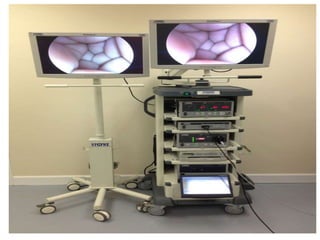
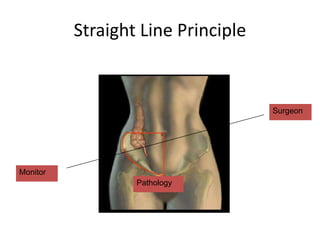
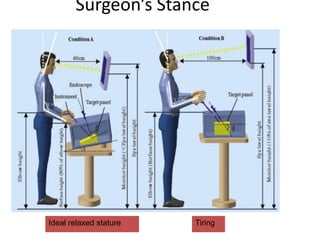
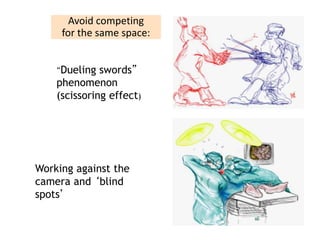
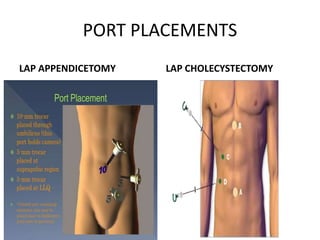
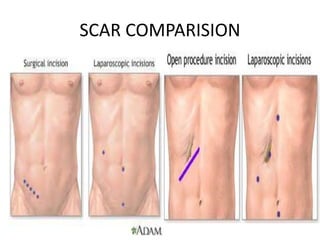
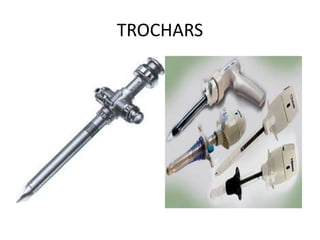
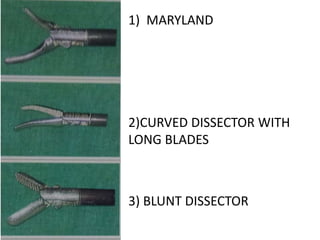
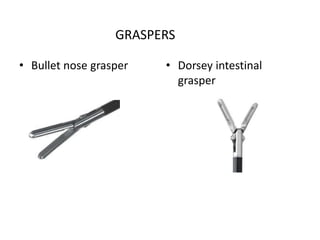
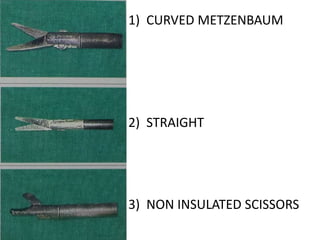
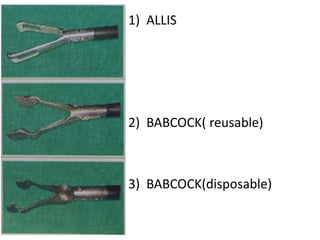
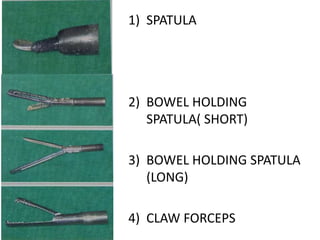
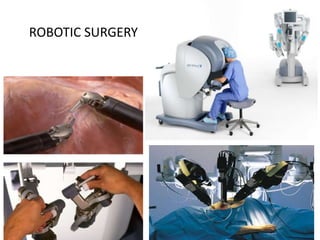
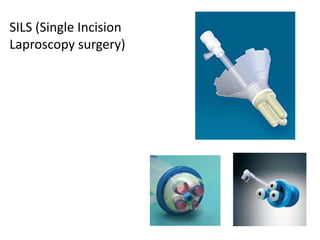
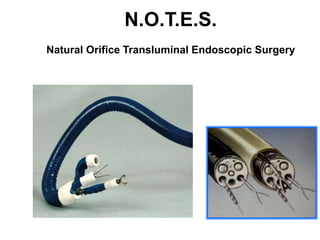
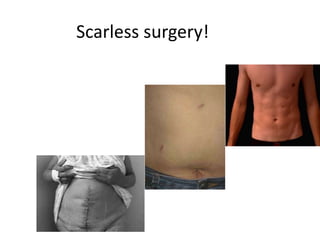
This document discusses the basic principles of laparoscopy. It describes the key differences between laparoscopic and open surgery for both patients and surgeons. For patients, laparoscopic surgery results in less pain, faster recovery times, and quicker return to normal activities due to smaller incisions. For surgeons, laparoscopy provides a magnified view but with altered tactile response and two-dimensional images. The document outlines the typical laparoscopic setup including the endoscope, light source, camera, monitor, insufflator, trocars and various instruments. It also lists some common laparoscopic procedures that can be used for diagnostic and operative purposes.