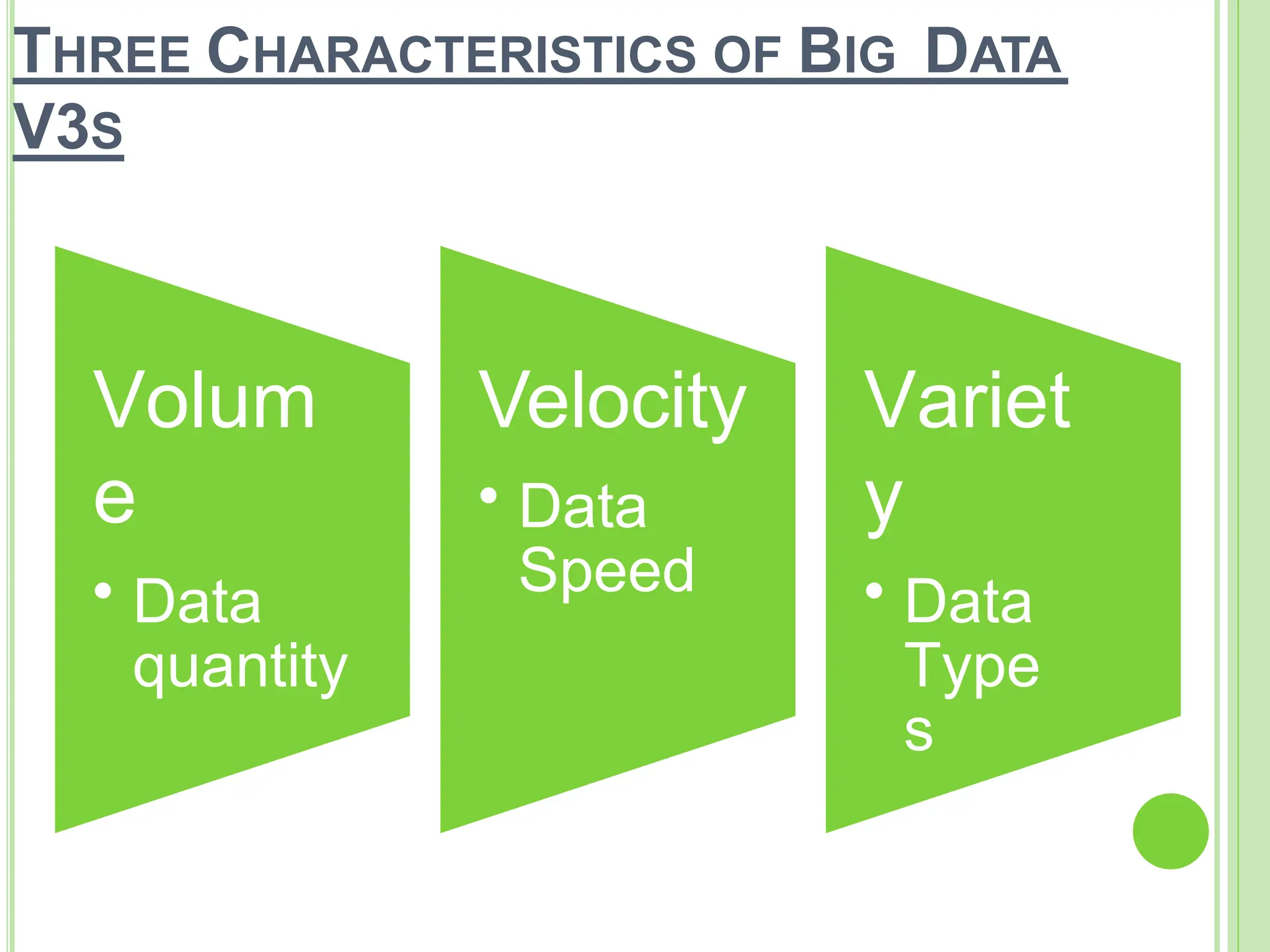
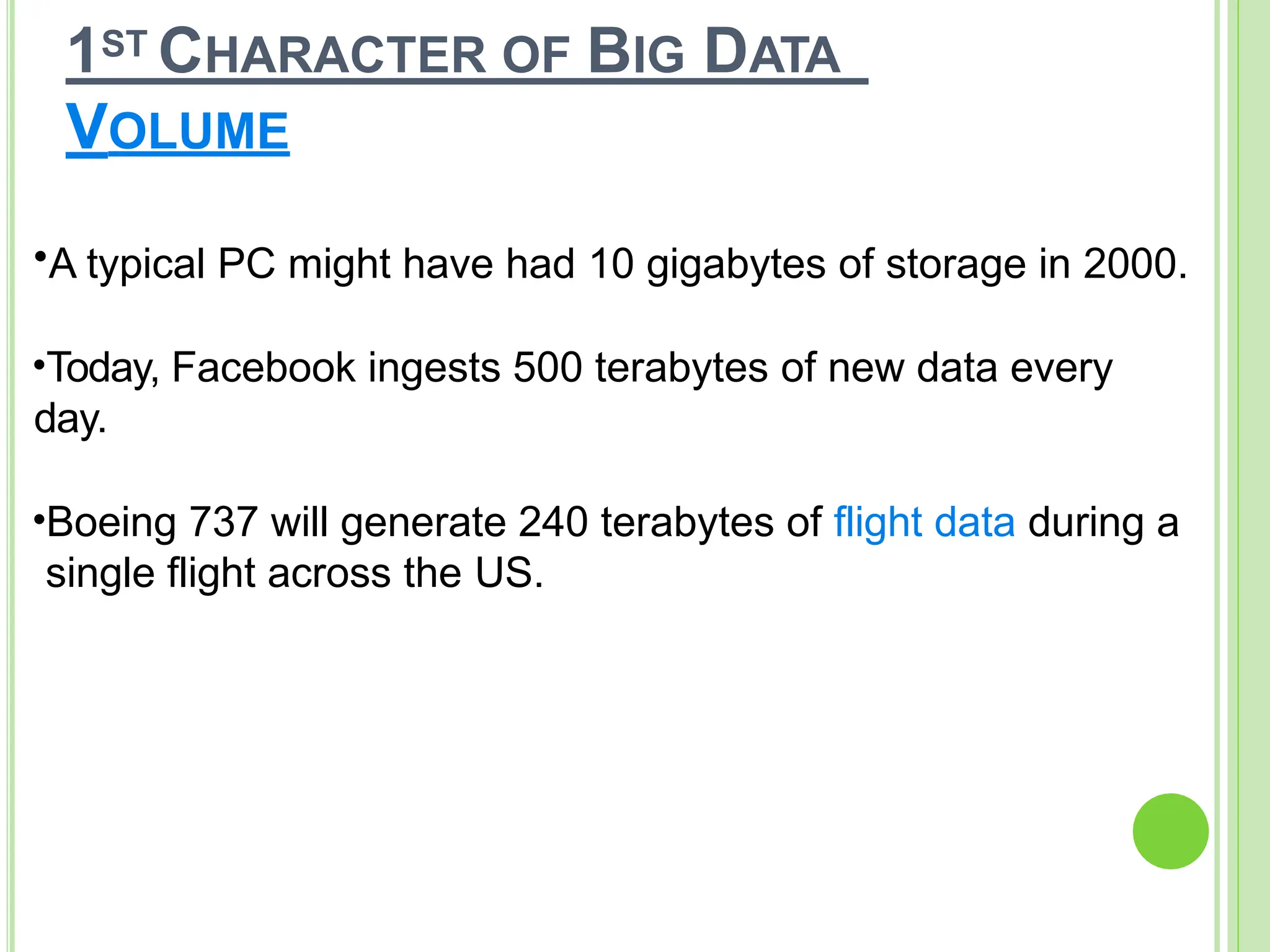
