Congestive heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Common causes include high blood pressure, cardiomyopathy, abnormal heart rhythms, and coronary artery disease. Symptoms include fluid retention leading to peripheral edema and pulmonary edema. Treatment involves reducing preload and afterload on the heart to increase cardiac output and relieve symptoms. Key drug classes used are diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, vasodilators, and inotropic drugs. Non-pharmacological treatments include sodium and fluid restriction and exercise. The goal of treatment is management of symptoms and slowing disease progression.


![Why the word “Congestion”?
The term [“congestive” heart failure] is often
used as one of the common symptoms is
congestion that means there is accumulation of
fluid in tissues.
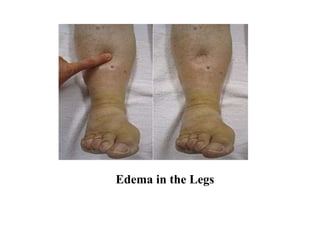
Specifically, congestion takes the form of
water retention and swelling (edema)
peripheral edema and pulmonary edema as
well as ascites.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugsusedintheheartfailure-180116134140/85/Basic-understandings-in-the-Heart-Failure-3-320.jpg)










































![REFERENCES
• Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical
Pharmacology. 7th Ed. New Delhi. Jaypee
Brothers Medical Publishers. 2013. p. 512-
524.
• Klabaunde R. Cardiovascular Pharmacology
Concepts [Internet]. cvpharmacology.com.
2018 [cited 2018 Jan 11]. Available from:
http://www.cvpharmacology.com/clinical%20t
opics/heart%20failure-4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugsusedintheheartfailure-180116134140/85/Basic-understandings-in-the-Heart-Failure-49-320.jpg)
