The document discusses key concepts in quantum mechanics including wave functions, probability, operators, expectation values, and normalization. Some main points:
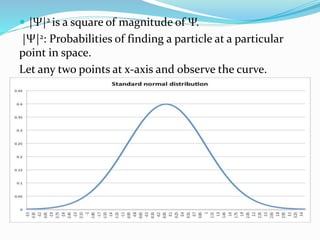
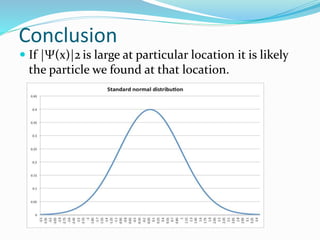
- The wave function Ψ is a complex function that represents the quantum state of a system and |Ψ|2 gives the probability of finding a particle in a particular location.
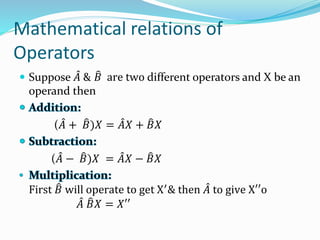
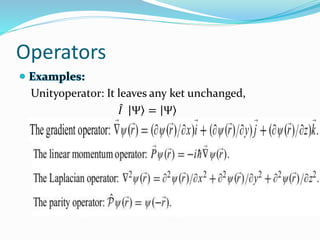
- Operators connect the wave function to observable physical quantities. Expectation values provide the average value that would be obtained from many measurements.
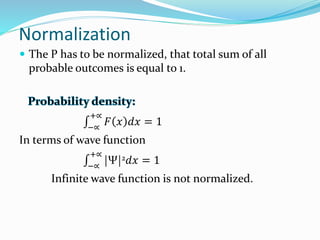
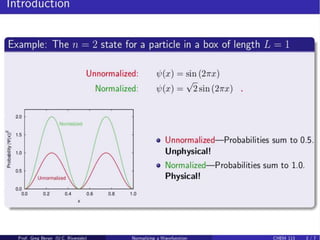
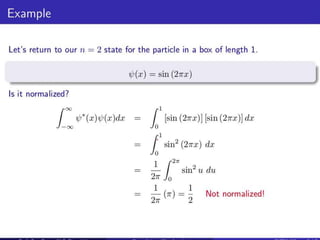
- For a wave function to represent a physical state, it must be normalized such that the total probability across all possible values equals 1.