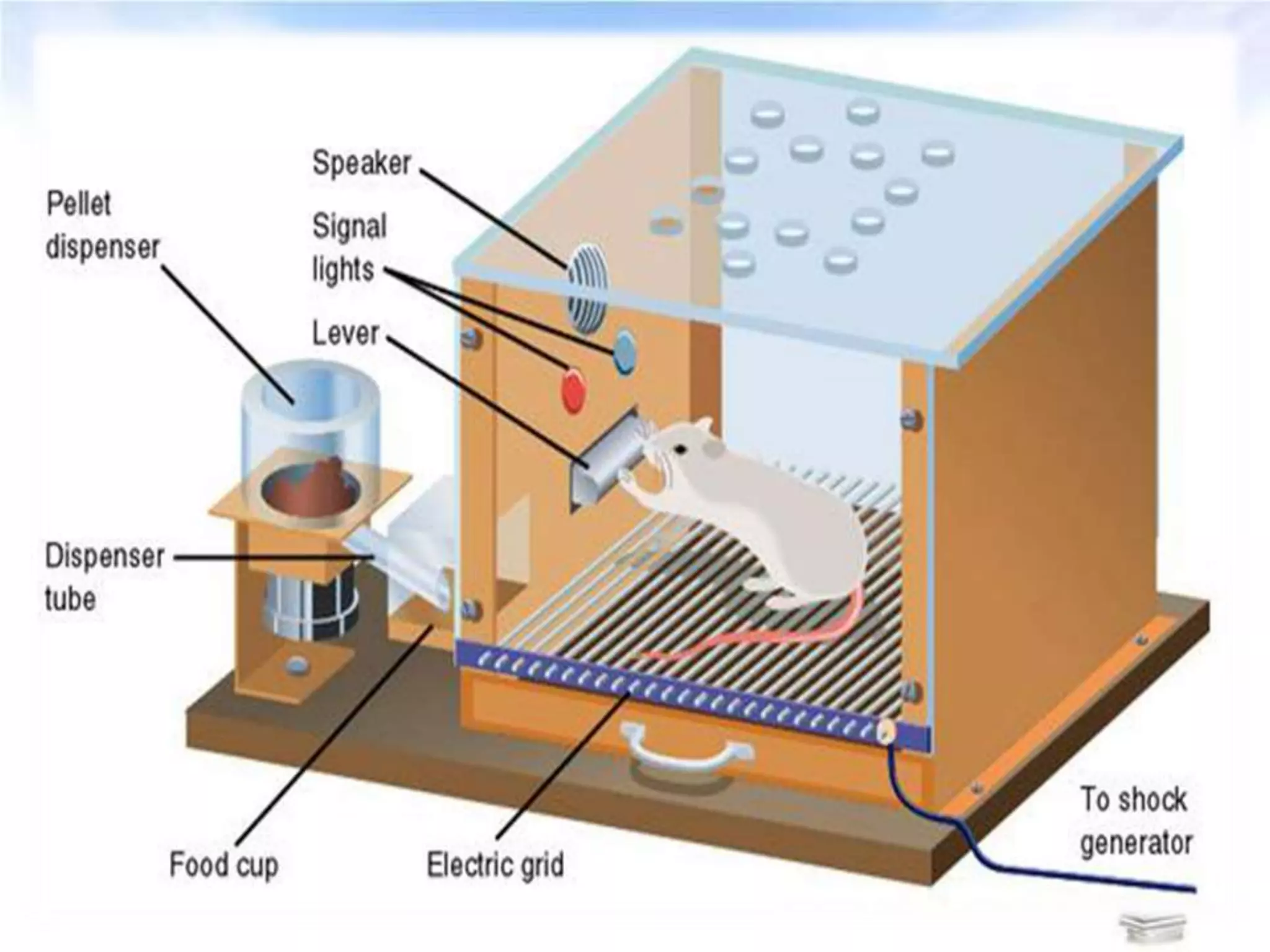
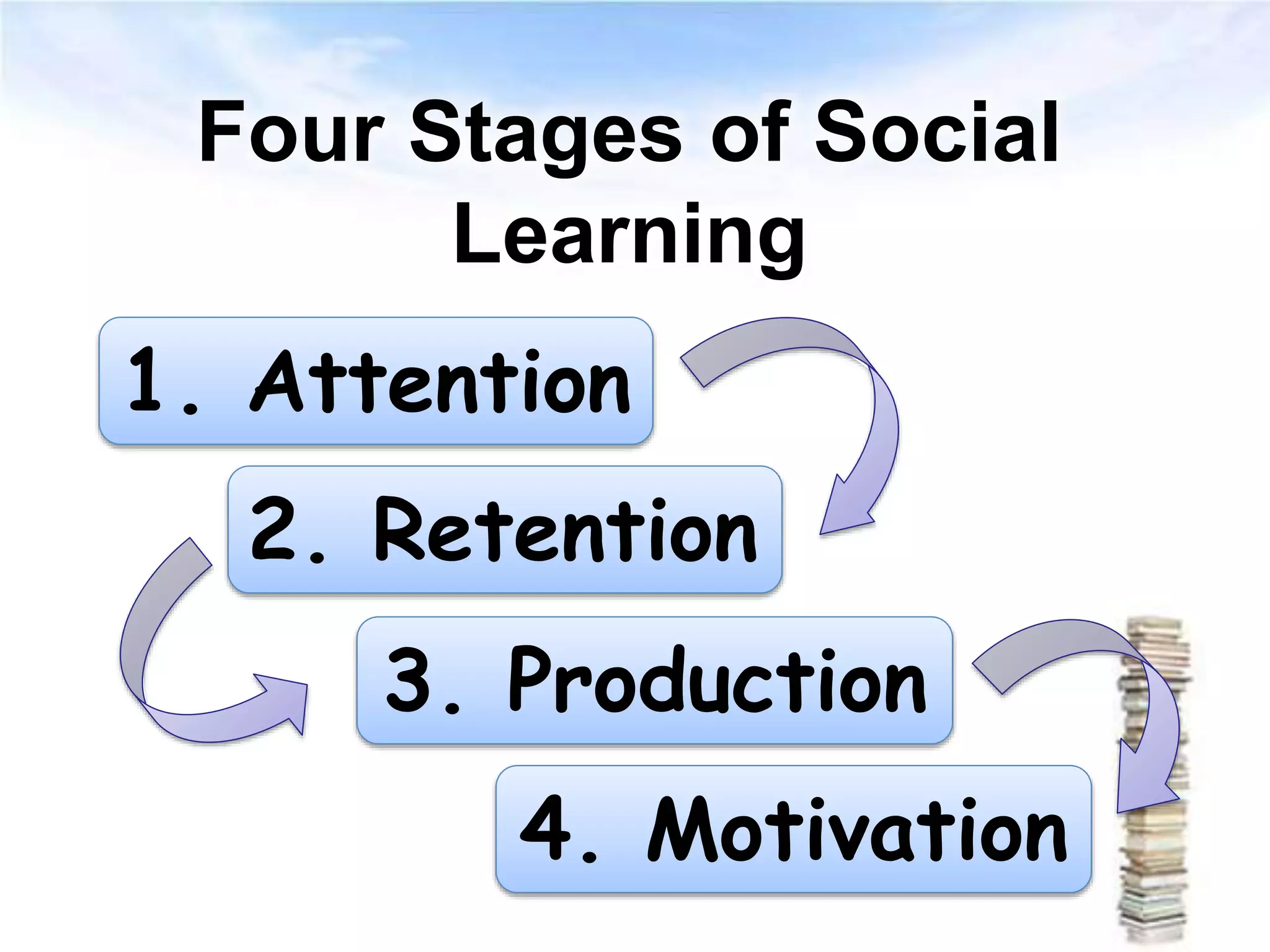
The document outlines key concepts of behaviorist learning theories, including observable interactions, stimulus-response situations, and operant conditioning. It discusses the role of positive and negative reinforcement, as well as punishment, in shaping behavior, along with Albert Bandura's social learning theory that emphasizes vicarious learning. Additionally, it highlights strategies for effective teaching, such as breaking down skills, regular feedback, and direct instruction.