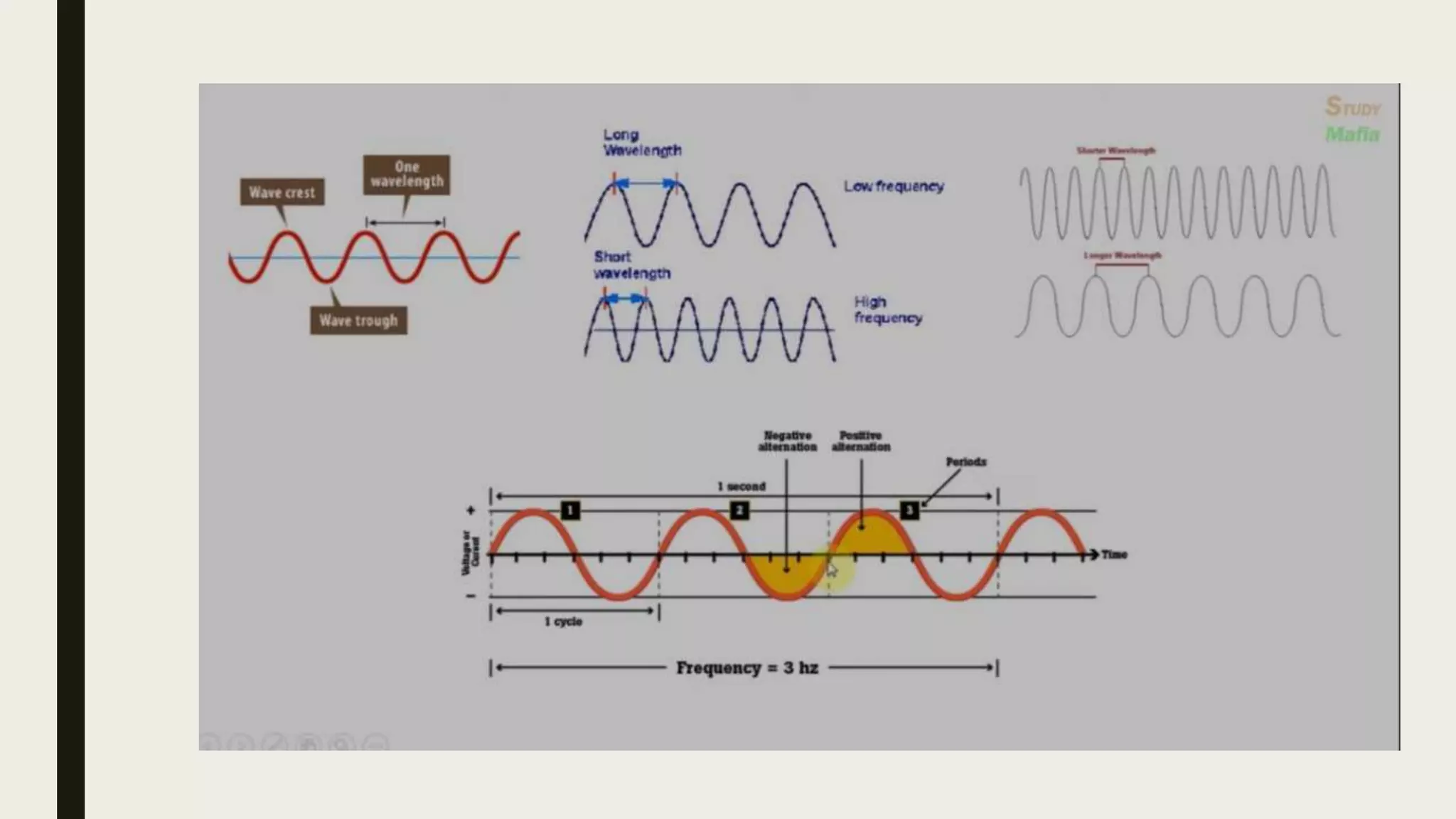
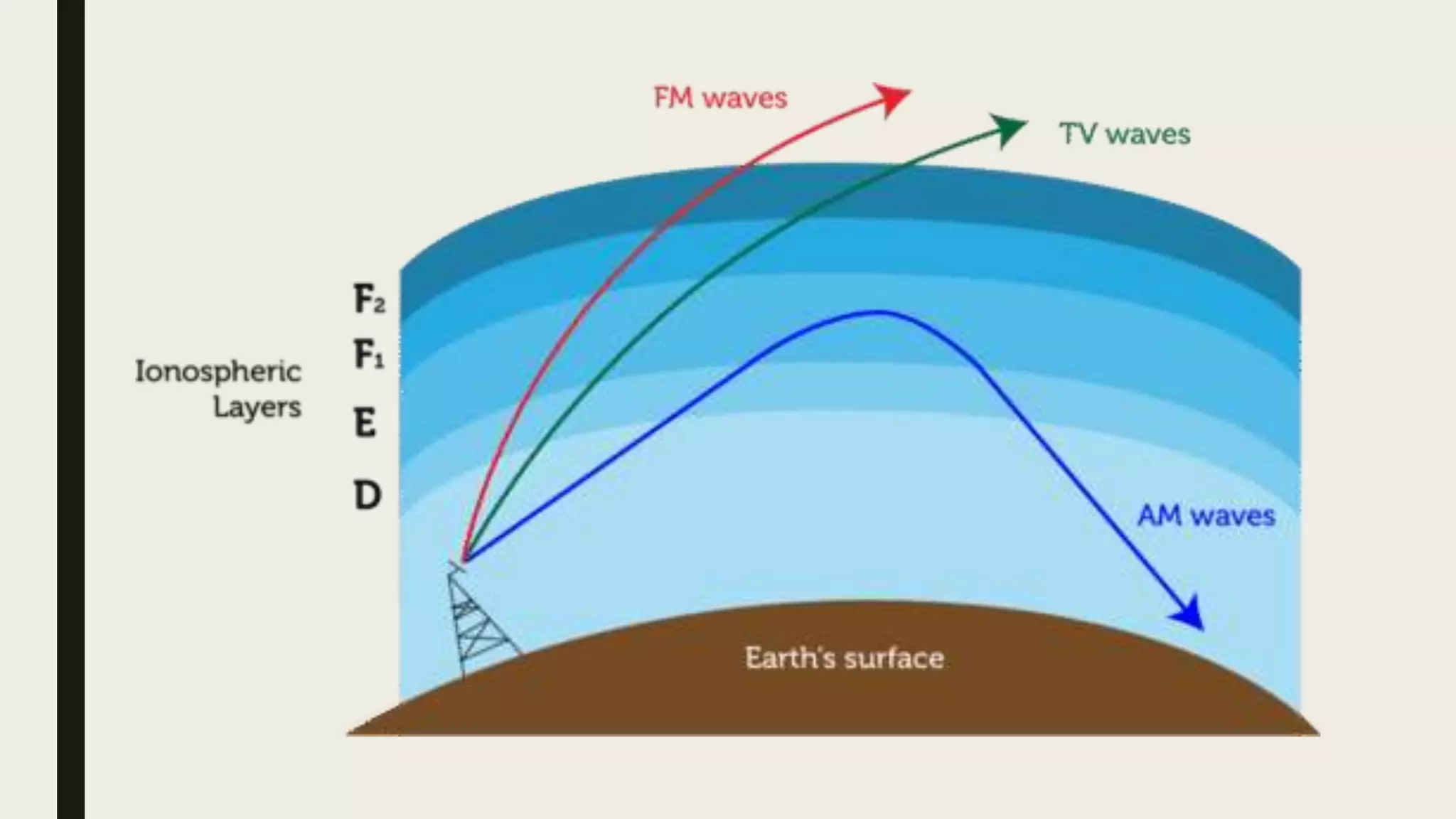
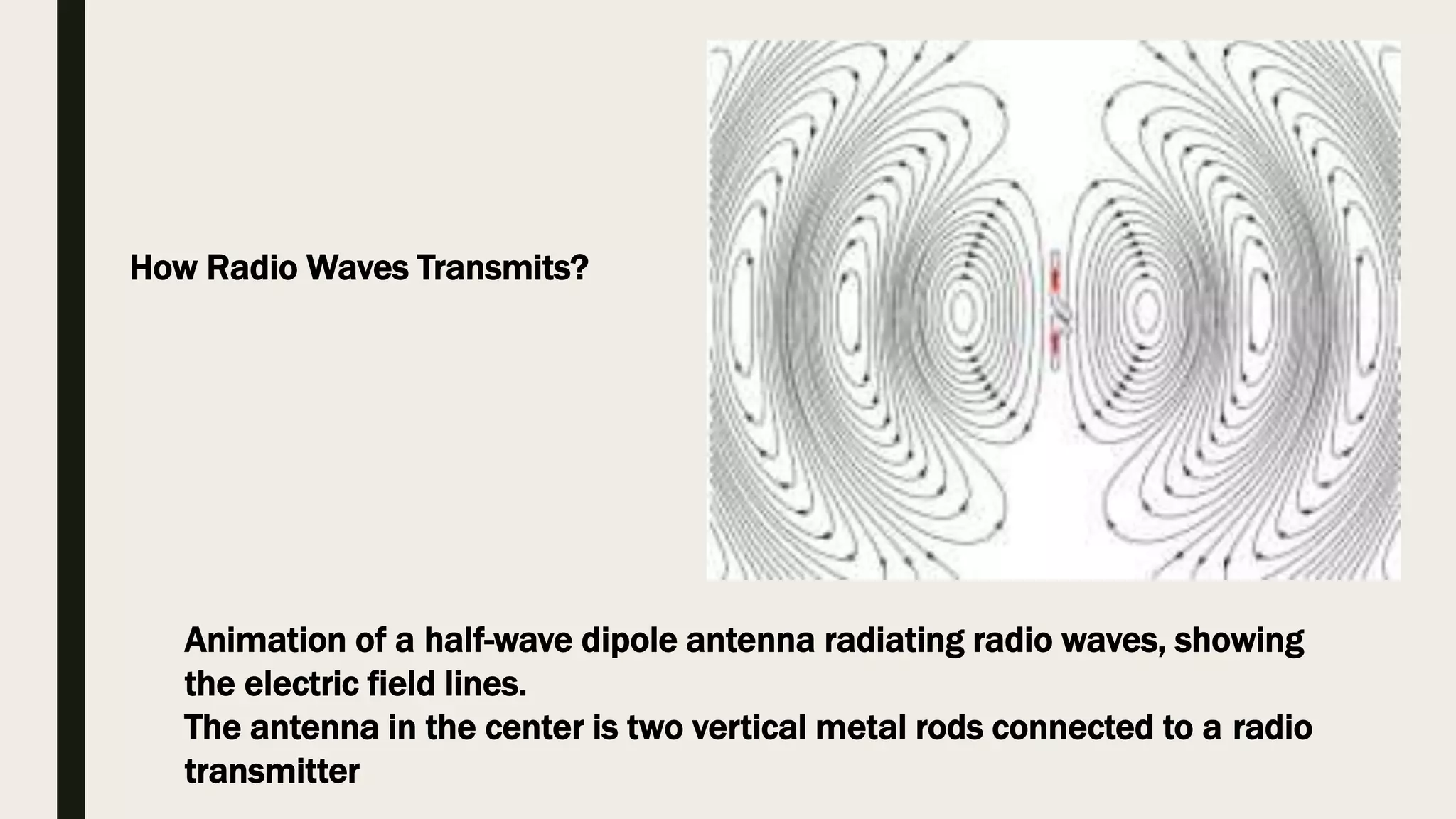
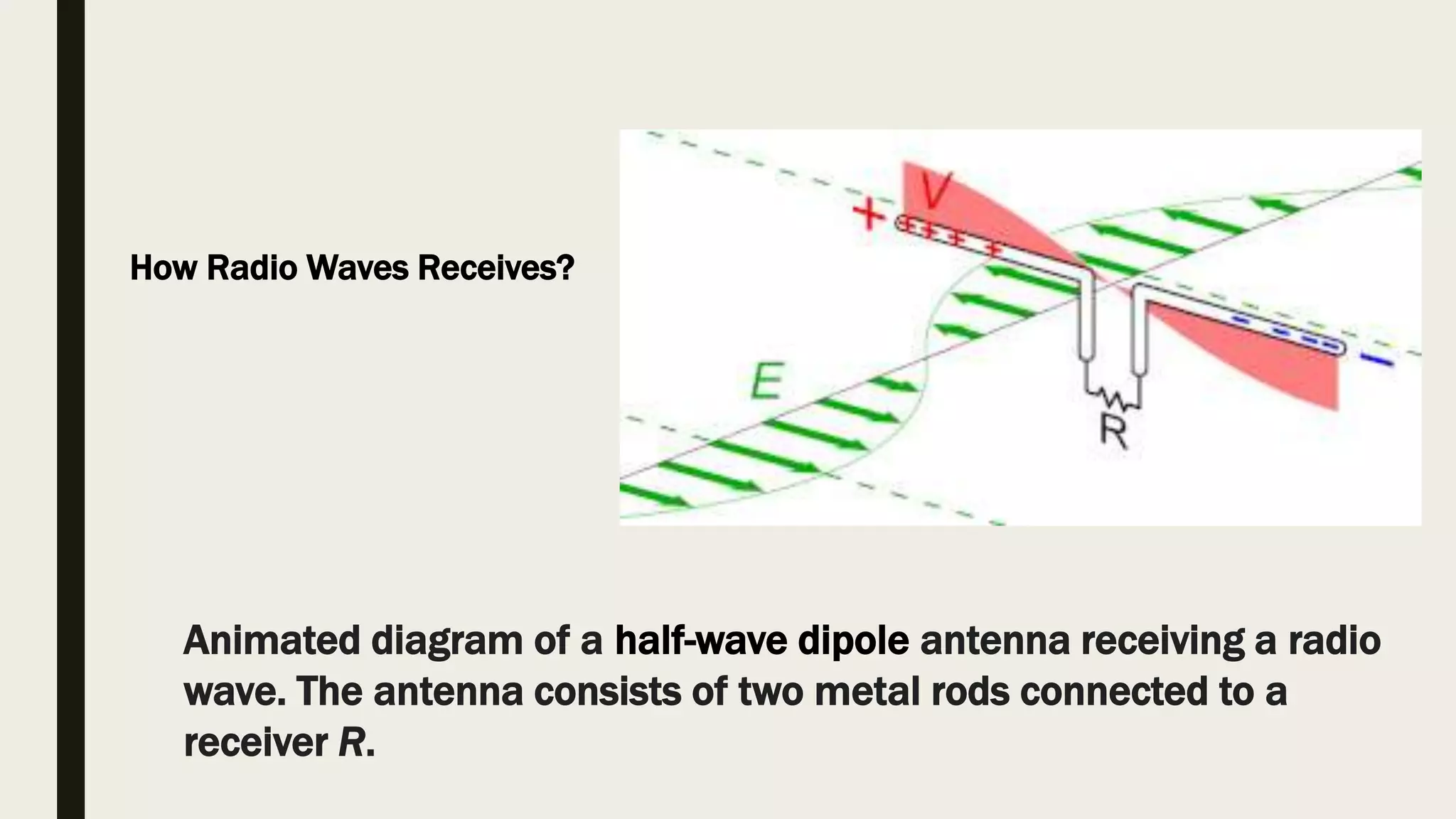
Radio waves are electromagnetic waves that can transmit data without a physical medium. They are generated by radio transmitters and have wavelengths between 1 millimeter and 100 kilometers. Radio waves are able to travel long distances and are received by antennas connected to radio receivers. Common uses of radio waves include wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, mobile phones, broadcast television and radio, GPS, and military communication.