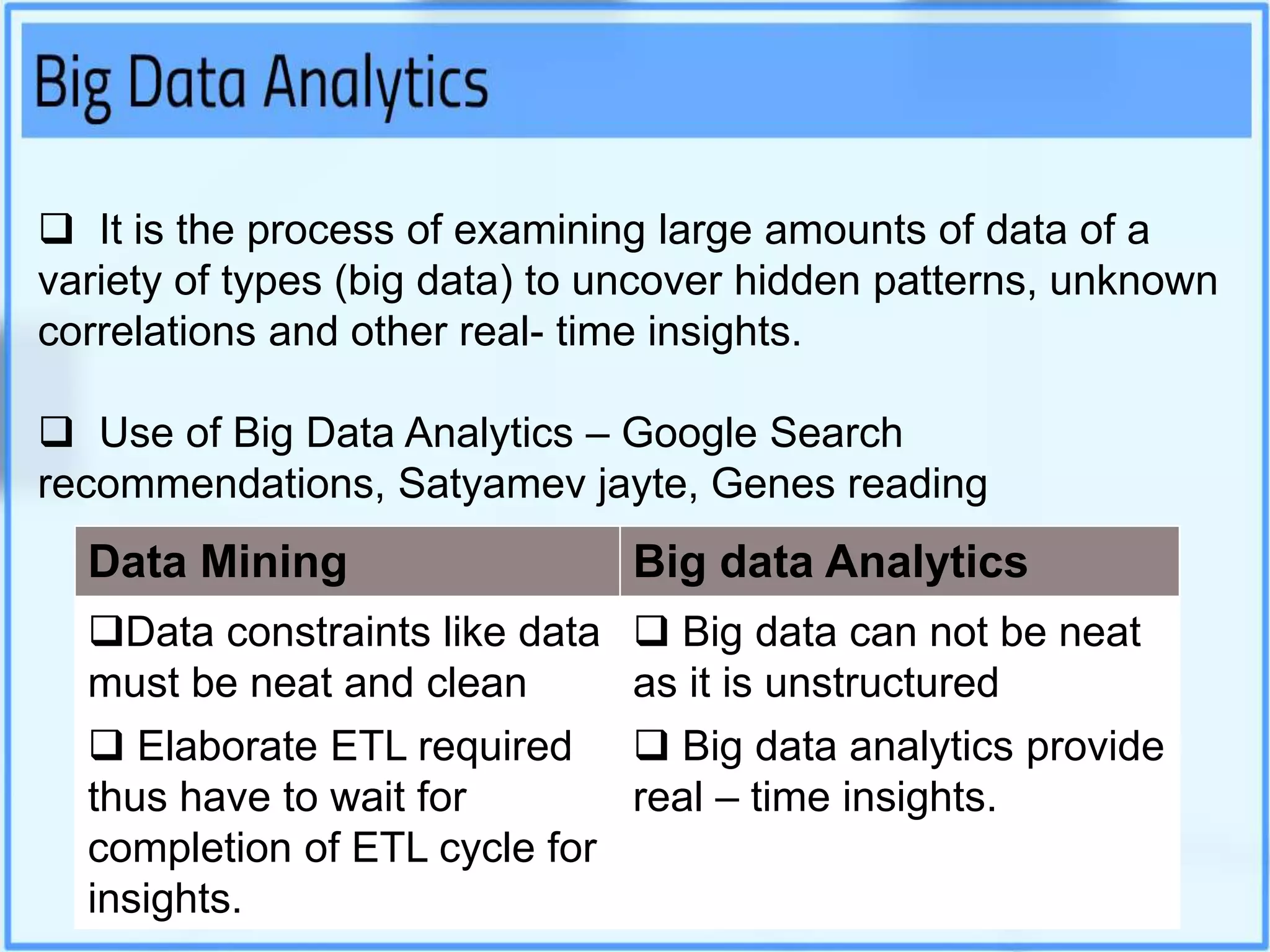
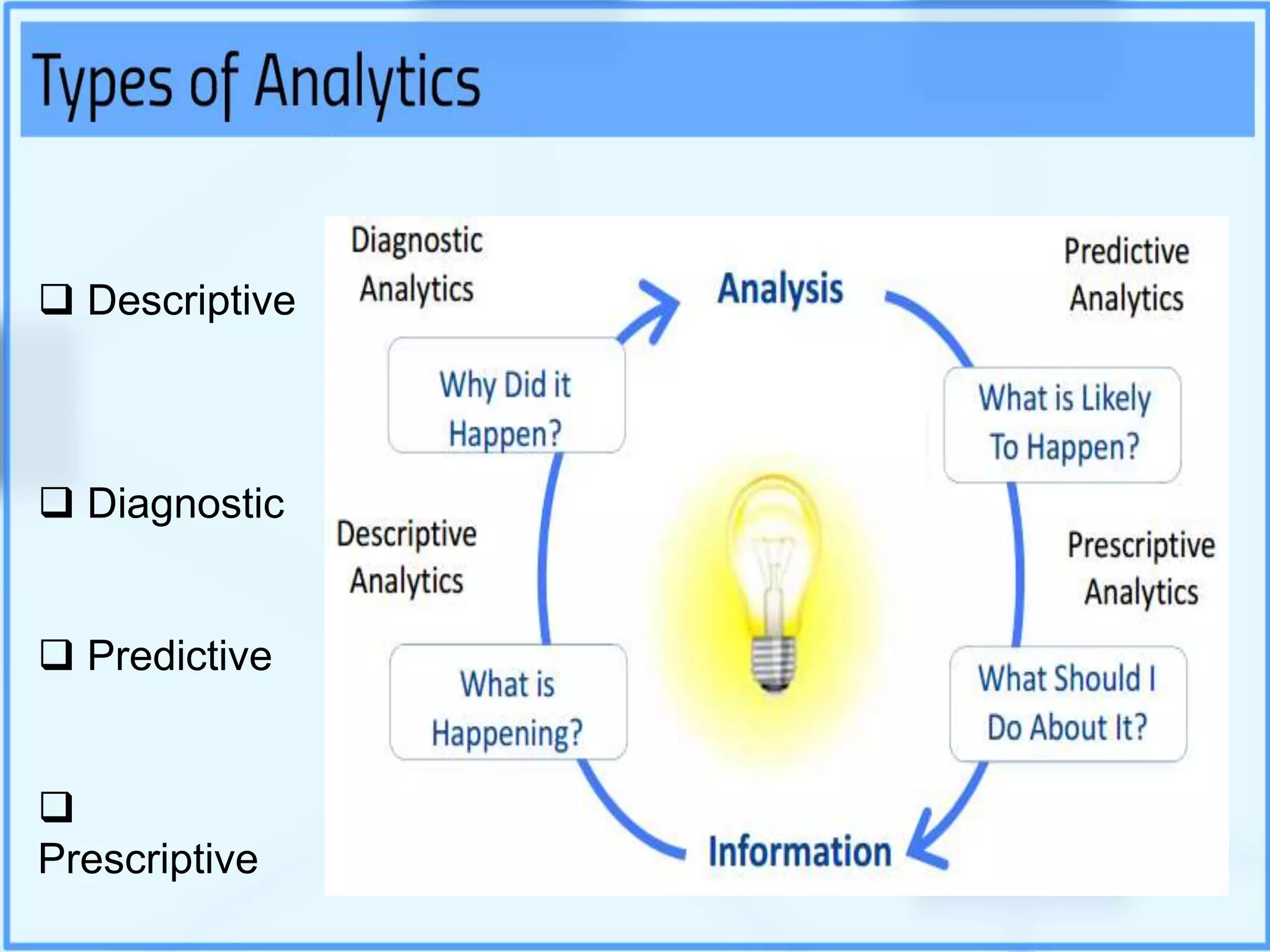
