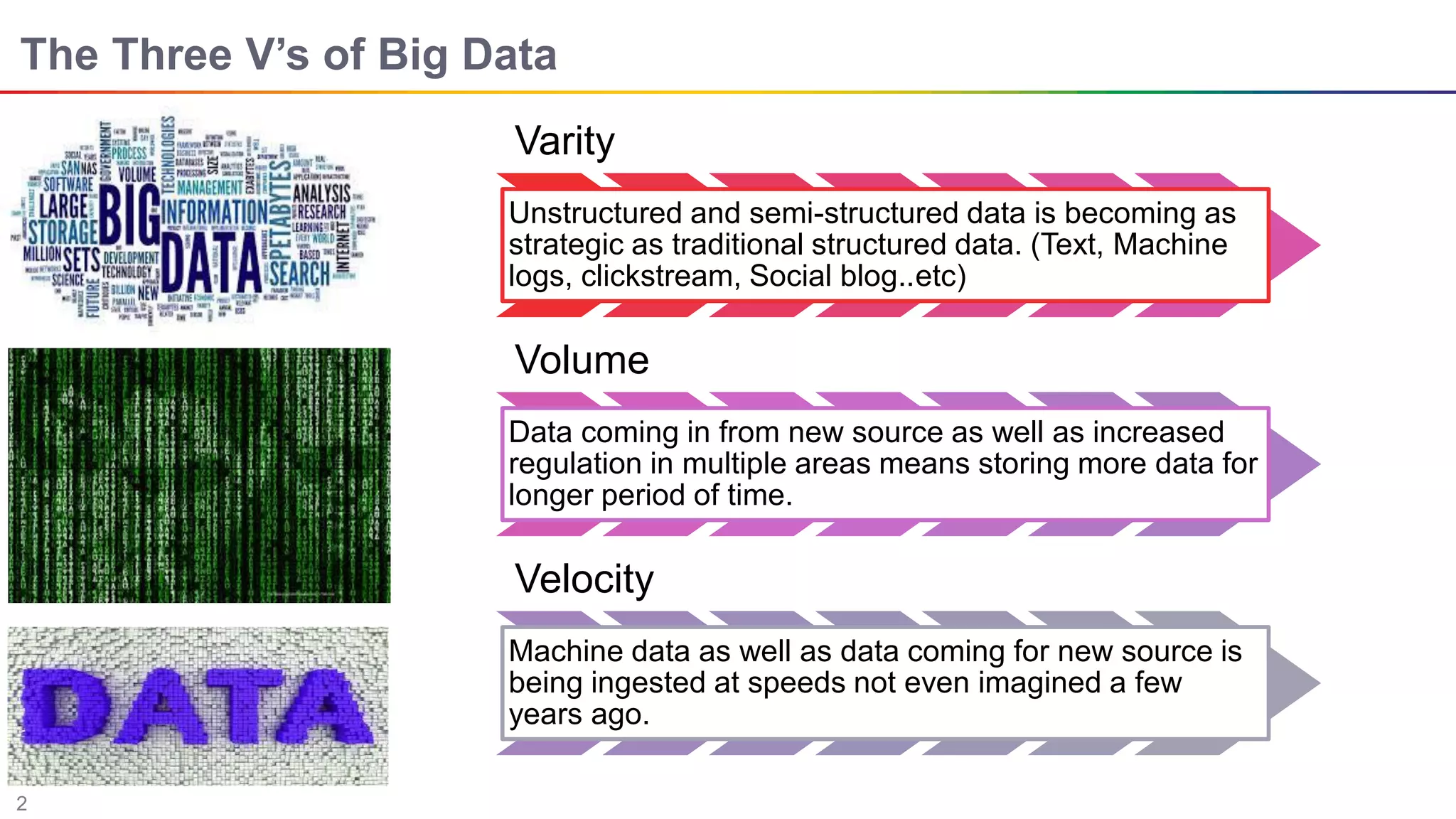
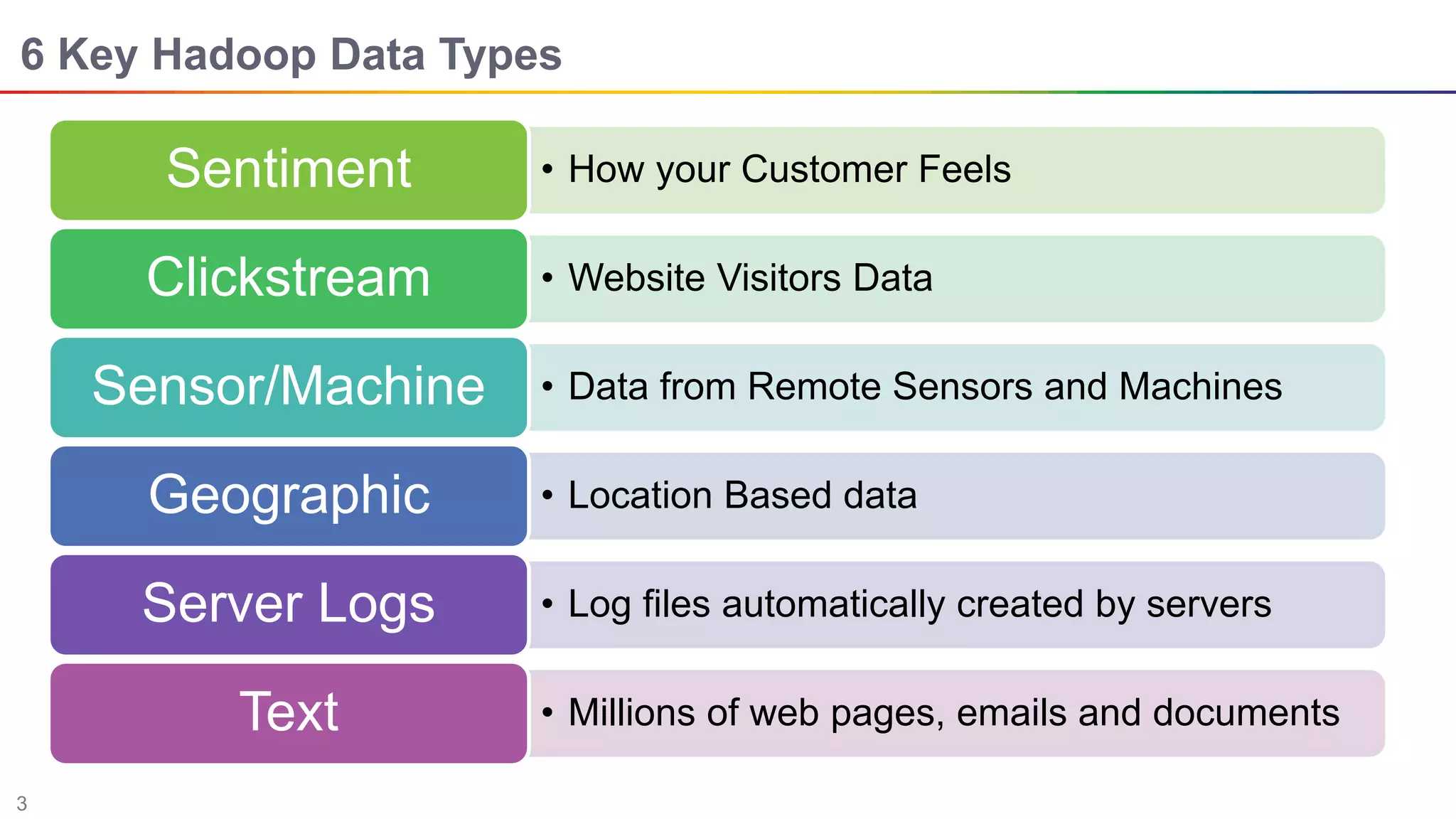
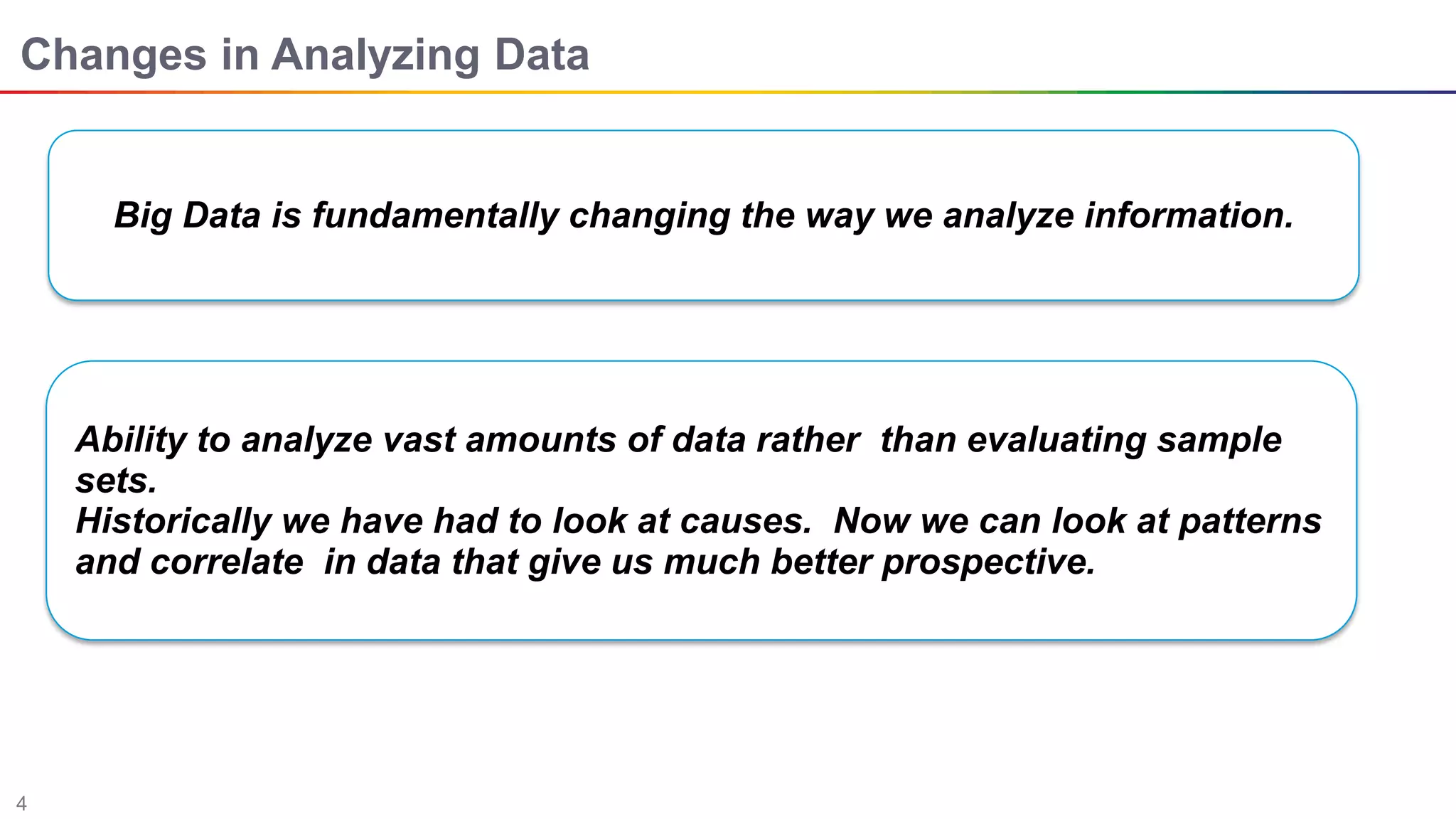
