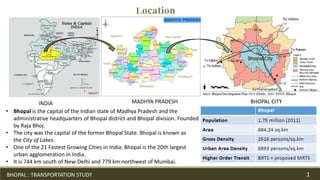
This document provides information about transportation in Bhopal, India. It discusses the history and evolution of development in Bhopal. It notes that the city's population and urban area have expanded rapidly in recent decades. The document analyzes transportation infrastructure such as roads, railways, and the airport. It also examines the formal and informal public transportation systems, issues they face regarding integration, infrastructure, and ridership, and potential solutions to improve transportation in Bhopal.