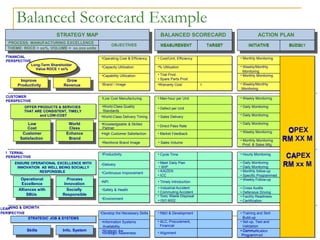
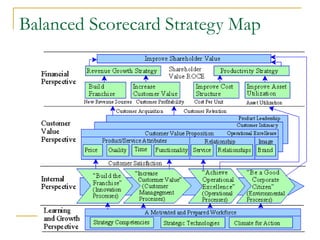
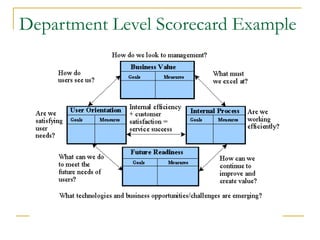
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and management system that monitors organizational performance against strategic goals. It was developed in the 1990s by Kaplan and Norton as an alternative to traditional performance measures that only consider financial perspectives. The Balanced Scorecard provides a balanced approach across financial, customer, internal business process, and learning and growth perspectives. It helps organizations execute strategy by translating strategic objectives into measurable goals and linking strategic measures to critical business activities.