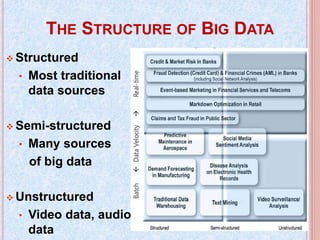
This document provides an introduction to big data, including its key characteristics of volume, velocity, and variety. It discusses why big data has become important due to the growth in data storage capacities and processing power. Examples are given of the large amounts of data generated daily by companies like Google, Facebook, and Walmart. The document also outlines some common tools and concepts used for big data, including Hadoop and MapReduce, as well as applications in various industries. It discusses the impacts of big data on IT and the benefits organizations can realize, such as increased innovation. The future of big data is predicted to be strong with continued growth in data volumes and investment in data management software.