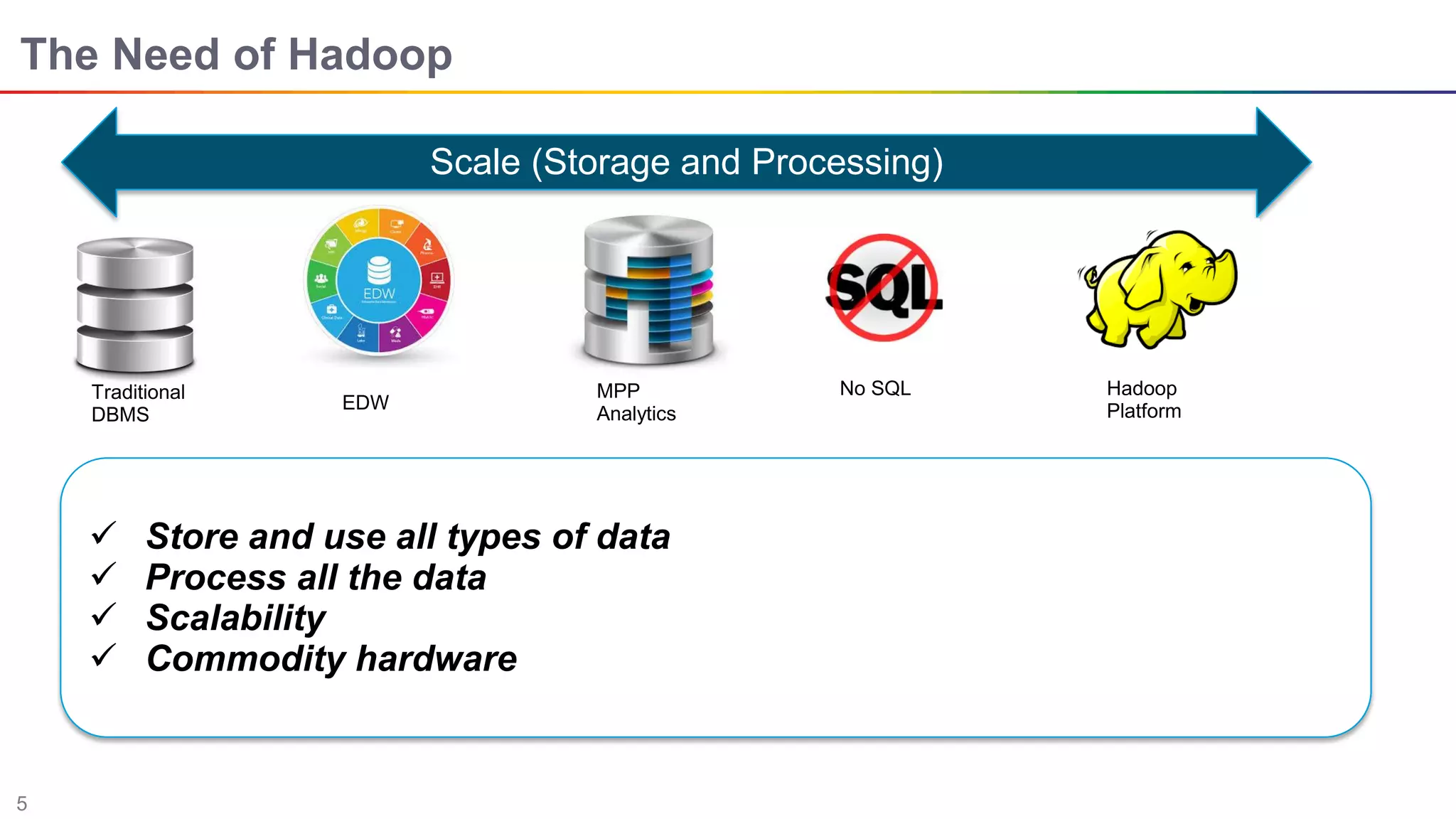
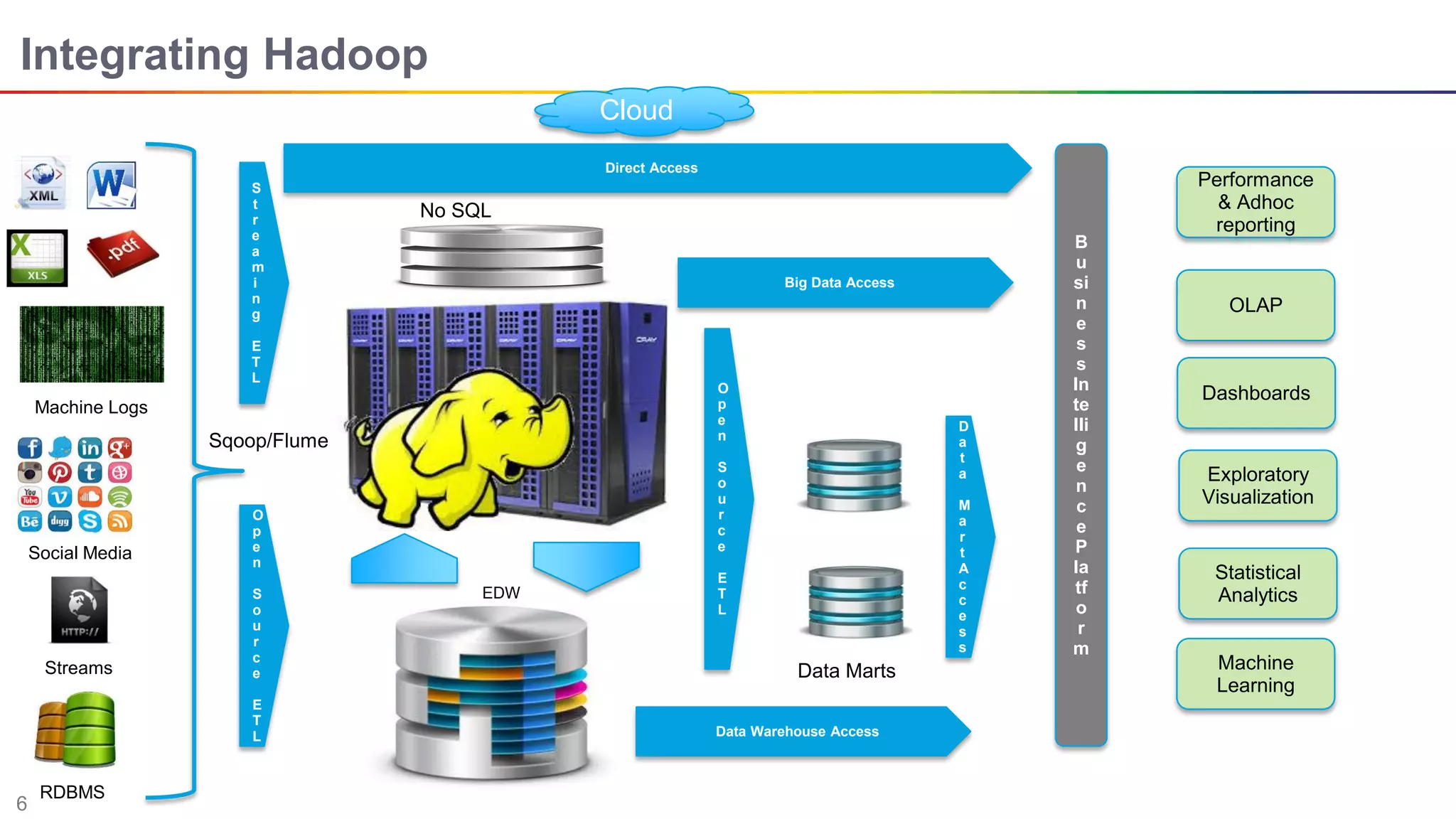
