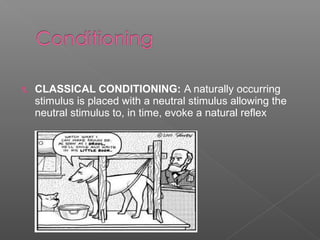
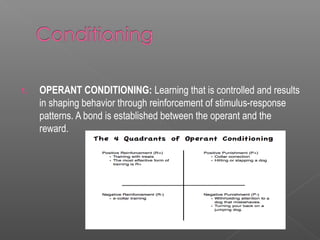
Behaviorism is a theory that human and animal behavior can be explained through conditioning without reference to internal mental states. It is based on the idea that behaviors are learned through positive and negative reinforcement. The two main types of conditioning are classical and operant conditioning. Key behaviorist theorists include Ivan Pavlov, B.F. Skinner, and Albert Bandura. Behaviorism is applied in education through use of stimuli, rewards, and reinforcement to shape student behavior and motivate learning.