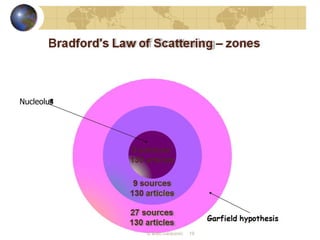
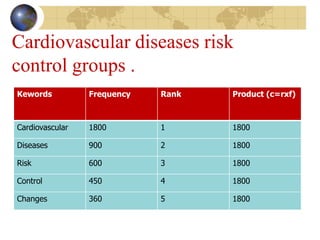
Bibliometrics is the application of mathematical and statistical methods to analyze publications. It is used to study written communication and measure outputs. Common bibliometric methods are citation analysis and content analysis. Bibliometrics helps identify key journals, rank publications, evaluate research output, and measure the usefulness of information services. Important bibliometric laws include Lotka's law, Bradford's law, and Zipf's law, which describe publication and word frequency distributions.