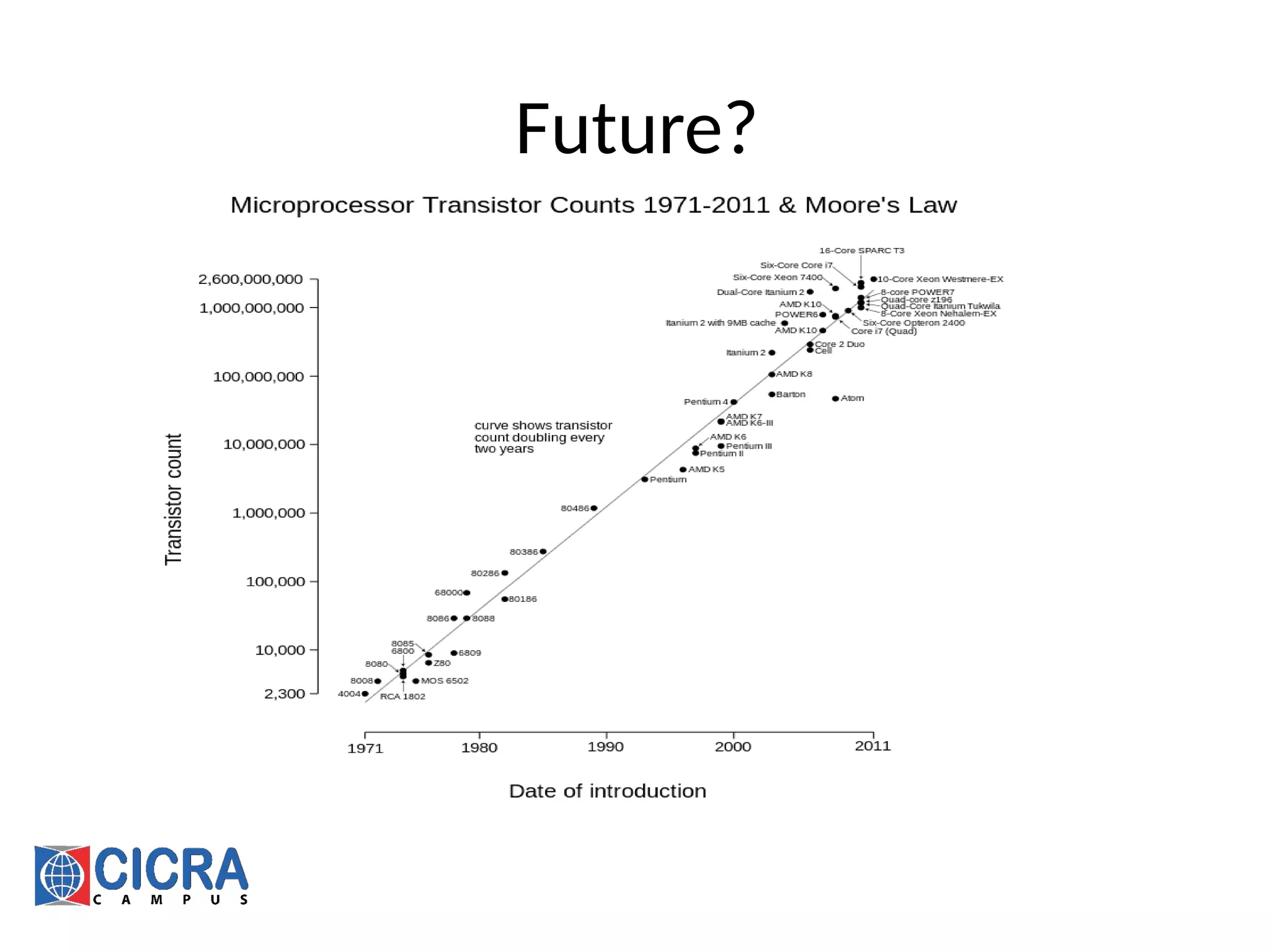
The document outlines an introductory course on Information and Communication Technology (ICT), covering its definition, history, and components including hardware, software, and human interaction. It details the evolution of computers from early machines to the present era characterized by artificial intelligence and cloud computing. Career paths in ICT are also discussed, emphasizing the importance of foundational knowledge and proficiency in programming.


