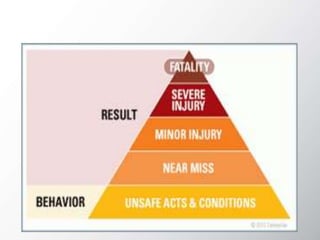
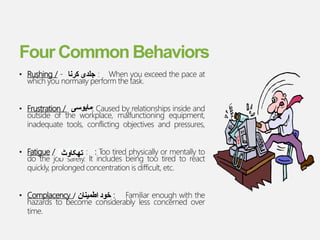
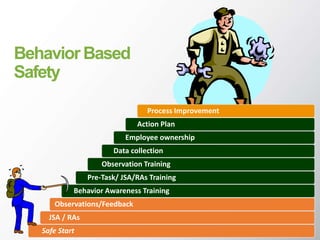
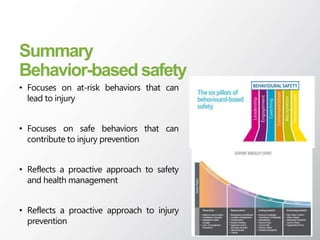
The document discusses Behavior Based Safety (BBS), which focuses on identifying and changing at-risk behaviors through observation, feedback, and encouraging safe behaviors. The goals of BBS include increasing safety, productivity, and morale while reducing accidents and injuries. It is presented as a proactive approach to safety management and injury prevention. The key aspects of BBS involve identifying critical safety-related behaviors, gathering data on workplace safety, providing feedback, and engaging employees to improve safety culture continuously. Phases of implementation include assessing safety culture, training leaders and employees, monitoring progress, and motivating employees to adopt safe behaviors.