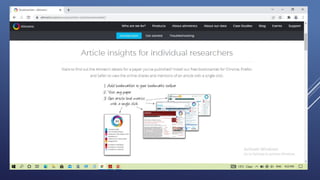
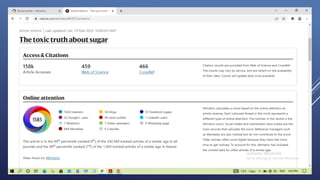
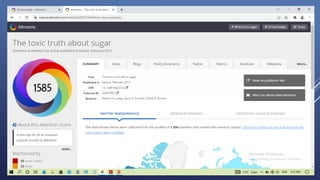
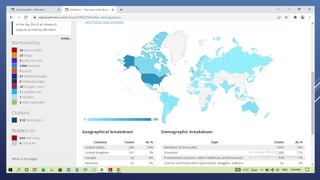
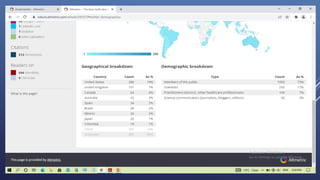
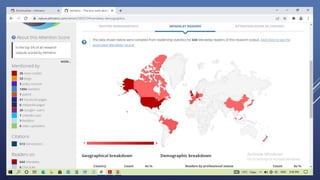
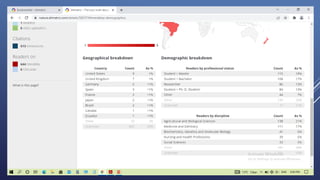
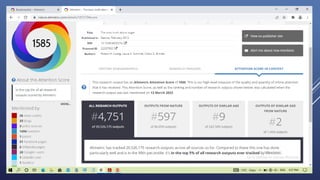
Altmetrics are alternative metrics to traditional citations that measure the online attention and impact of scholarly works. They capture how research outputs are discussed and shared on social media and other online platforms. This document provides an introduction to altmetrics, explaining how they originated from the shift to online scholarly communication. It describes various altmetrics providers and the types of metrics they collect for different research outputs like articles, books, data, and software. The benefits of altmetrics for researchers and their role in libraries and information science are also summarized.