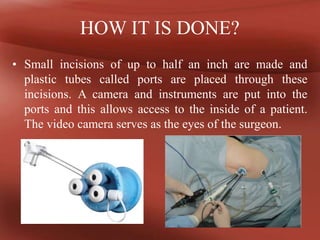
Laparoscopy involves using a video camera and thin instruments inserted through small abdominal incisions to perform surgery. It allows internal organs to be viewed and manipulated with less pain and faster recovery compared to open surgery. Common uses include appendectomy, gallbladder removal, and hernia repair. Perioperative nurses provide care before, during, and after laparoscopy by assessing patients, relieving anxiety, maintaining aseptic technique, and ensuring effective airway clearance and pain management.