![Course Overview
• Introduction to ICT [4 hours] – This lecture
• ICT Infrastructure [8 hours]
• Maths Behind IT [2 hours]
• Internet and Web [4 hours]
• Software Engineering [4 hours]
• Data and Databases [4 hours]
• Graphics and Video Games [2 hours]
• Social Media [ 2 hours]
• Mobile Computing [2 hours]
• Security and Forensics [2 hours]
• Digital and Information Literacy [2 hours]
• ICT Policies and Governance [1 hour]
• Ethics in IT [1 hour]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoict-181009101330/75/Introduction-to-ICT-3-2048.jpg)
![What is ICT? (contd.)
• What does the WIKI says ?
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Information_and_commun
ications_technology]
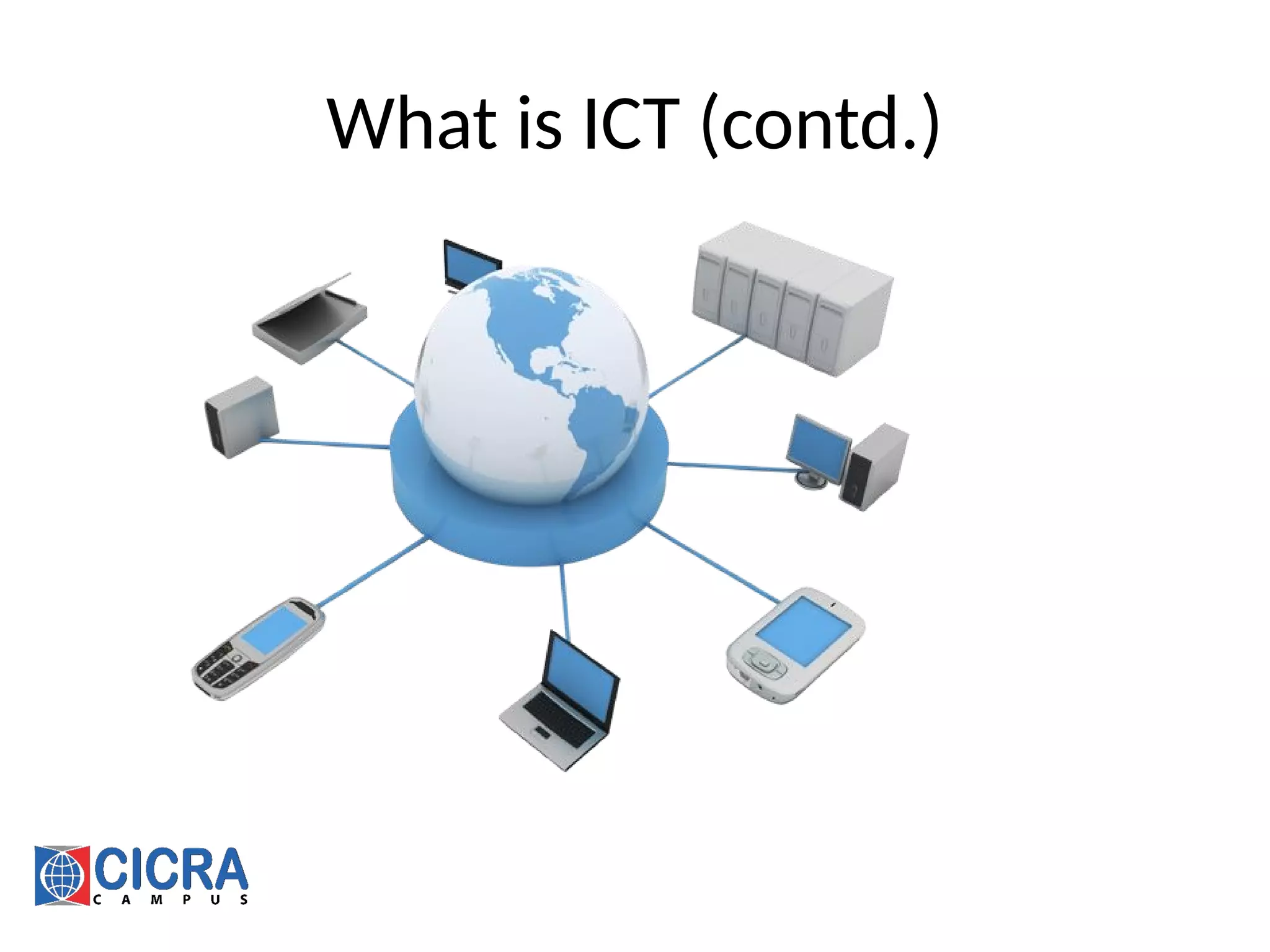
Information and communication technology (ICT) is an extended term for
information technology (IT) which stresses the role of unified communications
and the integration of telecommunications (telephone lines and wireless
signals), computers as well as necessary enterprise software, middleware,
