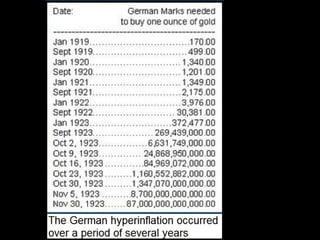
Between the 1920s and 1930s, several attempts were made to prevent future wars in Europe after World War 1, but they faced challenges. The Kellogg-Briand Pact outlawed war but lacked enforcement. The League of Nations struggled due to its diverse membership and lack of enforcement powers. Meanwhile, countries like Germany, Italy, and Spain faced economic and political instability during this interwar period known as the "Age of Anxiety."