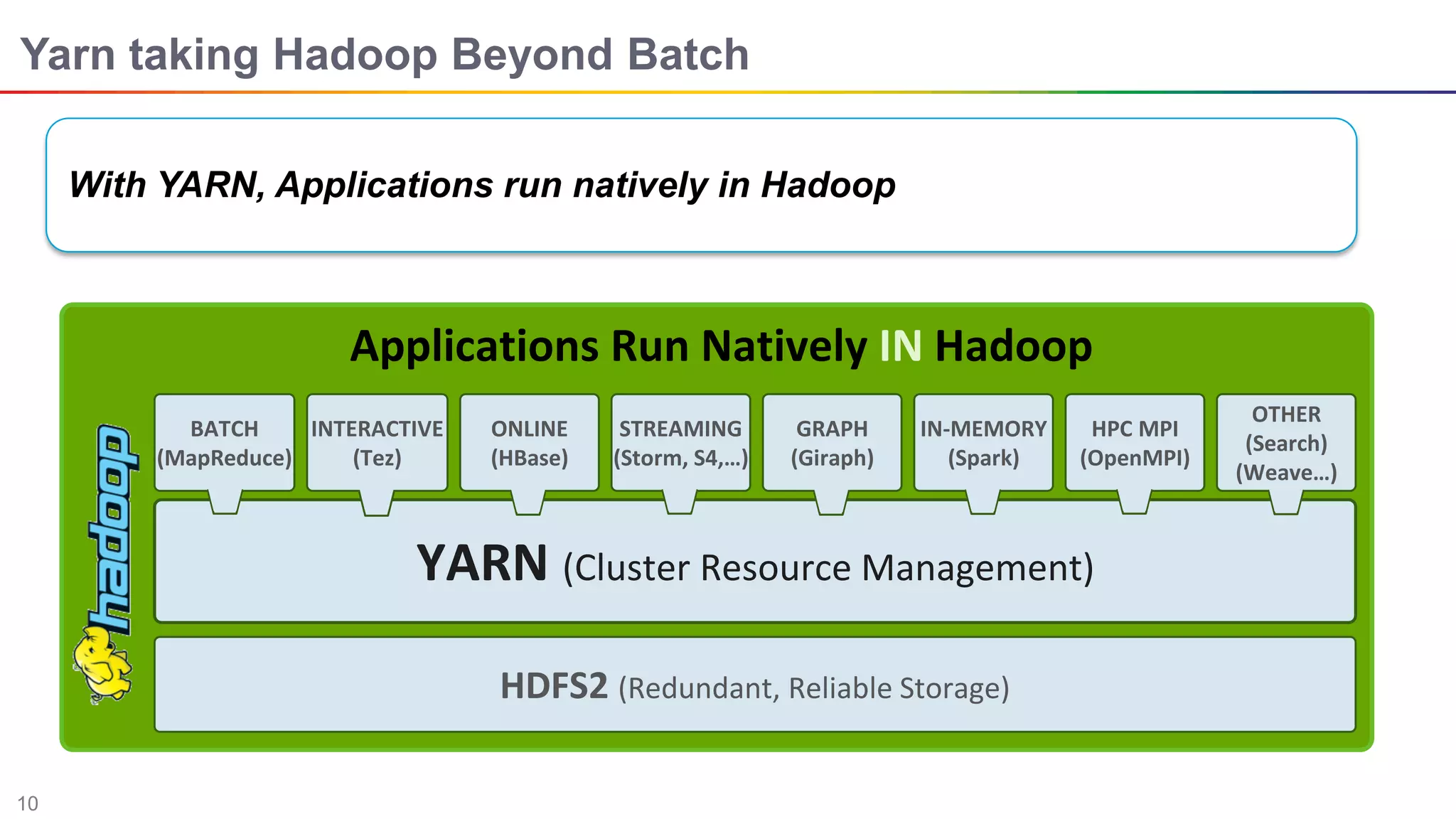
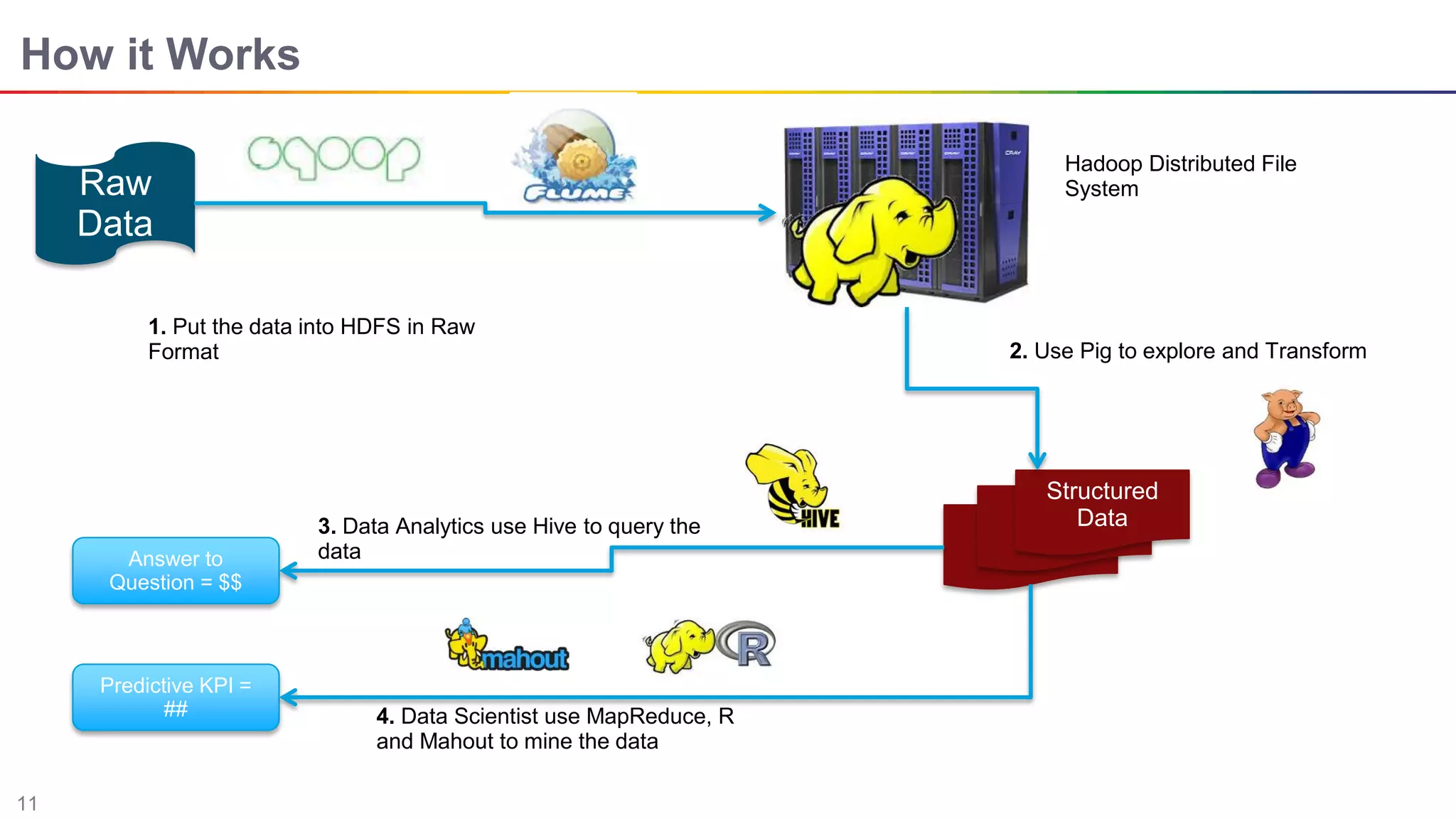
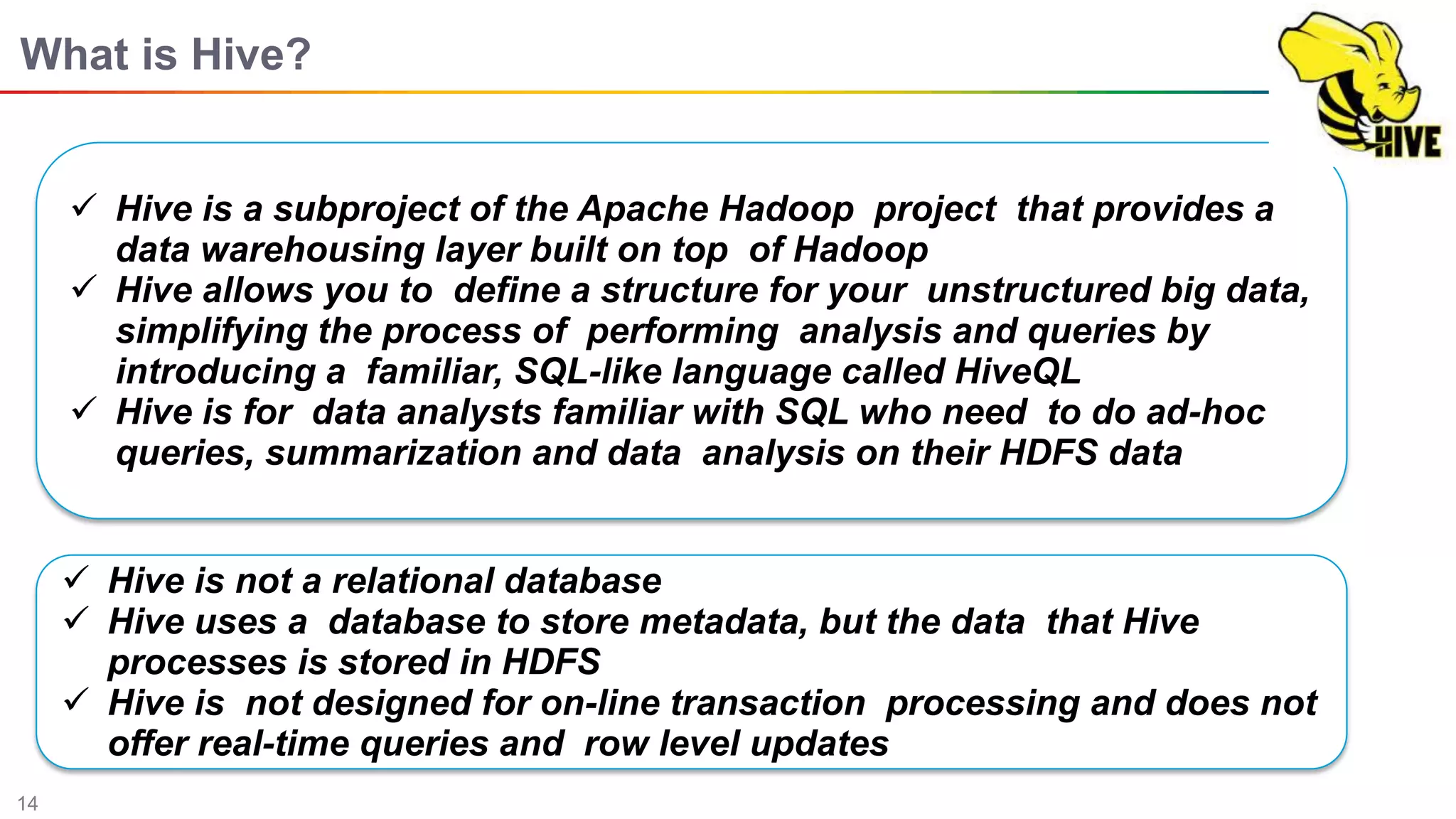