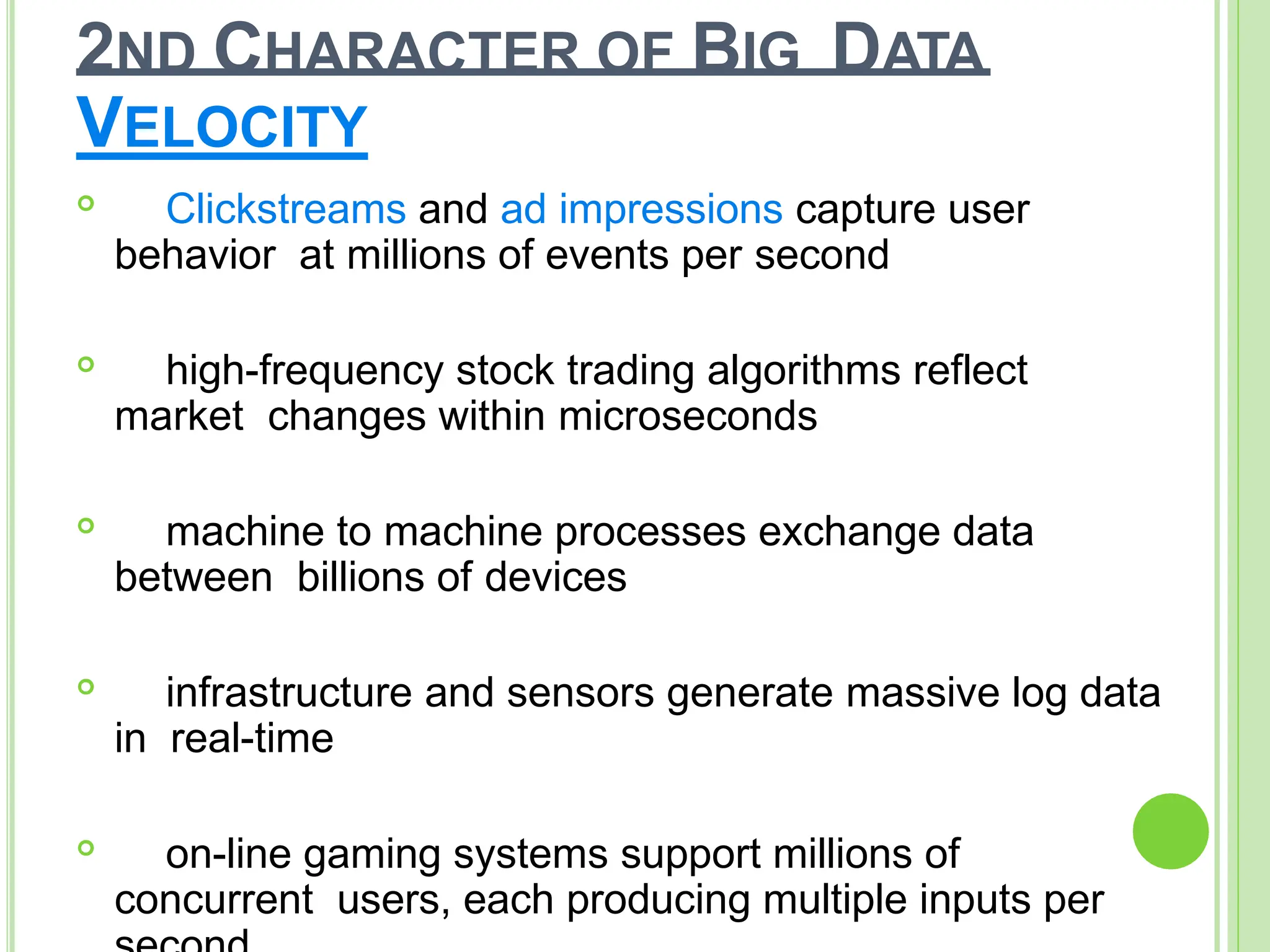
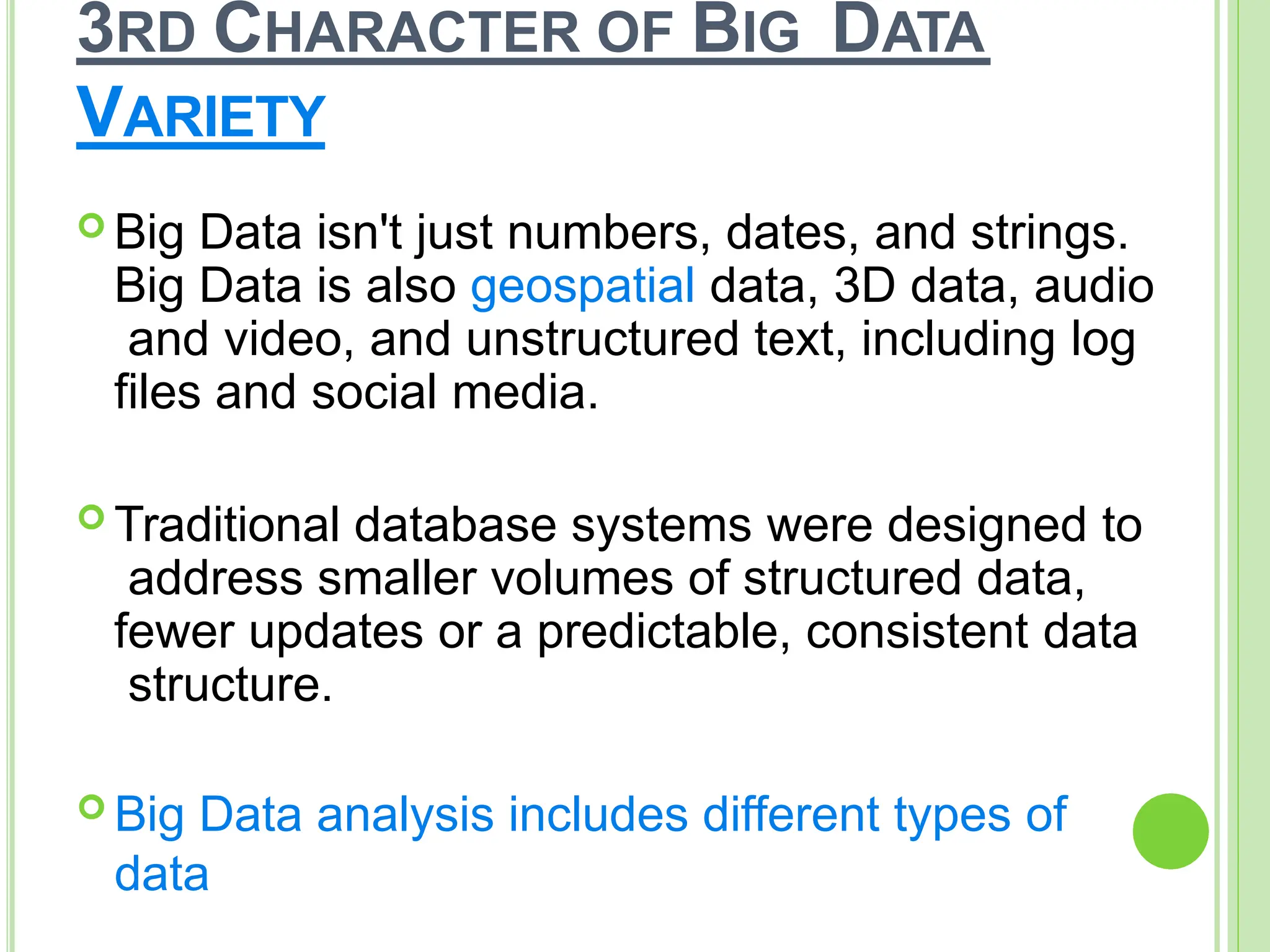
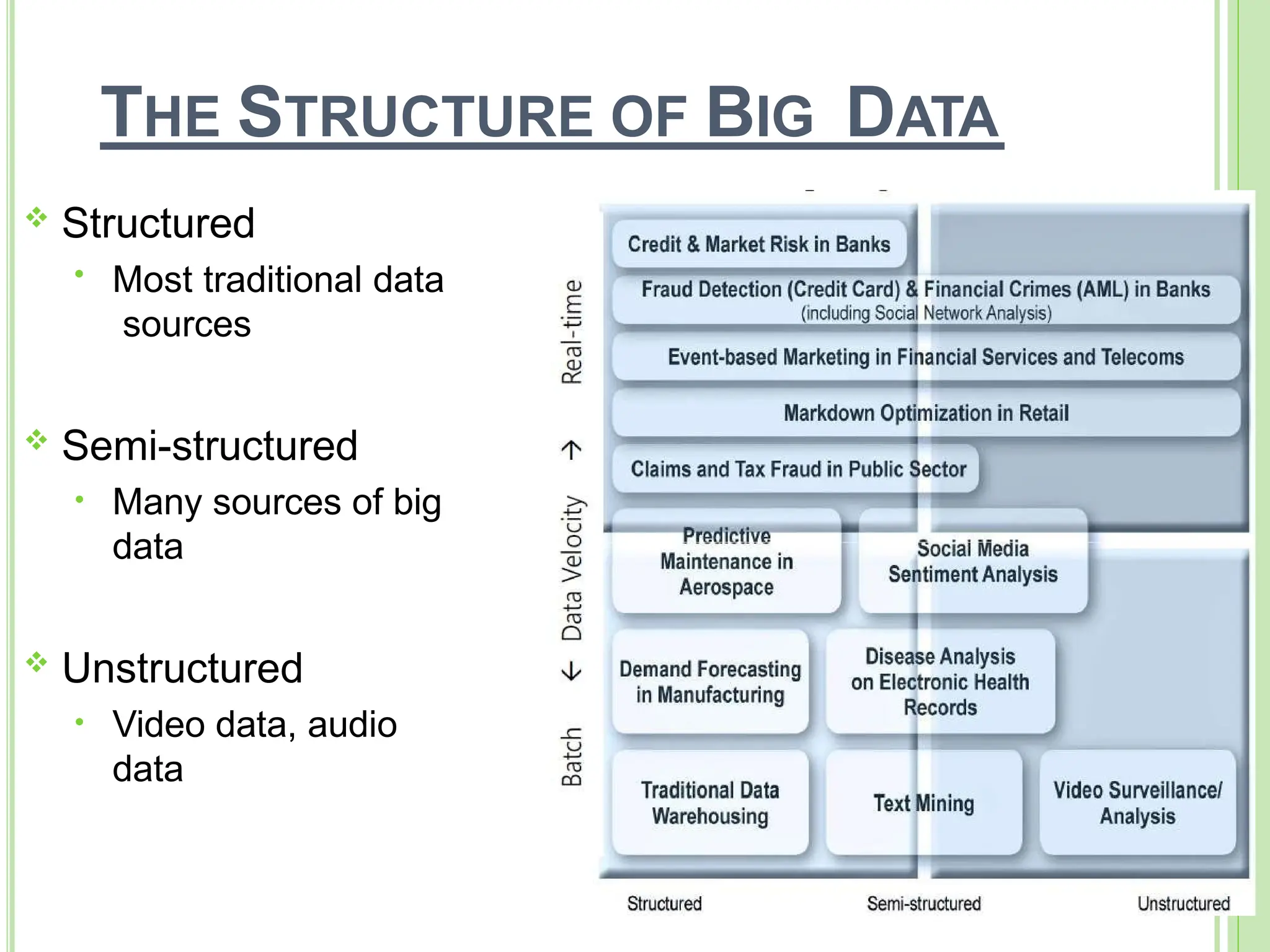
