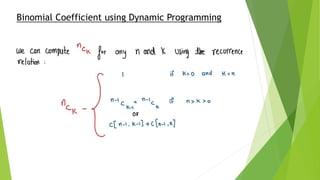
This document discusses using dynamic programming to solve the binomial coefficient and world series problems. It defines binomial coefficient as the number of ways to choose a subset of objects from a larger set. It then describes the world series problem as two teams competing in a series of games until one wins n games. A recursive formula is developed to calculate the probability of different outcomes. Dynamic programming is applied by storing probabilities in an array to speed up the algorithm and solve it in O(4n) time.