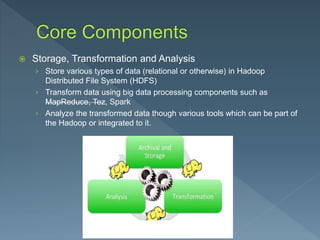
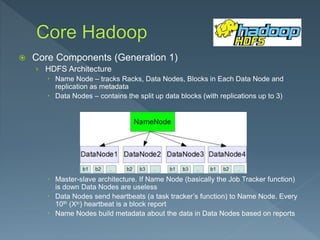
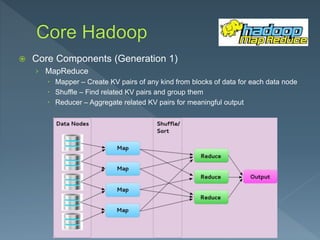
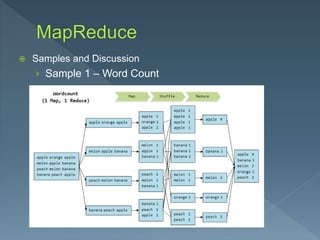
The document discusses the core components of Hadoop, including storage, transformation, and analysis using components like HDFS, MapReduce, Tez and Spark. It describes Generation 1 core components as HDFS for storage and MapReduce for processing. HDFS uses a master-slave architecture with the NameNode tracking metadata and DataNodes storing replicated blocks. MapReduce uses mappers to create key-value pairs, a shuffle to group related pairs, and reducers to aggregate pairs for output. Sample MapReduce jobs for word counting and tracking smart phones are provided.