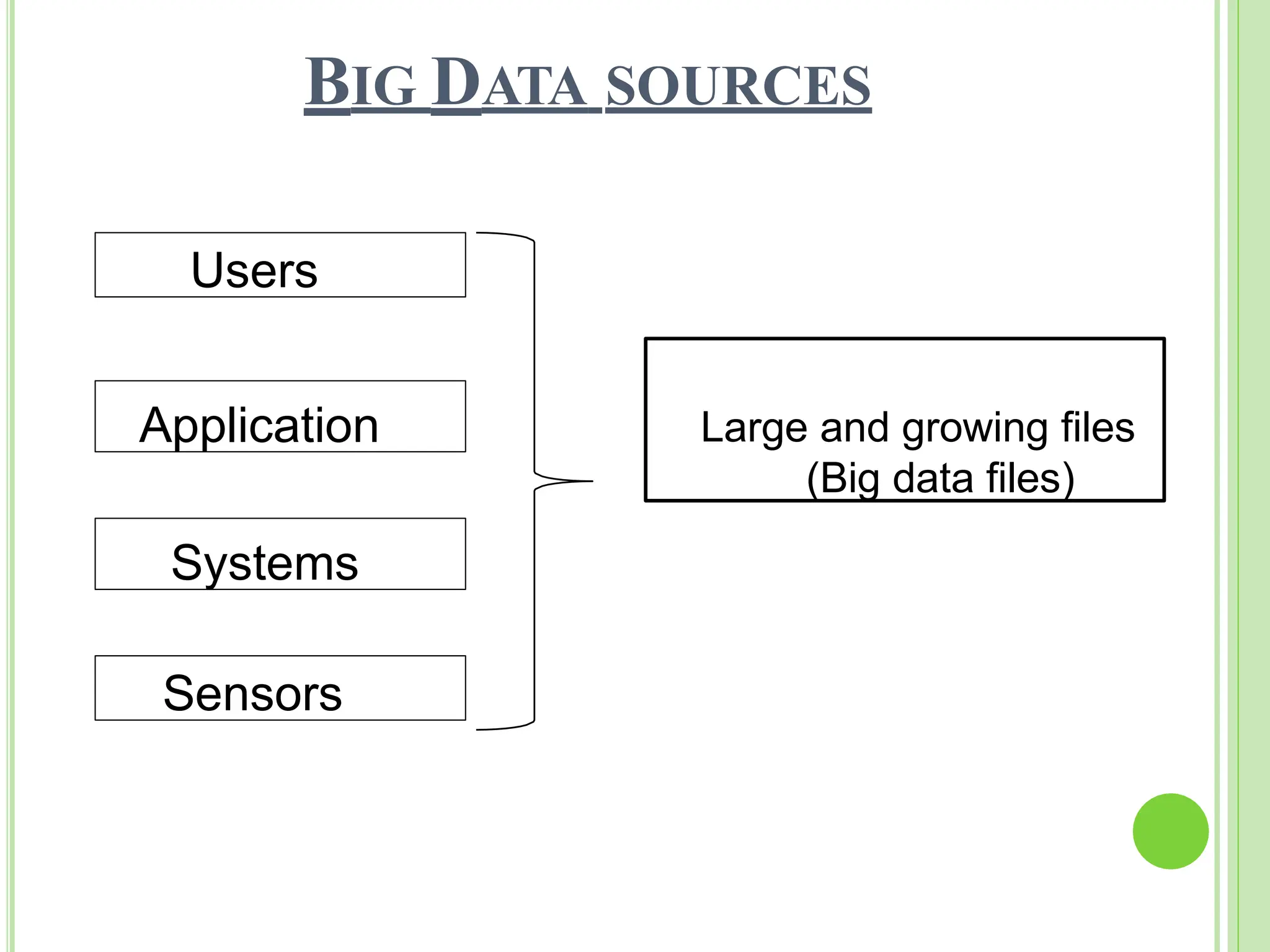
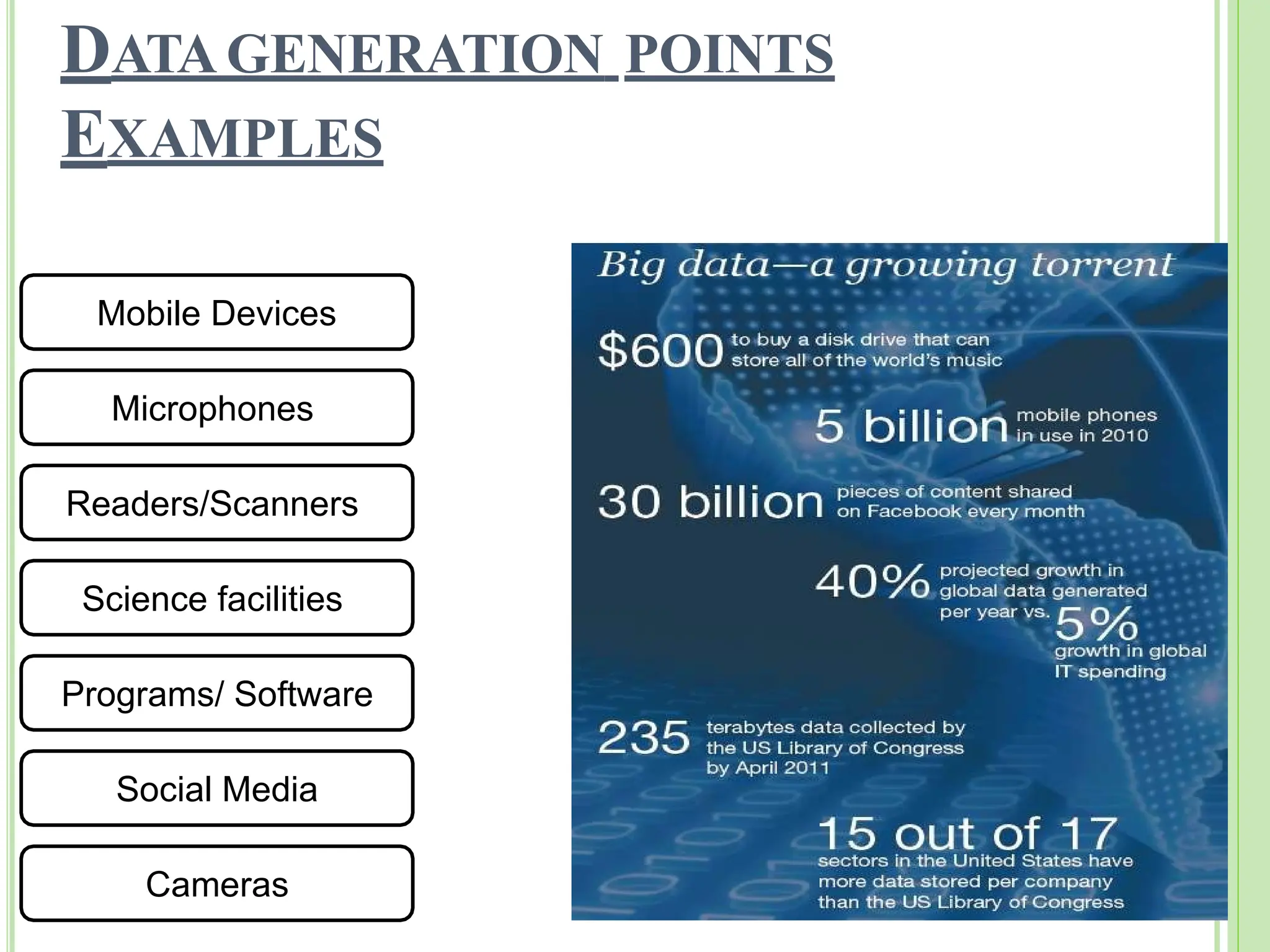
