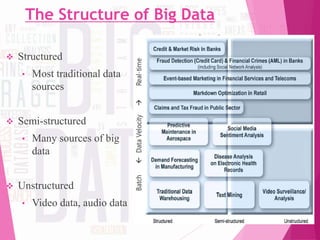
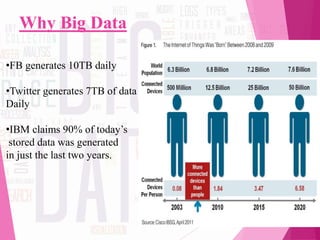
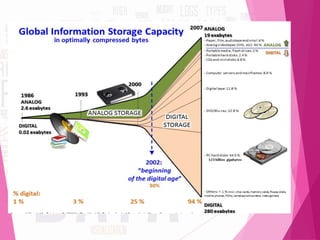
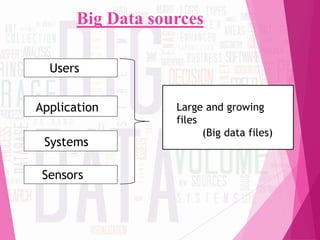
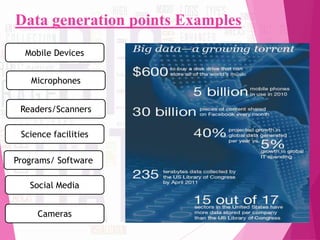
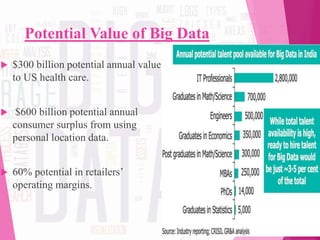
The document discusses 'big data,' its characteristics including volume, velocity, and variety, and the need for new approaches to process and analyze vast amounts of information. It highlights the sources, tools, applications, and potential benefits of big data in various sectors such as healthcare and retail, while also outlining the risks involved. Furthermore, it forecasts significant growth in the big data industry, emphasizing its value and impact on decision-making and economic opportunities.