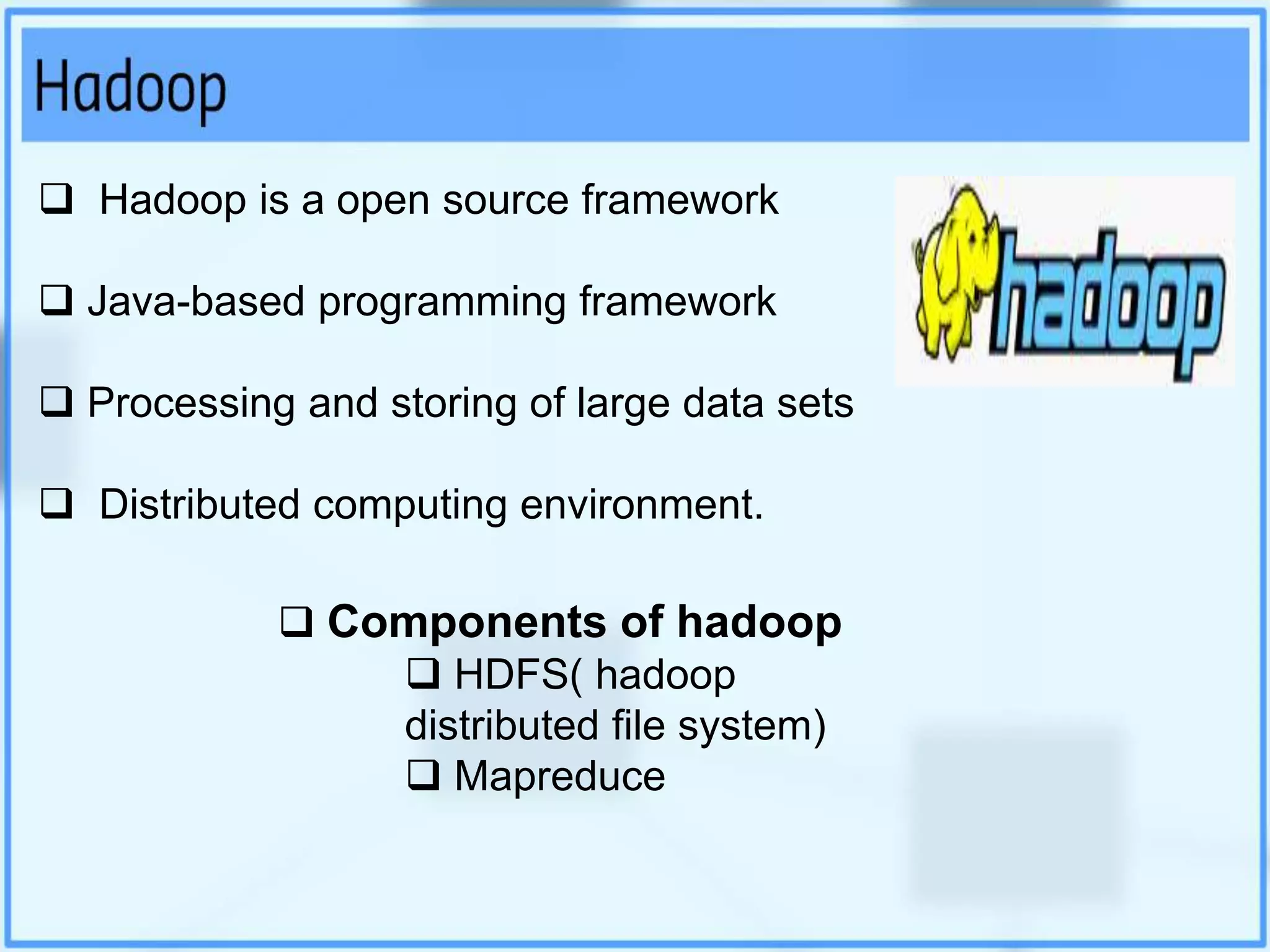
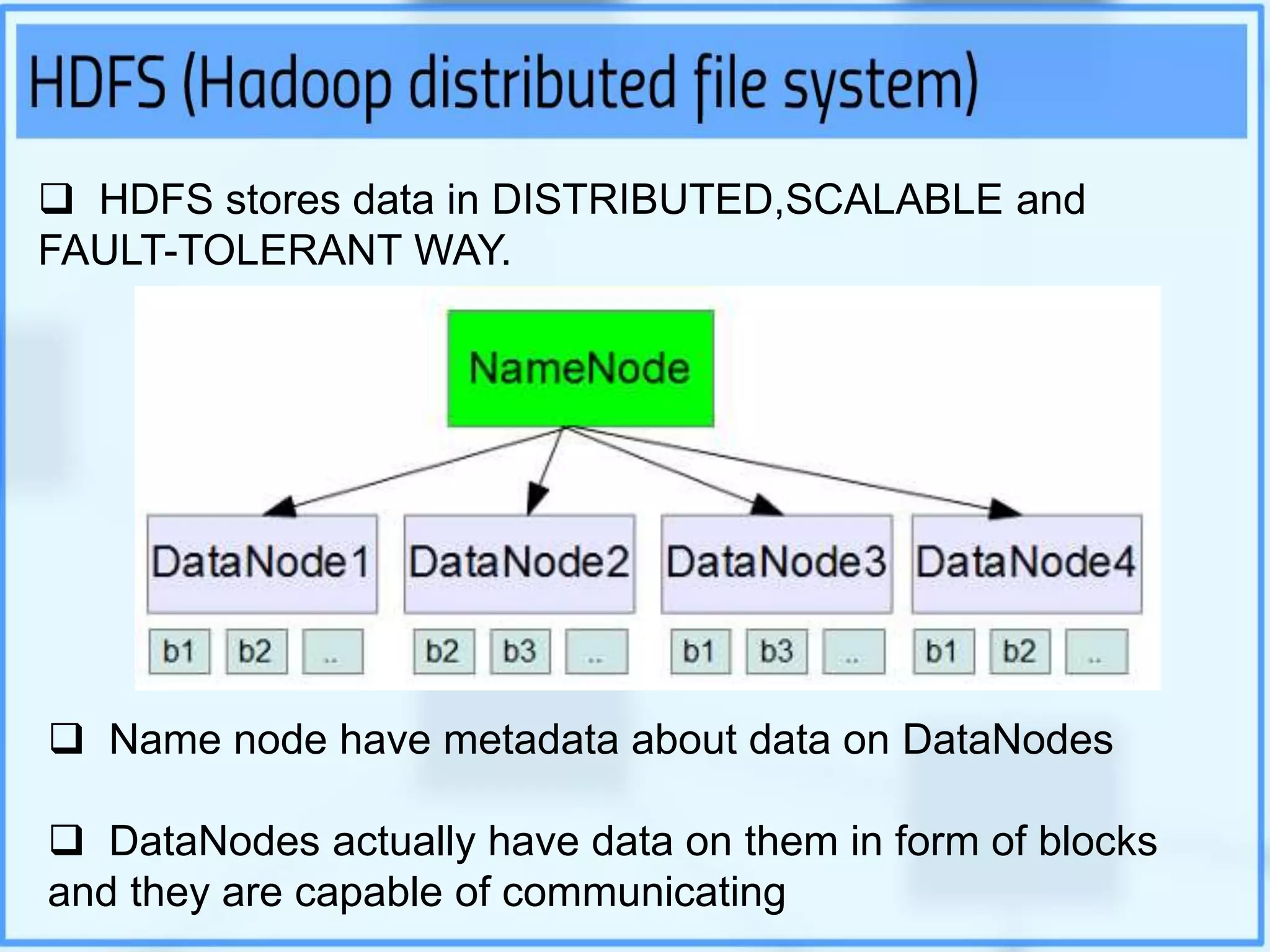
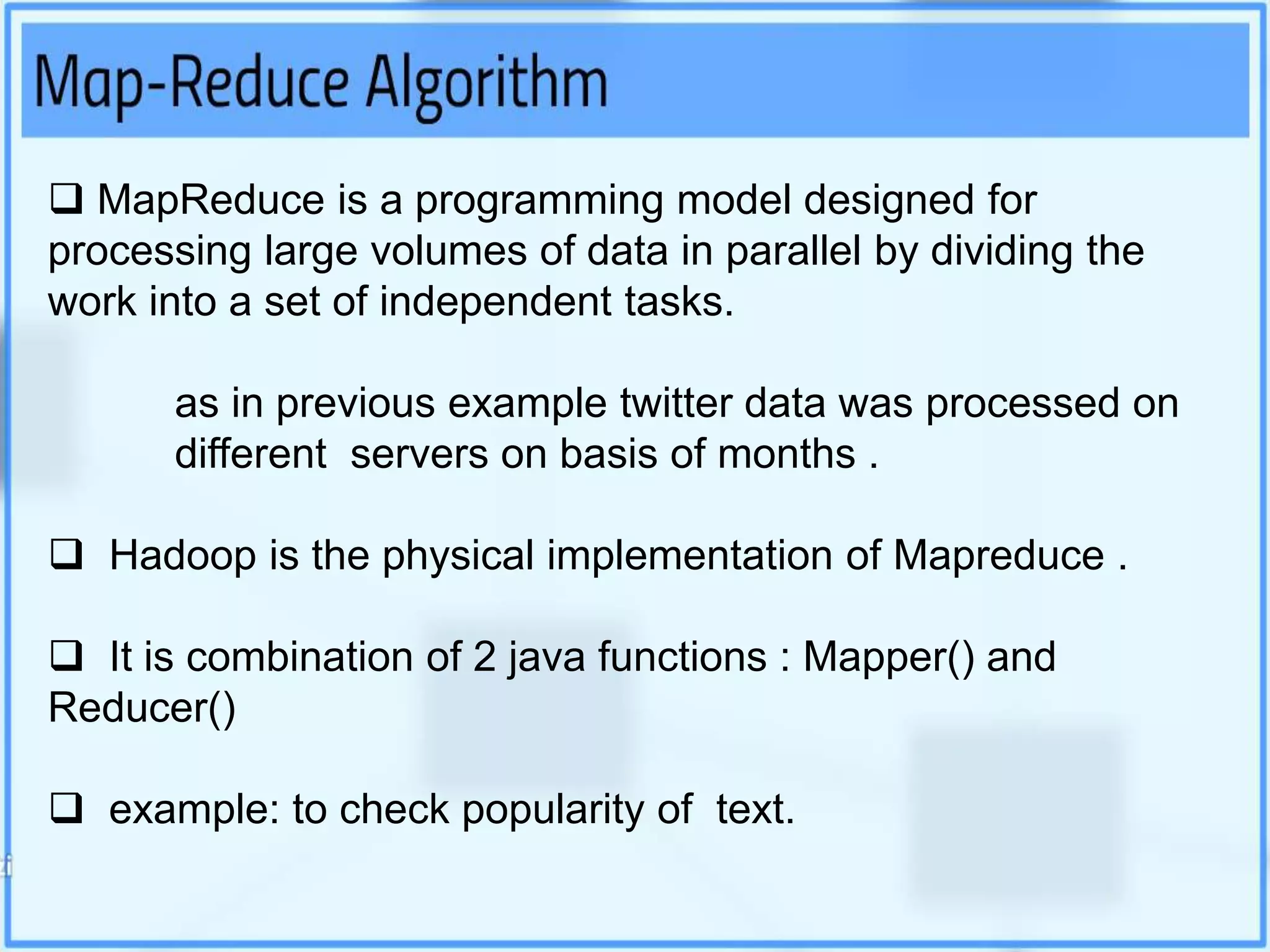