storage, and audio-visual systems, which enable users to access, store,
transmit, and manipulate information
• Further the website says,
“However, ICT has no universal definition, as "the concepts, methods and
applications involved in ICT are constantly evolving on an almost daily basis"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoict-181009101330/75/Introduction-to-ICT-5-2048.jpg)










![References – Mentioned with Thanks
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Information_and_communications_technology
[2] http://people.bu.edu/baws/brief%20computer%20history.html
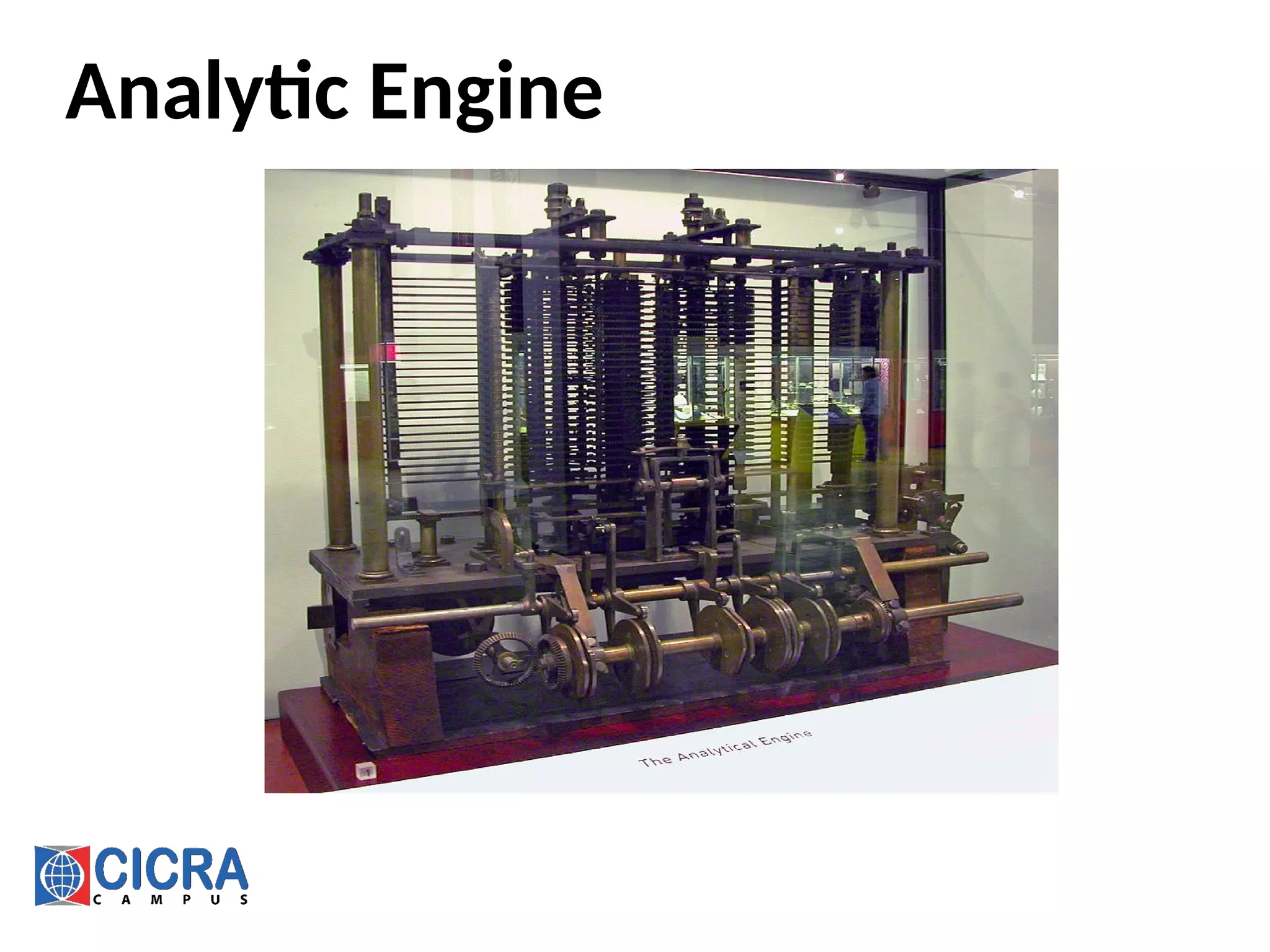
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analytical_Engine
[4] http://www.pimall.com/nais/pivintage/enic.html
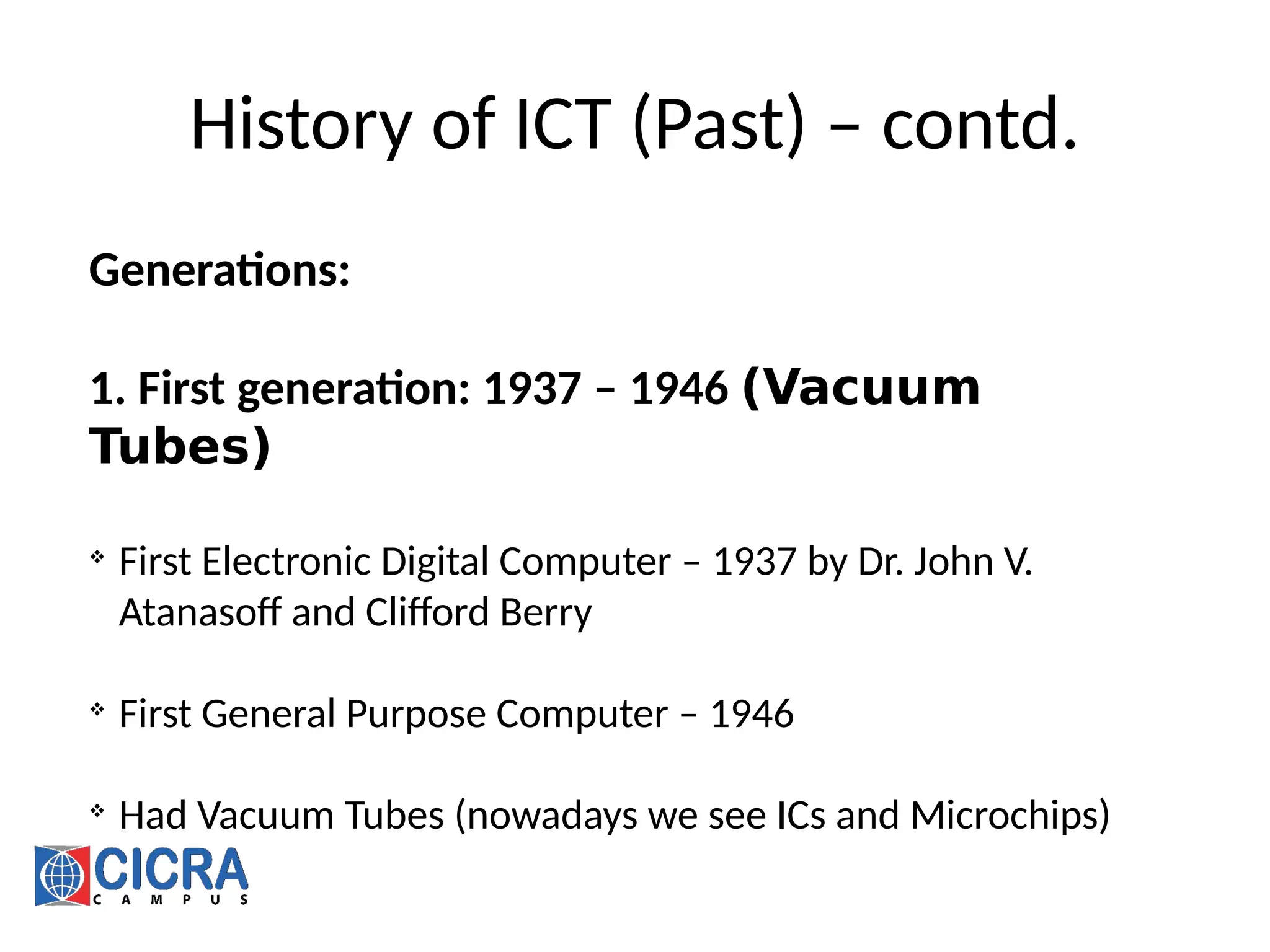
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ENIAC
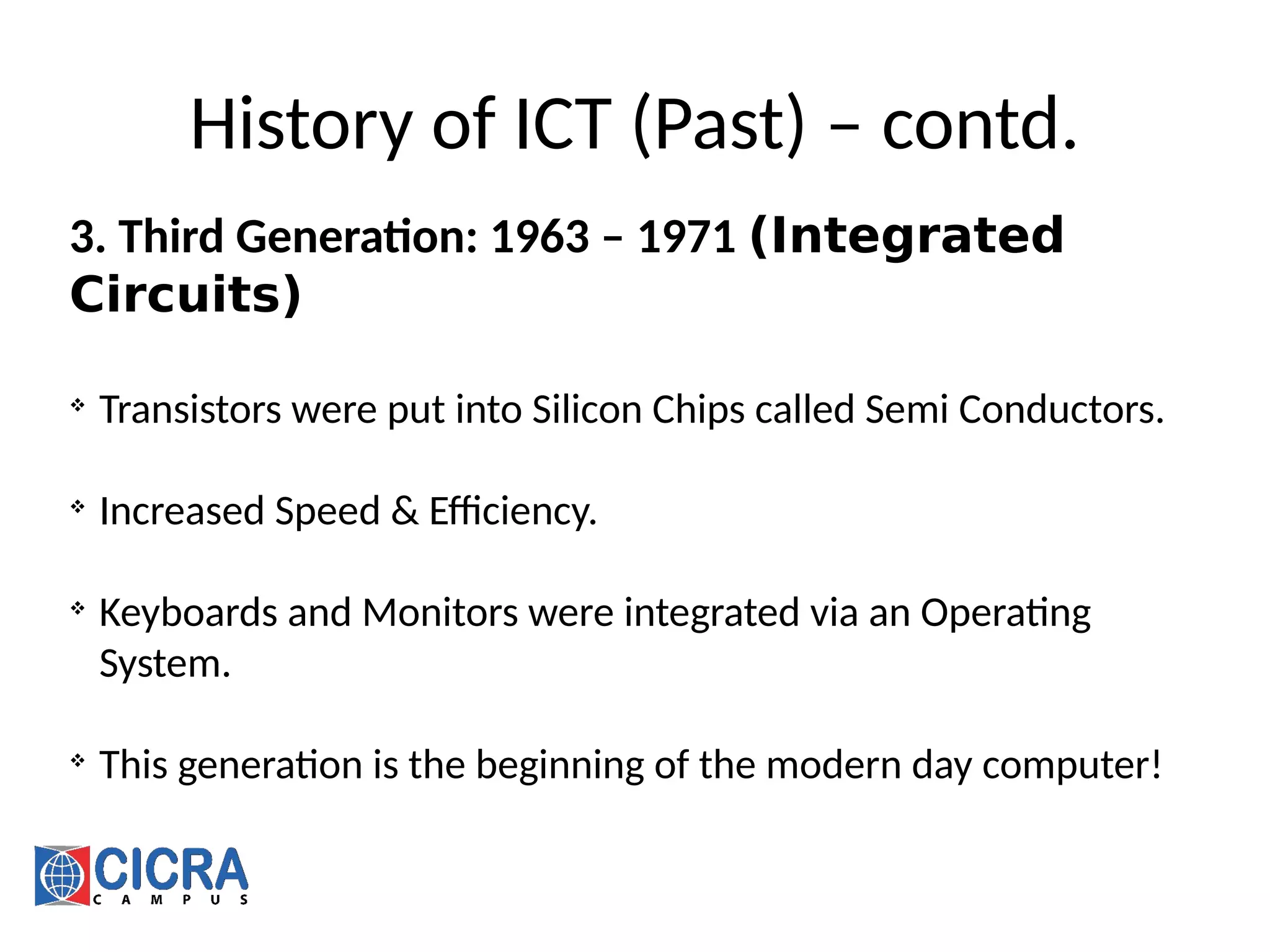
[6] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UNIVAC_I
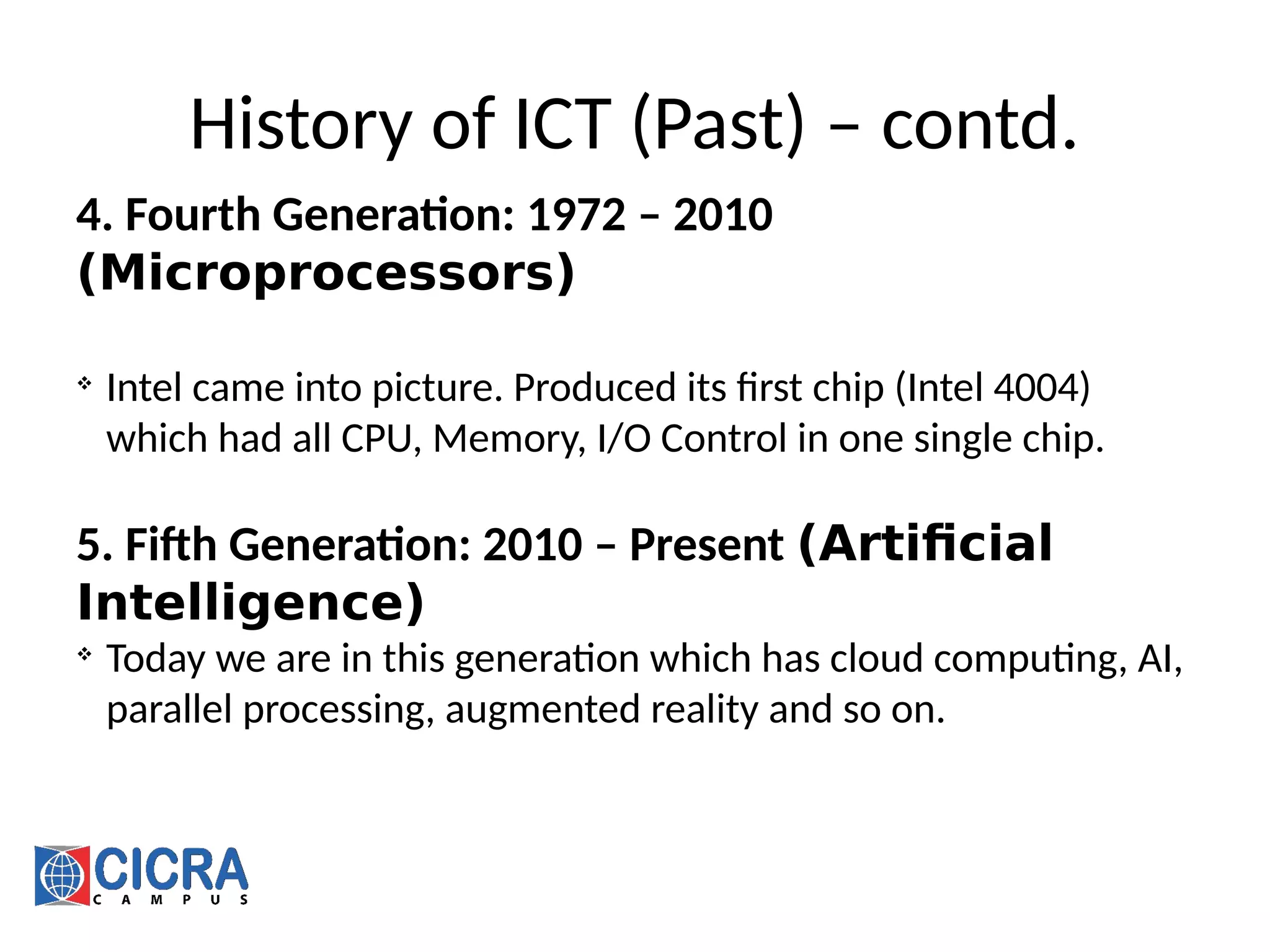
[7] https://www.ibm.com/cloud-computing/learn-more/what-is-cloud-computing/
[8]http://cpu.userbenchmark.com/
[9] http://spectrum.ieee.org/computing/software/the-2016-top-programming-languages
[10] http://btob.co.nz/business-news/five-generations-computers/
[11] http://computer.howstuffworks.com/augmented-reality.htm
[12] http://www.pcworld.com/article/2988179/computers/10-enthralling-visions-for-the-future-of-
computing.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoict-181009101330/75/Introduction-to-ICT-29-2048.jpg)