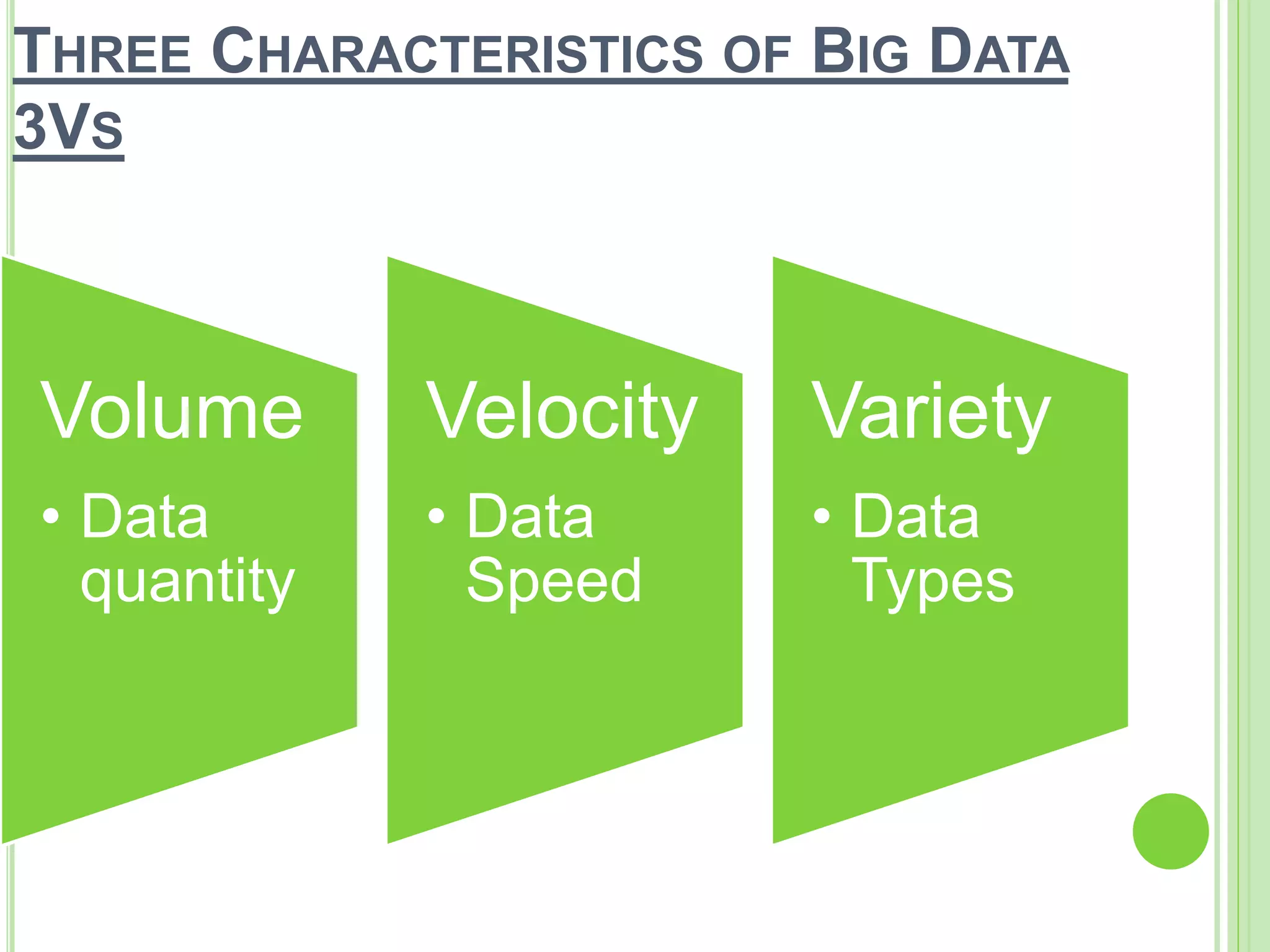
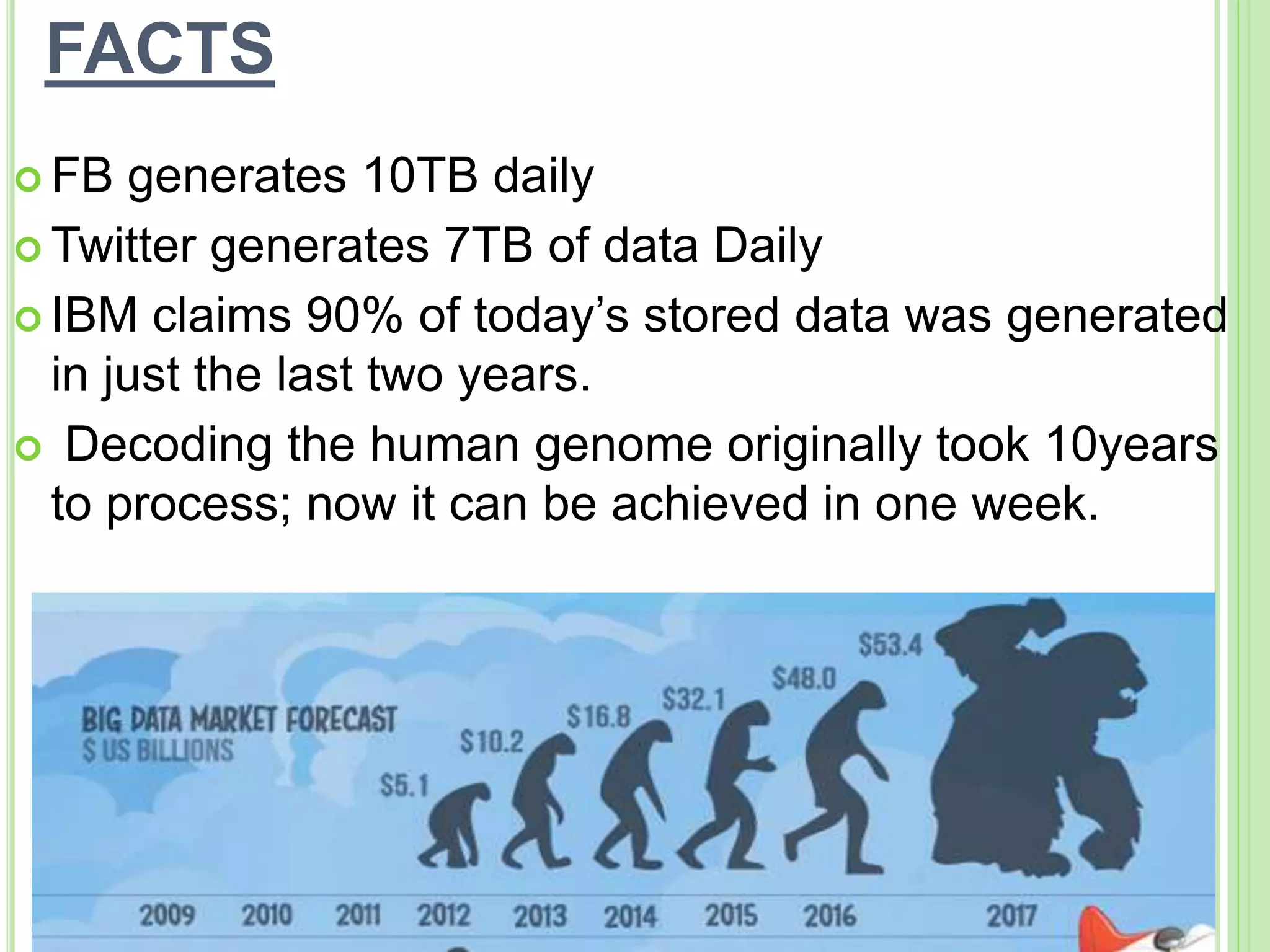
This document discusses big data, including its definition, characteristics of volume, velocity, and variety. It describes sources of big data like administrative data, transactions, public data, sensor data, and social media. It discusses processing big data using techniques like Hadoop MapReduce. It outlines benefits like real-time decision making but also drawbacks like security, privacy, and performance issues. It provides some facts about the size of data generated daily by companies and potential impacts and future growth of the big data industry and job market.