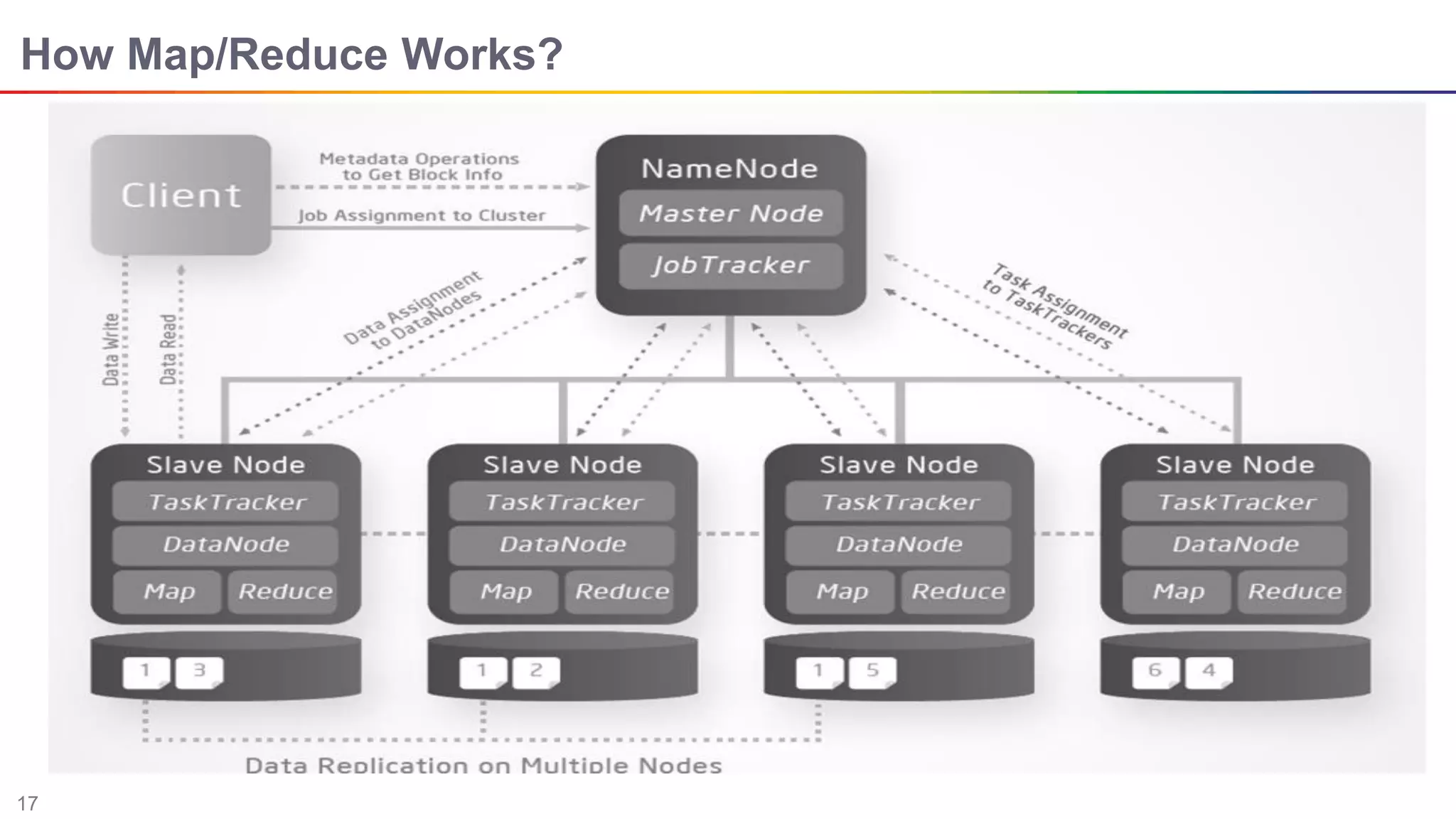
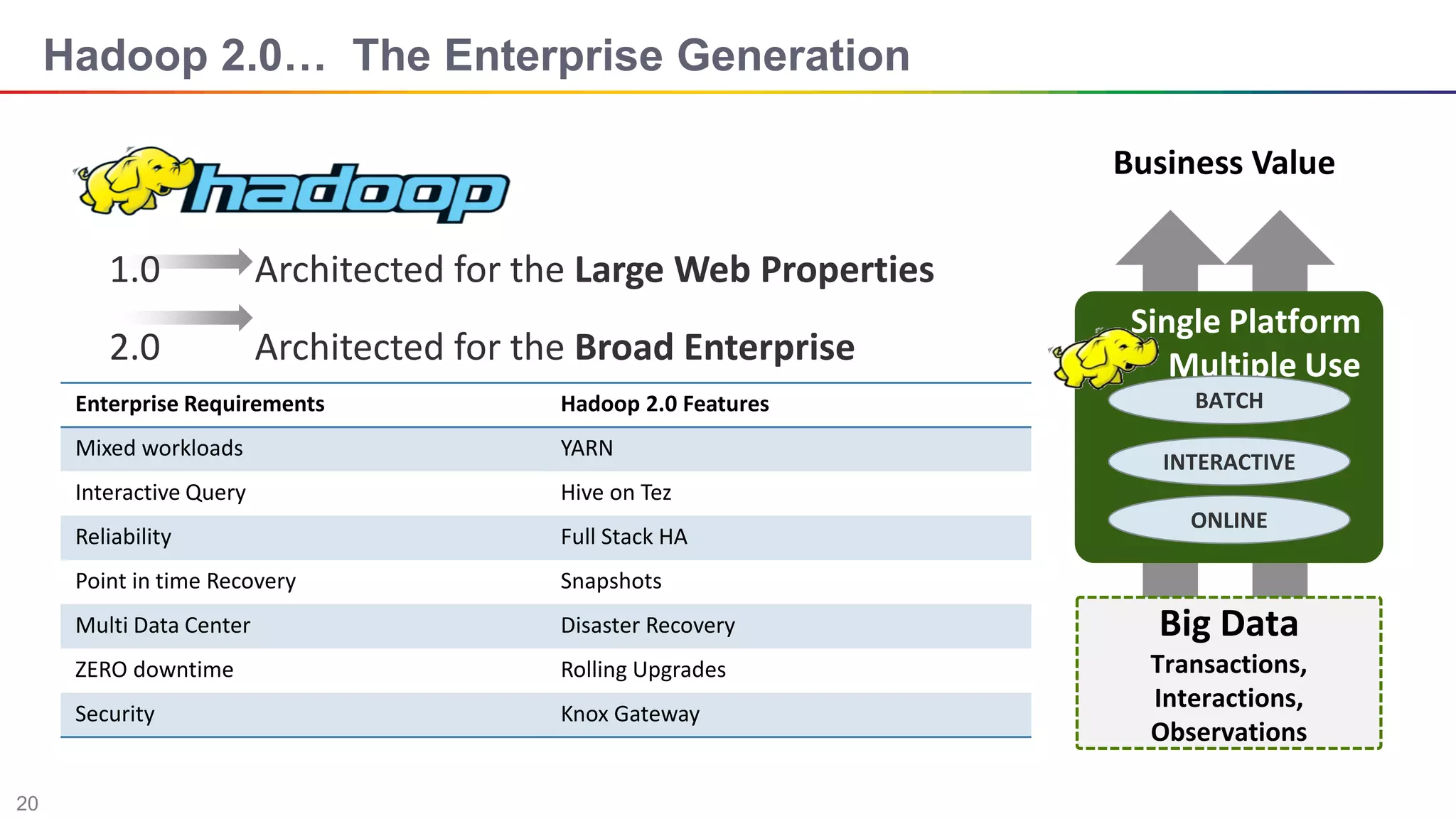
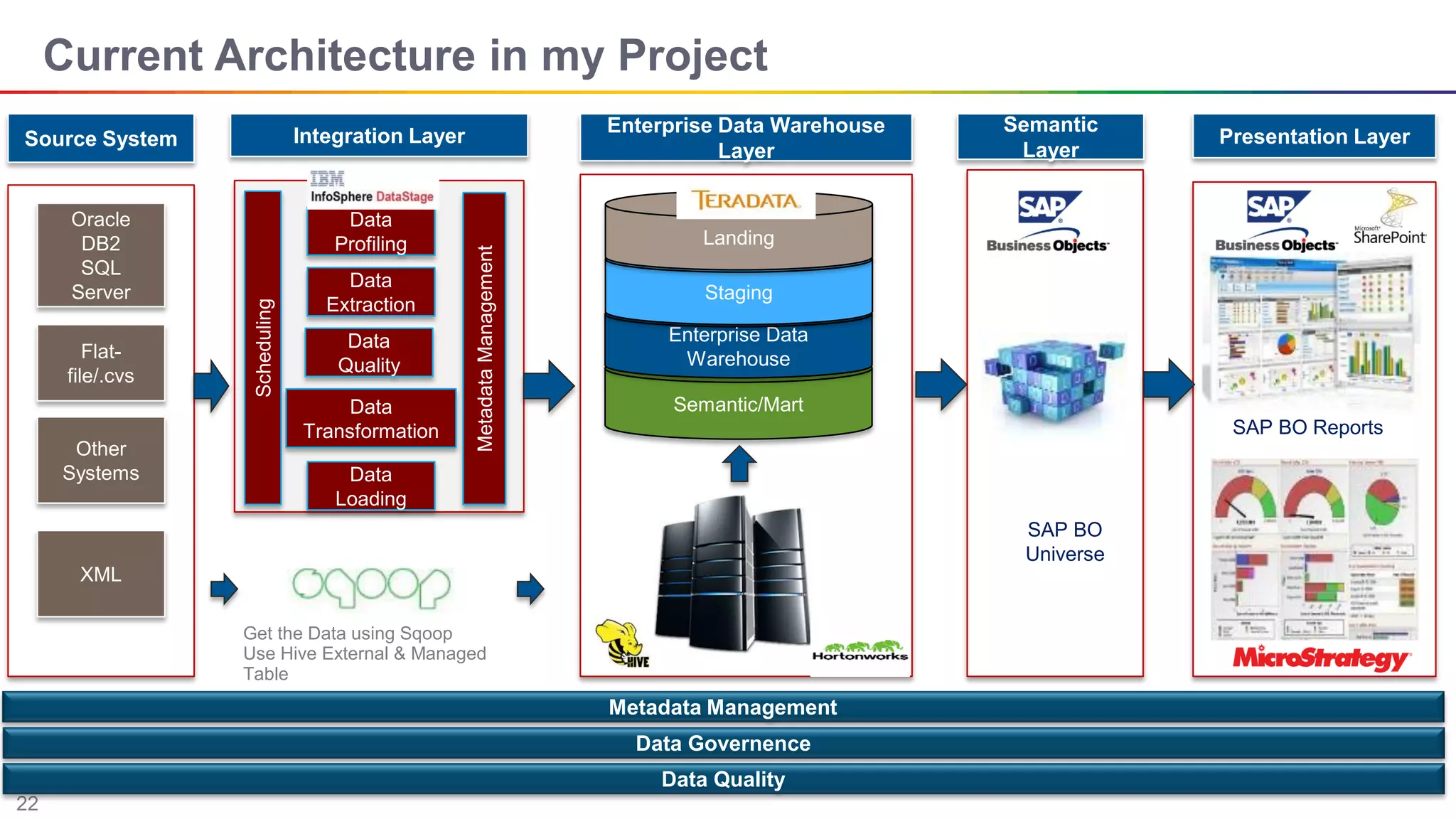