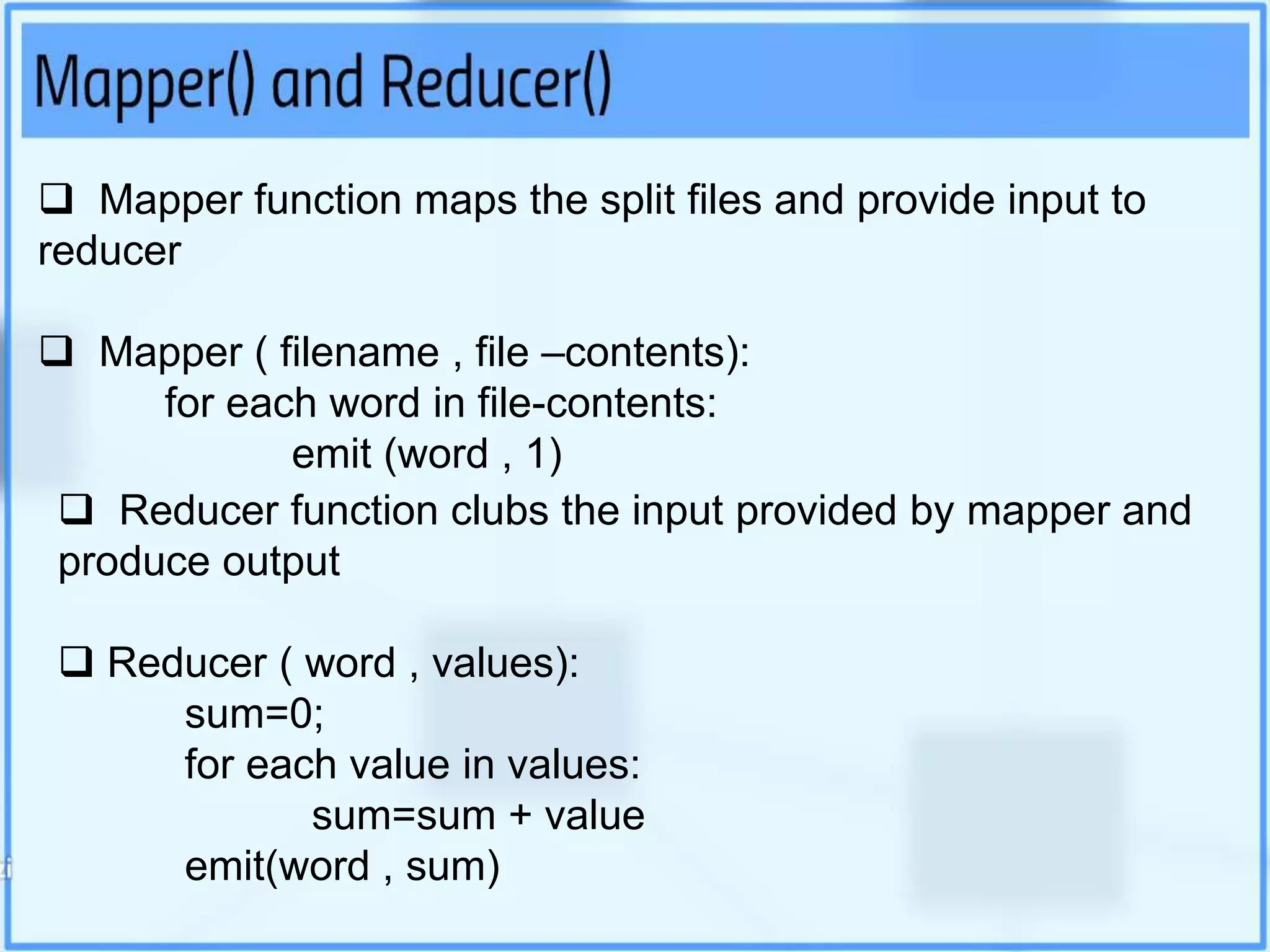
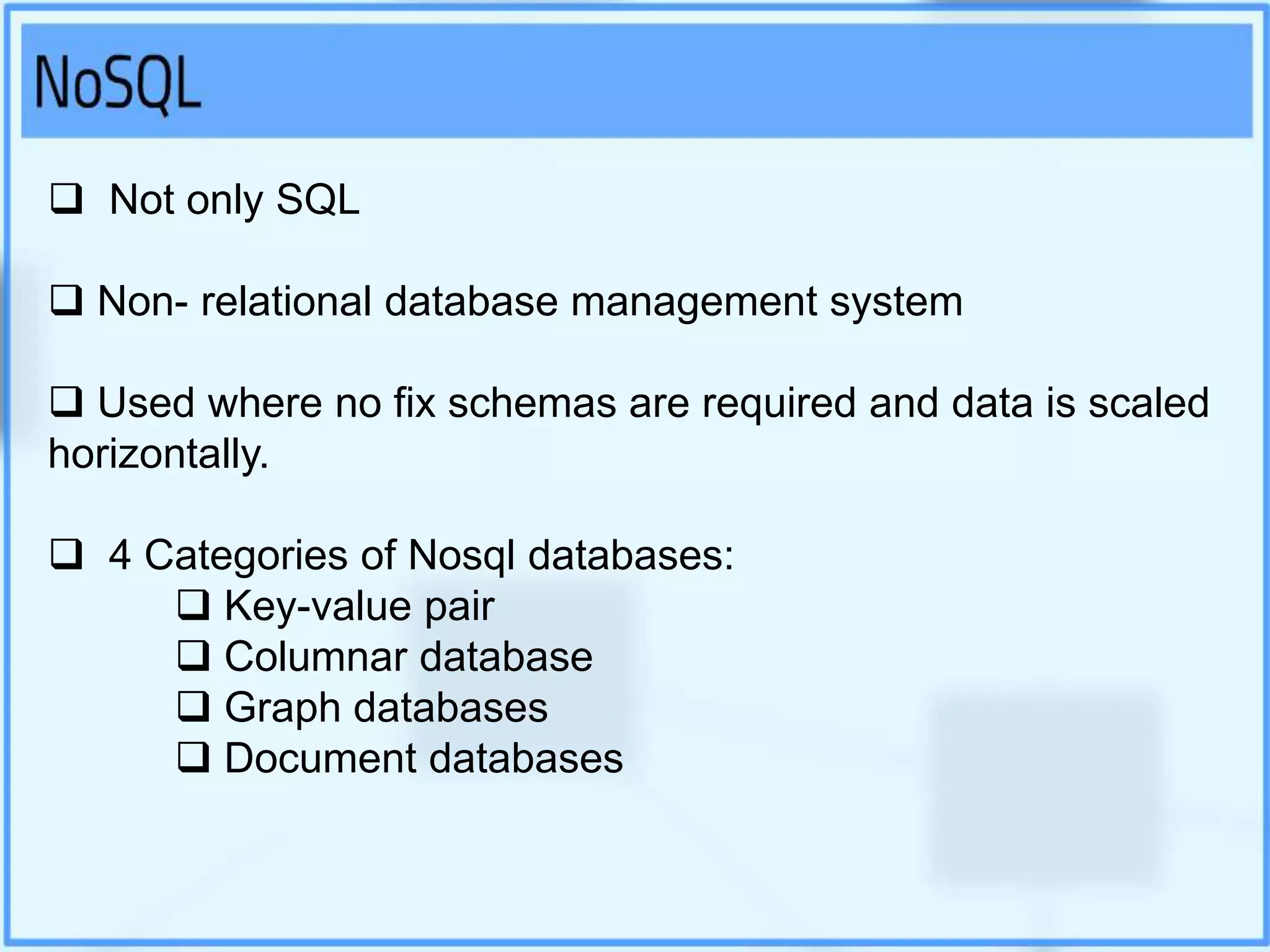