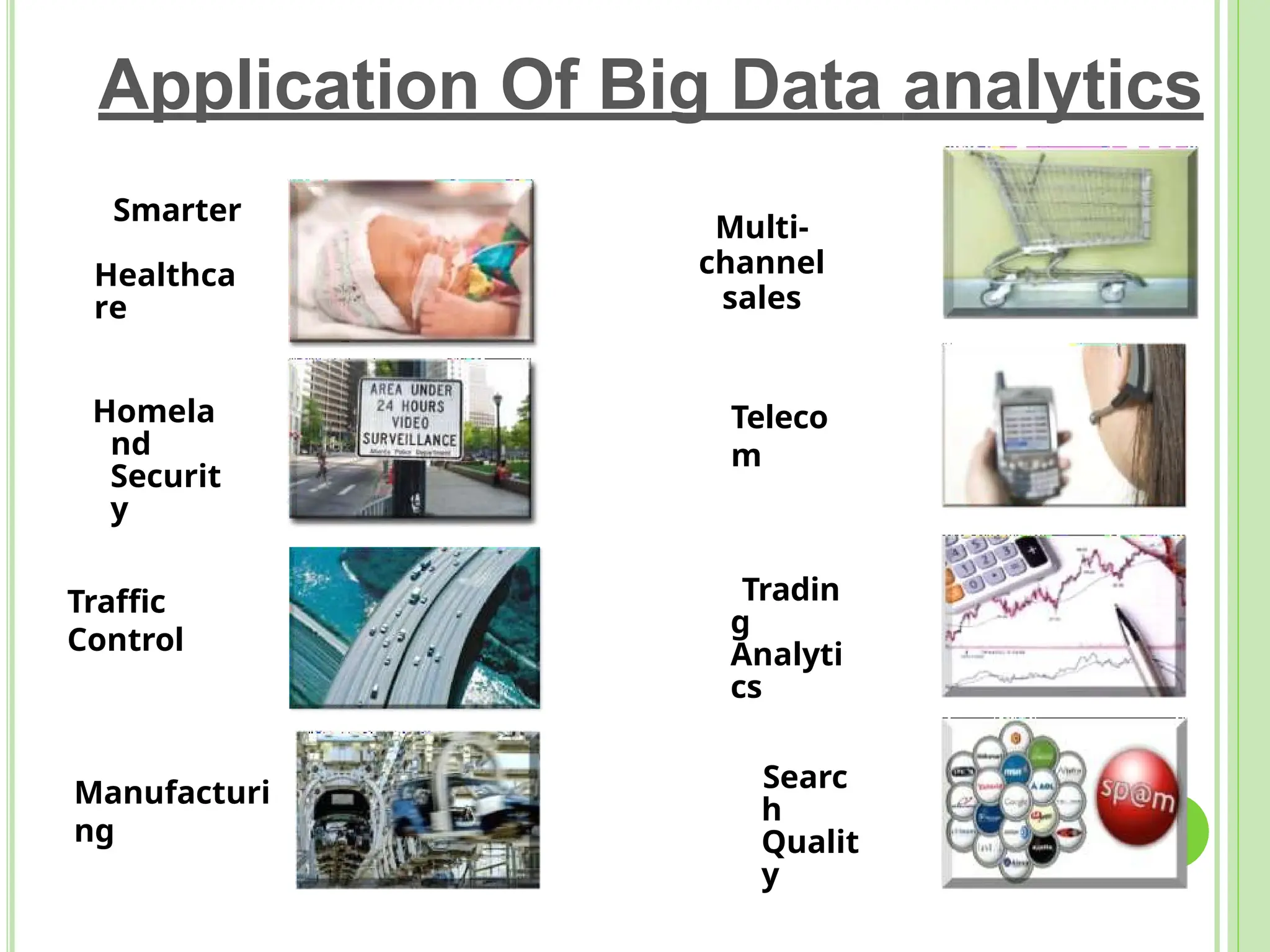
Big data refers to vast quantities of data that traditional computing methods cannot effectively analyze, characterized by its volume, velocity, and variety. It has transformed industries by enabling organizations to gain insights, make decisions, and drive efficiencies through advanced analytics. The rise of big data has led to an increased demand for IT jobs, particularly in data science, while also presenting challenges regarding data management and privacy.