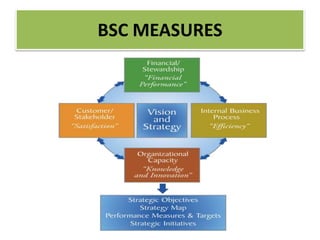
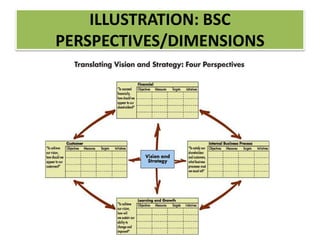
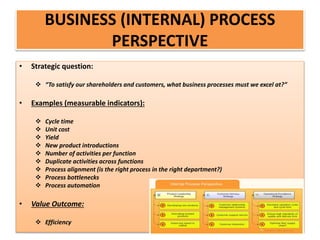
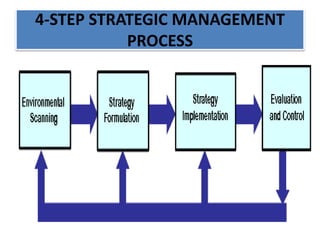
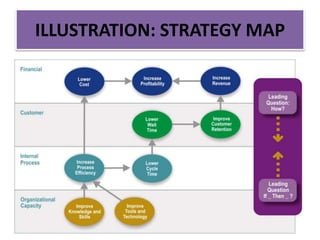
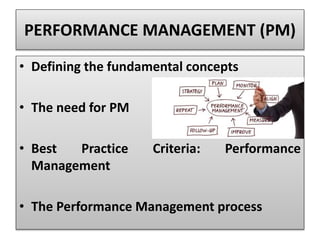
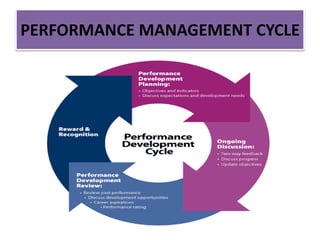
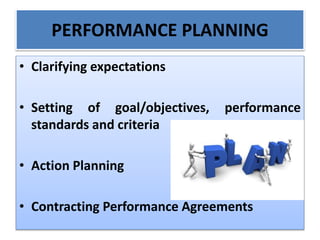
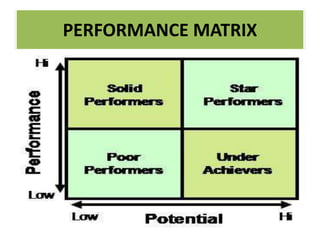
The document discusses best practices in transformational leadership and balanced scorecard (BSC) methodology, emphasizing the importance of leadership qualities, strategic planning, and performance management. It outlines the benefits of transformational leadership in motivating followers and details the four perspectives of BSC—learning and growth, business processes, customer, and financial—that guide organizational performance measurement. Additionally, it provides guidelines for implementing BSC effectively and evaluating performance management systems within organizations.