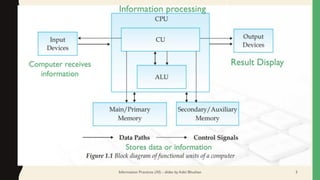
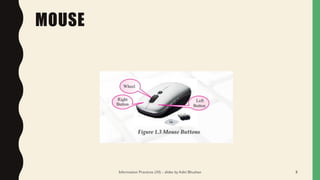
This document contains slides about basics of information technology. It discusses key concepts like data and information, components of a computer like input devices, output devices, CPU, and memory. It describes common input devices like keyboard, mouse, and scanners. Output devices discussed include monitors, printers, and speakers. The CPU is described as having a control unit, arithmetic logical unit, and memory unit. Different types of computer networks like LAN, MAN, and WAN are defined. Popular IT careers and trends like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are also mentioned.












![MEMORY UNIT
Memory
Unit
PRIMARY MEMORY (Main Mem)
[INTERNAL MEMORY]
ROM (Read Only Mem), non-
volatile memory, stores
information from manufacturer
RAM (Random Access Mem) –
volatile memory, hold
active data and
information
SECONDARY MEMORY (Aux. Mem)
[EXTERNAL MEMORY]
Pen-Drive, FD, CD, DVD, HDD, SDD, USB,
FLASH MEMORY
Information Practices (XI) - slides by Aditi Bhushan 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1ithsc-201003160351/85/Basics-of-Information-Technology-15-320.jpg)



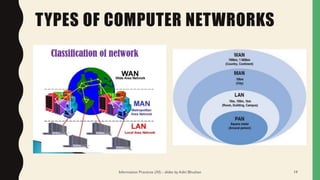

![METROPOLITAN AREA NETWORK
[MAN]
• These types of networks are larger than LANs but smaller than
WANs.
• They incorporate elements from both types of networks.
• MANs span an entire geographic area (typically a town or city,
but sometimes a campus).
• Ownership and maintenance is handled by either a single
person or company (a local council, a large company, etc.).
Information Practices (XI) - slides by Aditi Bhushan 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1ithsc-201003160351/85/Basics-of-Information-Technology-21-320.jpg)



