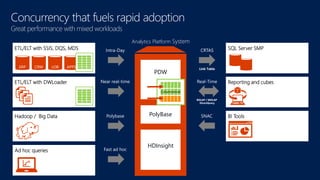
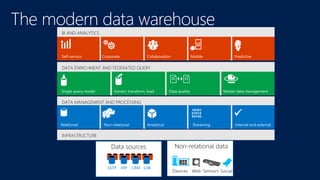
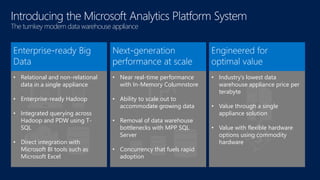
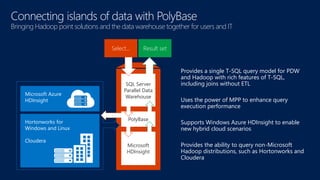
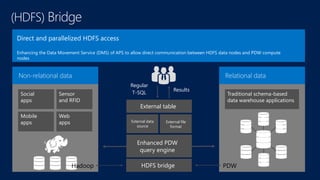
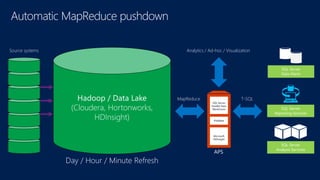
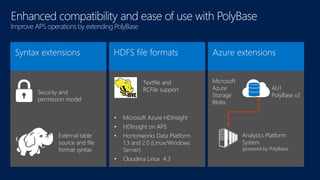
The document discusses modernizing a data warehouse using the Microsoft Analytics Platform System (APS). APS is described as a turnkey appliance that allows organizations to integrate relational and non-relational data in a single system for enterprise-ready querying and business intelligence. It provides a scalable solution for growing data volumes and types that removes limitations of traditional data warehousing approaches.












![CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE table_name
({<column_definition>}[,..n ])
{WITH (
DATA_SOURCE = <data_source>,
FILE_FORMAT = <file_format>,
LOCATION =‘<file_path>’,
[REJECT_VALUE = <value>],
…)};
1 Referencing external data source
2 Referencing external file format
3 Path of the Hadoop file/folder
4 (Optional) Reject parameters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modernizingyourdatawarehouseusingaps-141130115323-conversion-gate02/85/Modernizing-Your-Data-Warehouse-using-APS-19-320.jpg)
![CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE datasource_name
{WITH (
TYPE = <data_source>,
LOCATION =‘<location>’,
[JOB_TRACKER_LOCATION = ‘<jb_location>’]
};
1 Type of external data source
2 Location of external data source
Enabling or disabling of MapReduce
job generation
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modernizingyourdatawarehouseusingaps-141130115323-conversion-gate02/85/Modernizing-Your-Data-Warehouse-using-APS-20-320.jpg)
![CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT fileformat_name
{WITH (
FORMAT_TYPE = <type>,
[SERDE_METHOD = ‘<sede_method>’,]
[DATA_COMPRESSION = ‘<compr_method>’,
[FORMAT_OPTIONS (<format_options>)]
};
1 Type of external data source
2 (De)Serialization method [Hive RCFile]
3 Compression method
4 (Optional) Format Options [Text Files]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modernizingyourdatawarehouseusingaps-141130115323-conversion-gate02/85/Modernizing-Your-Data-Warehouse-using-APS-21-320.jpg)
![<Format Options> :: =
[,FIELD_TERMINATOR = ‘value’],
[,STRING_DELIMITER = ‘value’],
[,DATE_FORMAT = ‘value’],
[USE_TYPE_DEFAULT = ‘value’]
1 Column delimiter
2 Delimiter for string data types
3 To specify a particular date format
4 How missing entries are handled](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modernizingyourdatawarehouseusingaps-141130115323-conversion-gate02/85/Modernizing-Your-Data-Warehouse-using-APS-22-320.jpg)