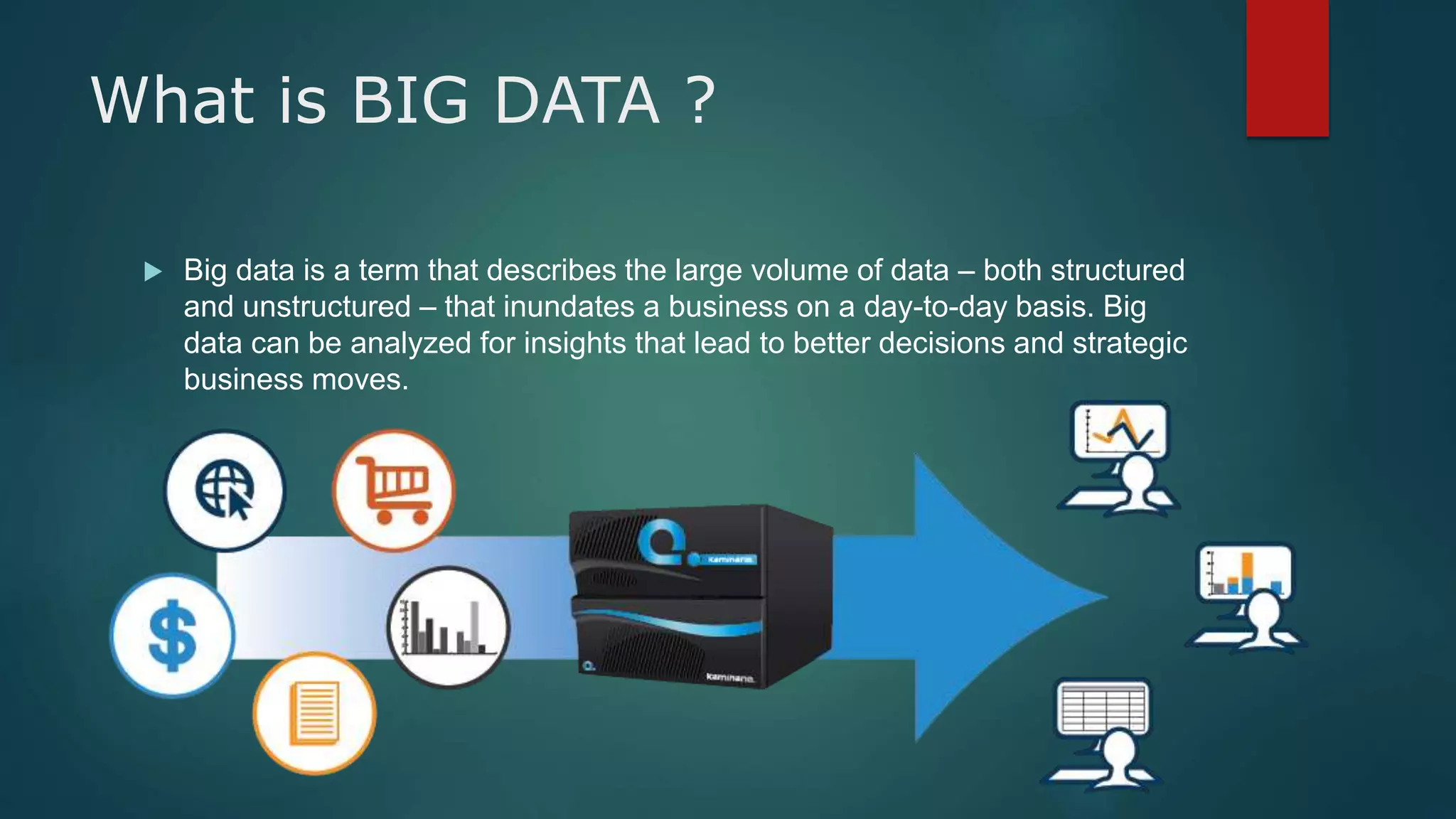
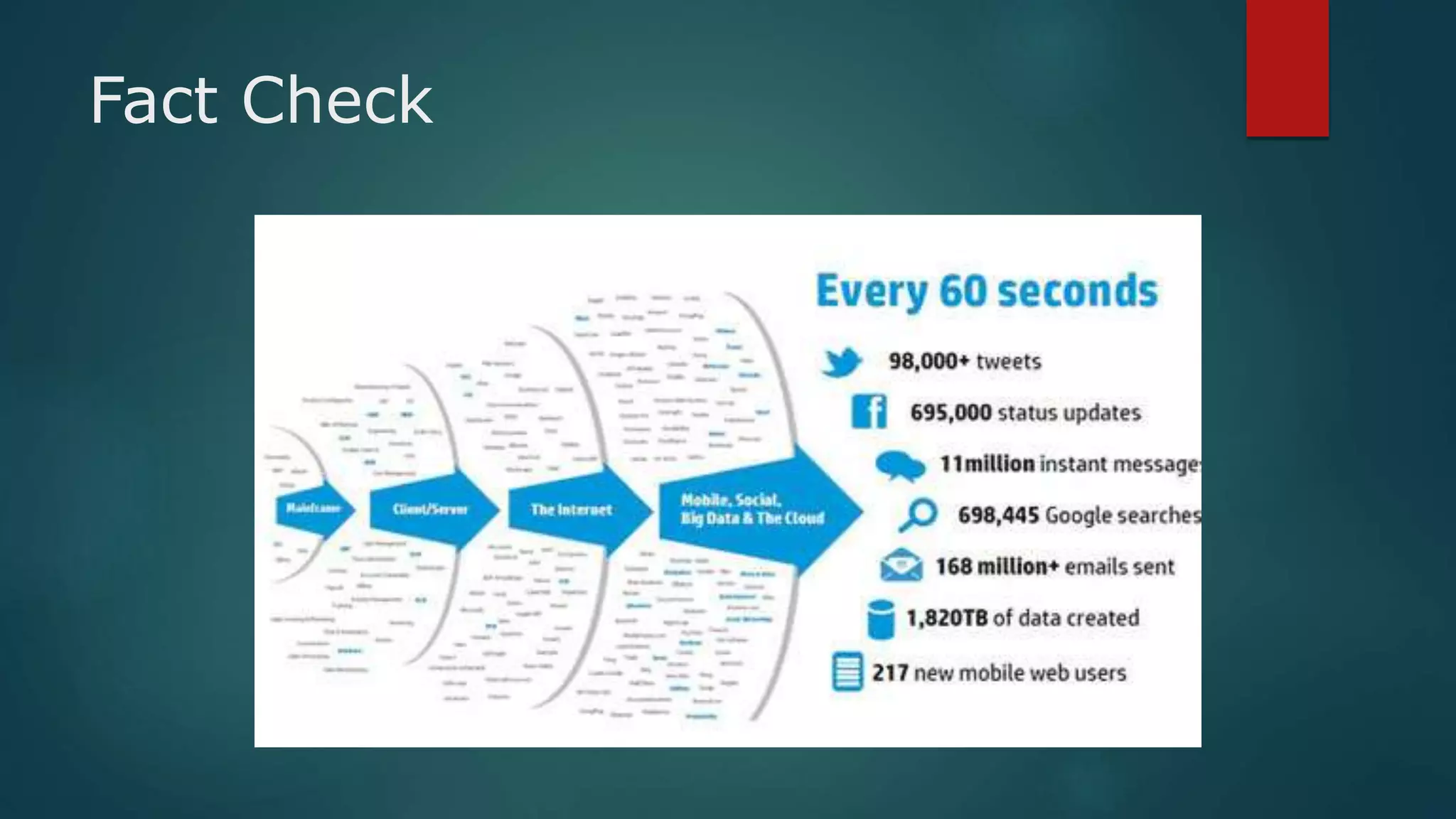
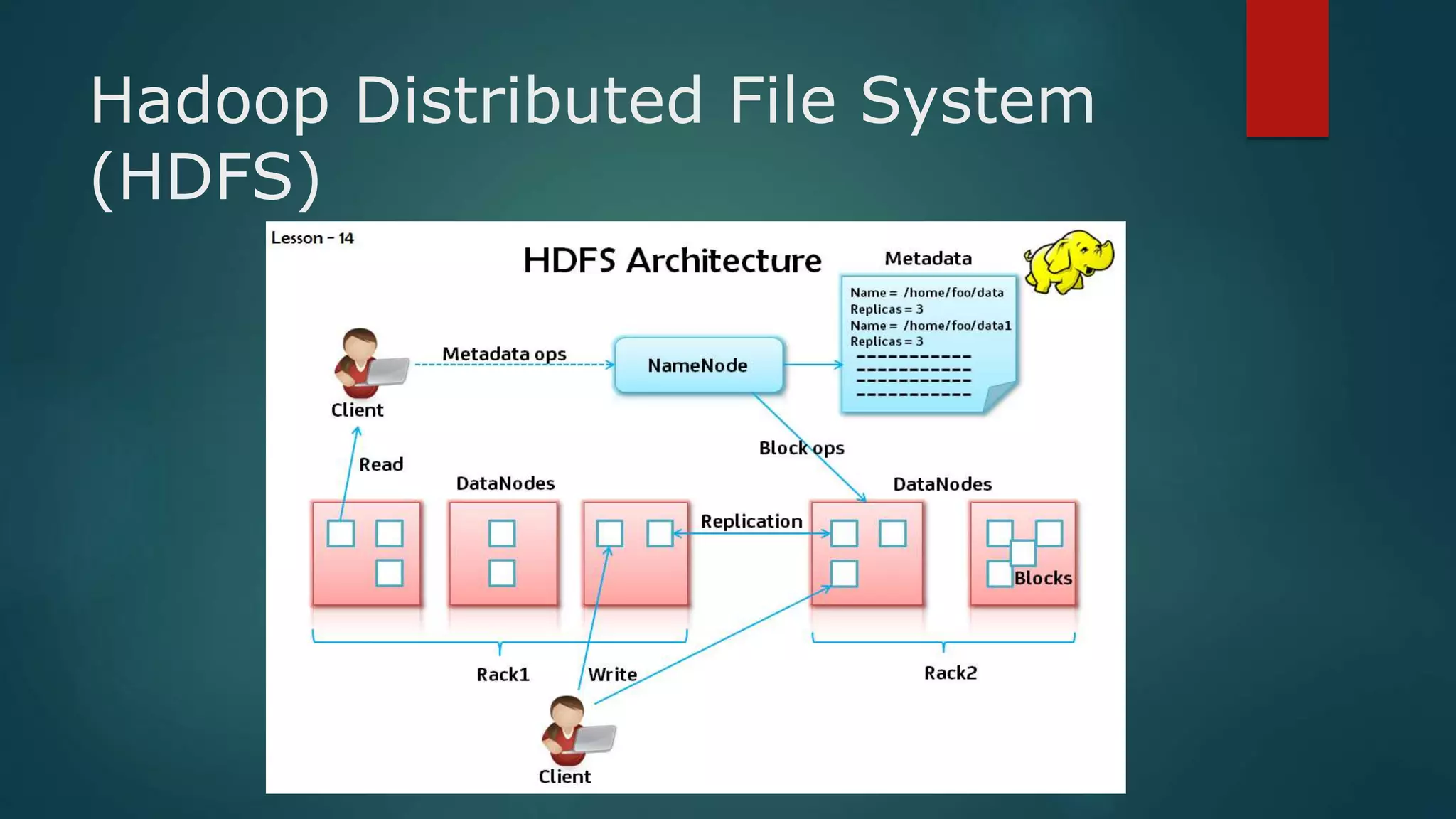
Big data refers to large volumes of structured and unstructured data from various sources like social media, business transactions, sensors, and devices. It has 3 key characteristics - velocity, variety, and volume. Hadoop is an open-source framework that allows storing and processing big data across clusters of commodity hardware. It uses HDFS for storage and MapReduce as a programming model to process data in parallel. Analyzing big data can provide insights for better decisions, cost reductions, and new product development.