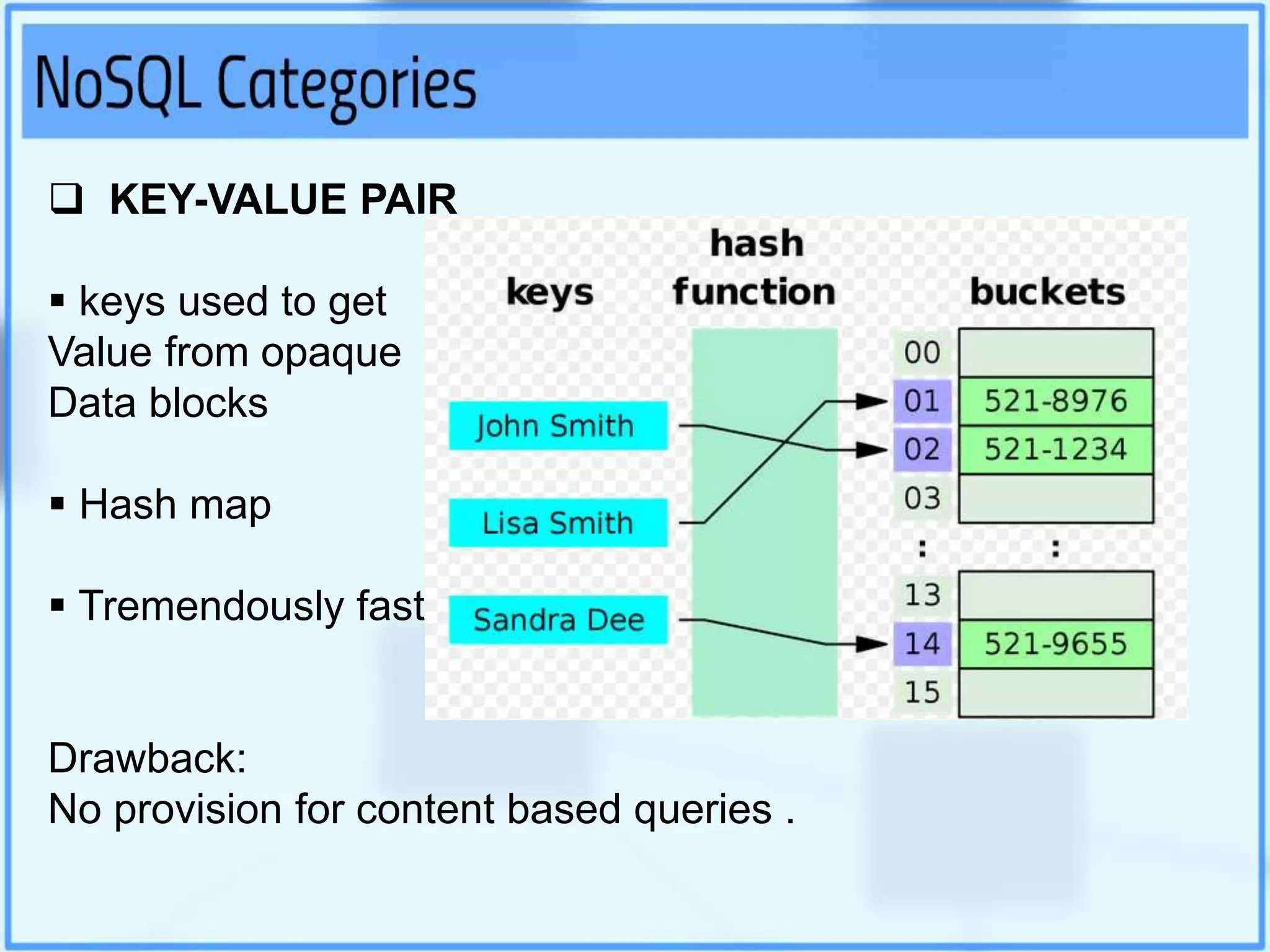
Big data analytics involves examining large datasets to uncover patterns and insights, facilitating applications like Google search recommendations. Traditional relational databases struggle to process big data, leading to the emergence of technologies such as Hadoop and NoSQL for effective data management. Key components of Hadoop include the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and MapReduce, which work together to store and process data in a distributed environment.