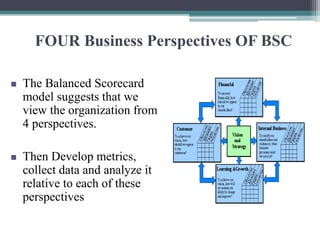
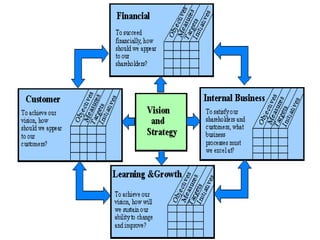
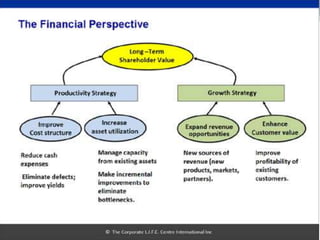
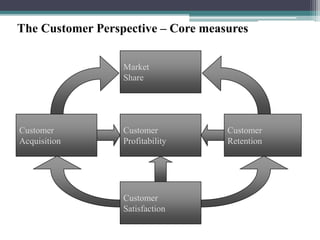
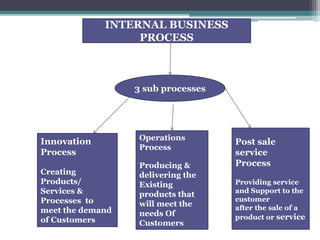
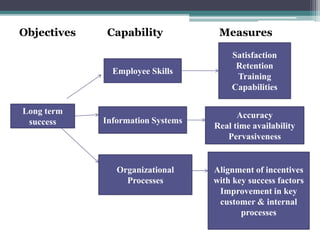
The document discusses the Balanced Scorecard, a strategic planning and management system used to align business activities with organizational vision and strategy. It does this by monitoring performance against strategic goals across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth. Key measures are identified for each perspective. The Balanced Scorecard framework translates strategy into objectives and measures across the four perspectives, allowing an organization to track strategic performance and progress.