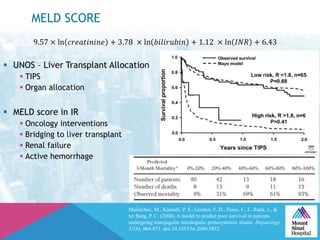
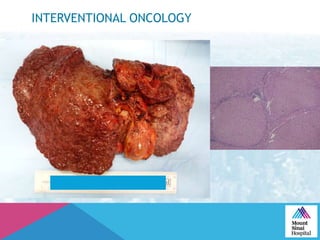
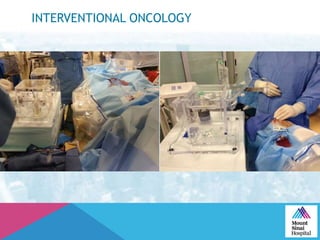
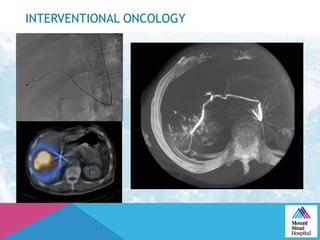
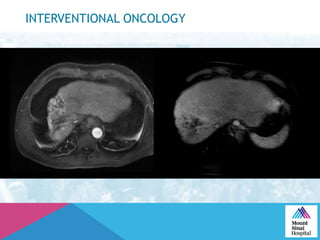
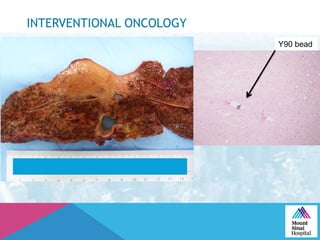
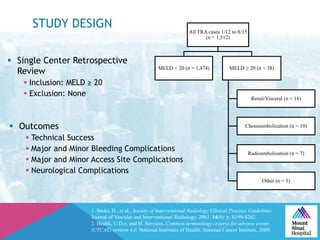
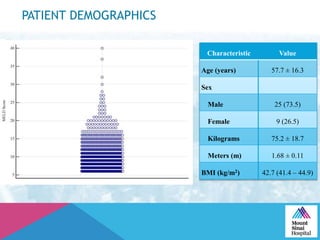
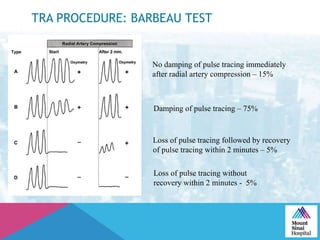
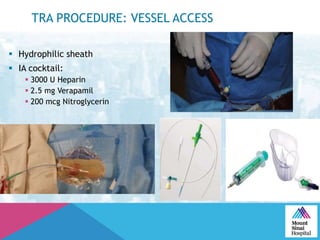
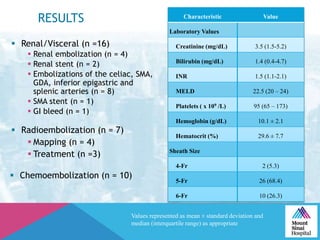
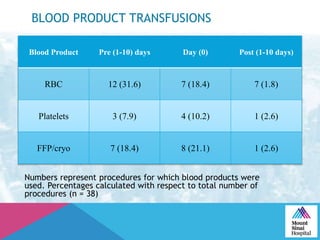
This document summarizes a study examining the use of transradial access (TRA) for non-coronary interventions in patients with severe hepatic dysfunction (MELD score ≥ 20). The study found TRA to be feasible in this high-risk population with a 100% technical success rate and very low rates of bleeding (0%) and access site (1 minor hematoma) complications. TRA in patients with liver dysfunction was shown to be safe and effective for renal/visceral interventions like embolization and stenting as well as radioembolization procedures, with few coagulation blood products required.