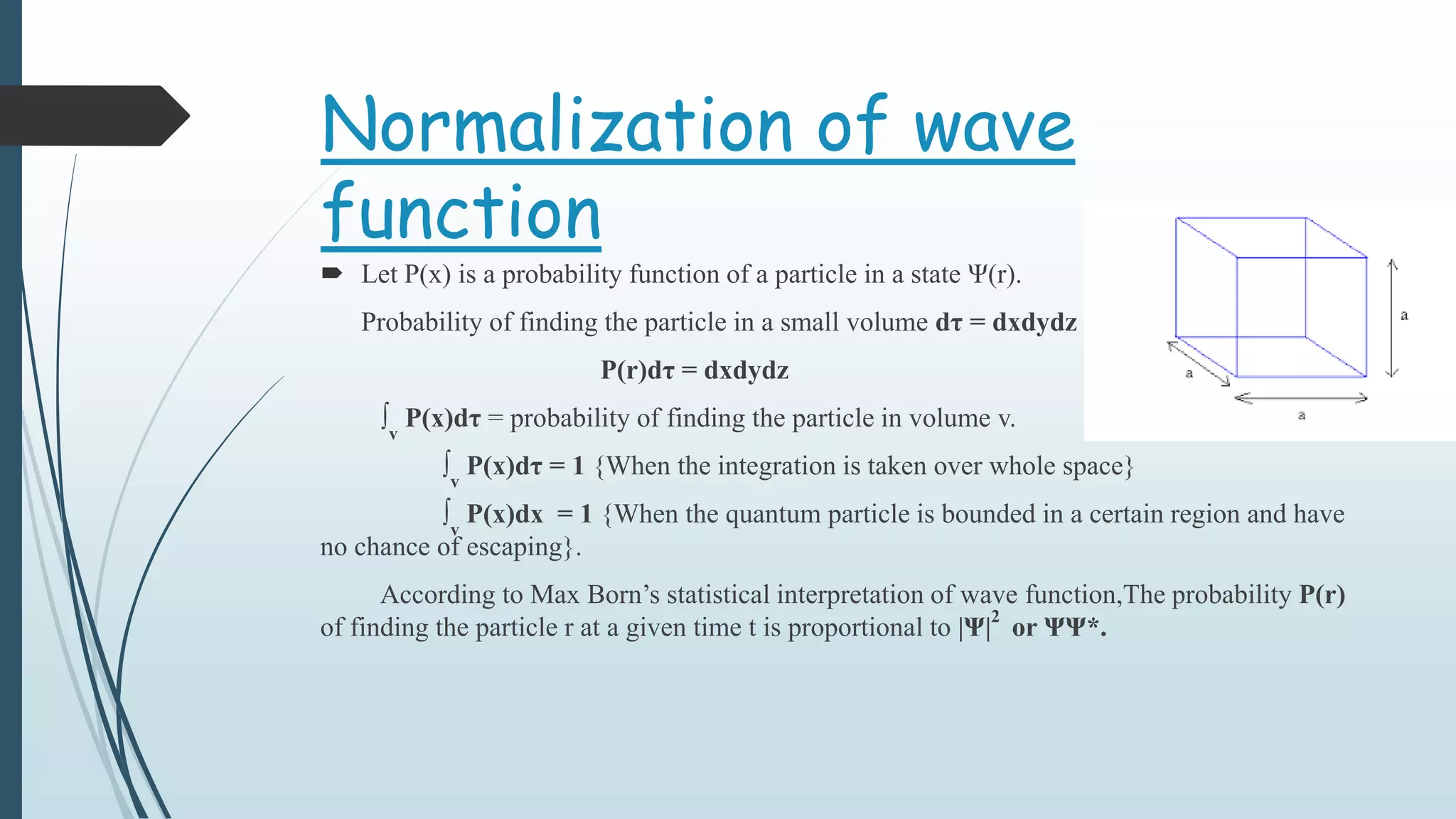
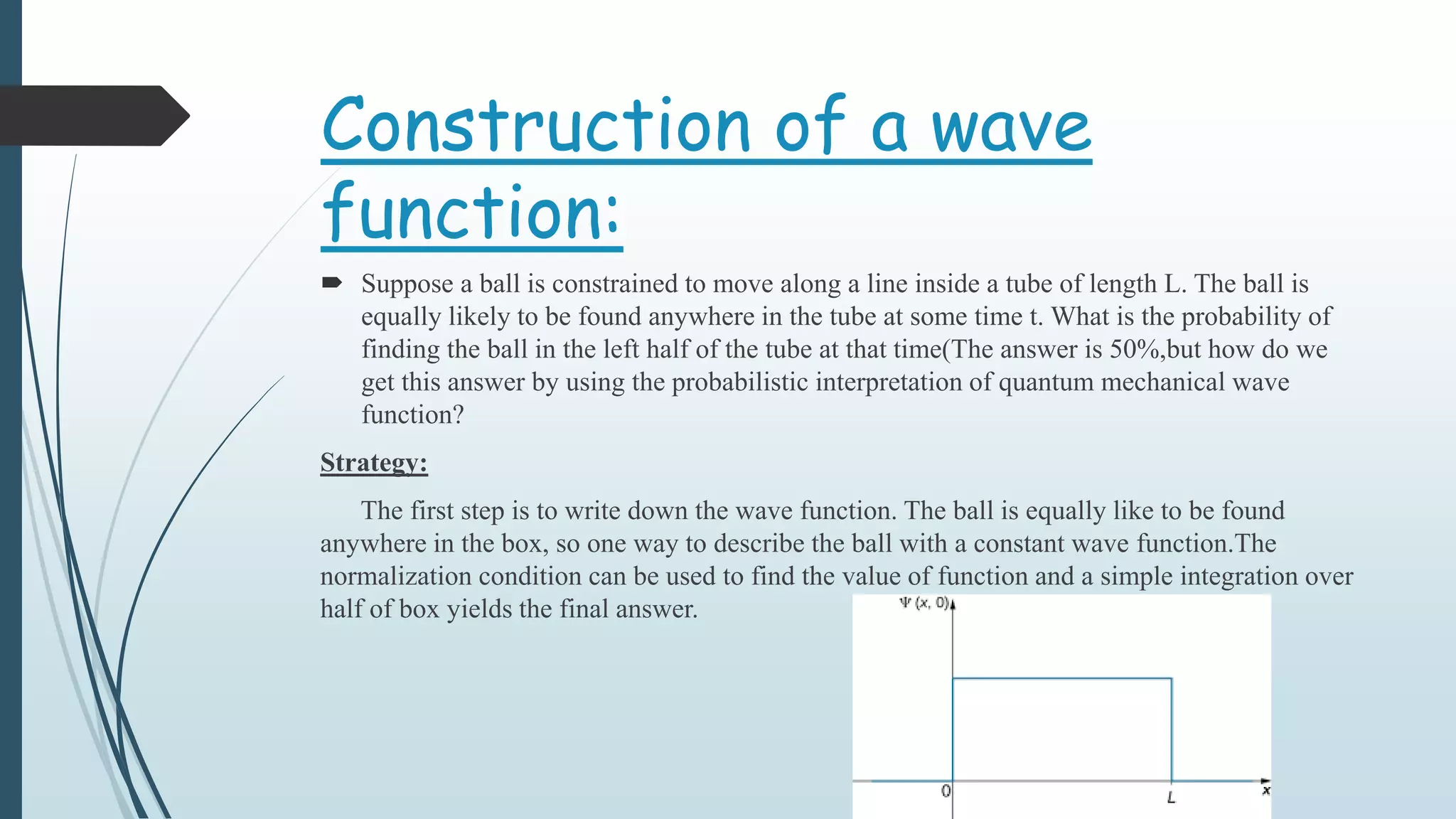
The wave function Ψ provides information about a quantum mechanical system. It is used to calculate the probability of finding a particle in a particular region of space. For example, if a ball is constrained to move in one dimension within a tube of length L, the wave function Ψ would be constant, with a value determined by the normalization condition. Integrating this wave function over the left or right half of the tube then gives the 50% probability of finding the ball in each half. Operators are used in quantum mechanics to extract measurable properties like position, momentum, or energy from the wave function.






![𝝏Ψ(x,t)
𝝏𝒙
= -k sin (kx-ωt) + 𝒊 kcos(kx-ωt)
𝝏Ψ(x,t)
𝝏𝒙
= 𝒊 k [ (cos(kx-ωt) + 𝒊 sin(kx-ωt)]
𝝏Ψ(x,t)
𝝏𝒙
= 𝒊 k Ψ(x,t)
𝝏Ψ(x,t)
𝝏𝒙
= 𝒊
𝒑
ħ
Ψ(x,t) { k =
𝟐𝝅
𝝀
=
𝟐𝝅
𝒉
P }
ħ
𝒊
𝝏Ψ(x,t)
𝝏𝒙
= p Ψ(x,t) { k =
𝑷
ħ
}
- 𝒊 ħ
𝝏Ψ(x,t)
𝝏𝒙
= p Ψ(x,t)
- 𝒊 ħ ∂∕∂x [Ψ(x,t)]= p [Ψ(x,t)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asadali-copy-230327174637-8d549f5c/75/Wave-function-9-2048.jpg)