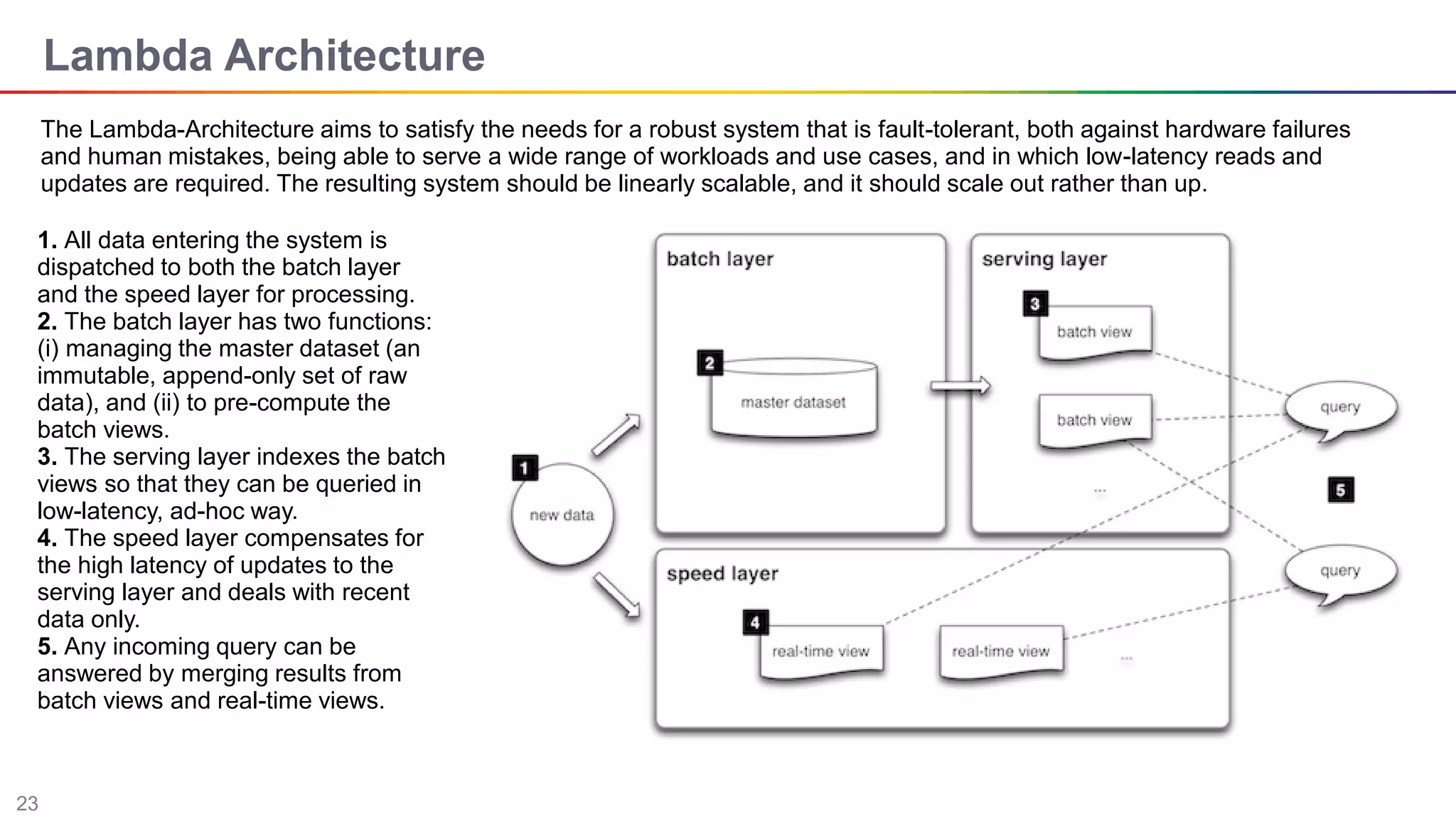
The document discusses big data and Hadoop. It describes the three V's of big data - variety, volume, and velocity. It also discusses Hadoop components like HDFS, MapReduce, Pig, Hive, and YARN. Hadoop is a framework for storing and processing large datasets in a distributed computing environment. It allows for the ability to store and use all types of data at scale using commodity hardware.